supercritical carbon dioxide → superkritični ugljikov dioksid
Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is a powerful, cheap, non-toxic and environmental friendly solvent. When used at a supercritical state (over 74 bar and 31 °C), it achieves similar solvating power as its organic competitors, such as hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents. Supercritical carbon dioxide is one of few solvents that can be unrestrictedly used for food processing.
analytical balance → analitička vaga
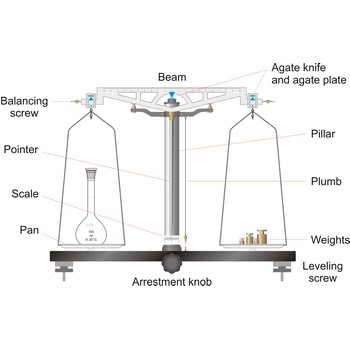
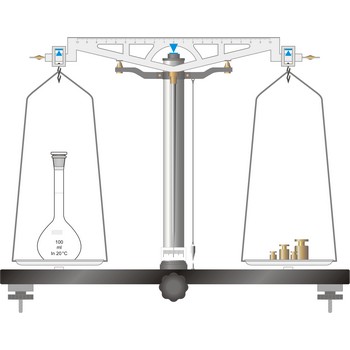
Analytical balances are instruments used for precise determining mass of matter. Analytical balances are sensitive and expensive instruments, and upon their accuracy and precision the accuracy of analysis result depends. The most widely used type of analytical balances are balances with a capacity of 100 g and a sensitivity of 0.1 mg. Not one quantitative chemical analysis is possible without usage of balances, because, regardless of which analytical method is being used, there is always a need for weighing a sample for analysis and the necessary quantity of reagents for solution preparation.
The working part of the balance is enclosed in a glass-fitted case. The baseplate is usually of black glass or black slate. The beam has agate knife-edges at its extremes, supporting stirrups from which balance pans are suspended. Another agate or steel knife-edge is fixed exactly in the middle of the beam on its bottom side. This knife-edge faces downwards and supports the beam. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
The principle of operation of a modern laboratory balance bears some resemblance to its predecessor - the equal arm balance. The older instrument opposed the torque exerted by an unknown mass on one side of a pivot to that of an adjustable known weight on the other side. When the pointer returned to the center position, the torques must be equal, and the weight was determined by the position of the moving weights.
Modern electronic laboratory balances work on the principle of magnetic force restoration. In this system, the force exerted by the object being weighed is lifted by an electromagnet. A detector measures the current required to oppose the downward motion of the weight in the magnetic field.
balance → vaga
Balance is an instrument to measure the mass (or weight) of a body. Balance beam type scales are the oldest type and measure weight using a fulcrum or pivot and a lever with the unknown weight placed on one end of the lever, and a counterweight applied to the other end. When the lever is balanced, the unknown weight and the counterweight are equal. The equal-arm balance consists of two identical pans hung from either end of a centrally suspended beam. The unequal-arm balance is made with one arm of the balance much longer than the other.
More modern substitution balances use the substitution principle. In this calibrated weights are removed from the single lever arm to bring the single pan suspended from it into equilibrium with a fixed counter weight. The substitution balance is more accurate than the two-pan device and enables weighing to be carried out more rapidly.
Electromagnetic force restoration balances also use a lever system but a magnetic field is used to generate the force on the opposite end of the lever and balance out the unknown mass. The current used to drive the magnetic coil is proportional to the mass of the object placed on the platform.
base → baza
Historically, base is a substance that yields an OH - ion when it dissociates in solution, resulting in a pH>7. In the Brønsted definition, a base is a substance capable of accepting a proton in any type of reaction. The more general definition, due to G.N. Lewis, classifies any chemical species capable of donating an electron pair as a base. Typically, bases are metal oxides, hydroxides, or compounds (such as ammonia) that give hydroxide ions in aqueous solution.
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
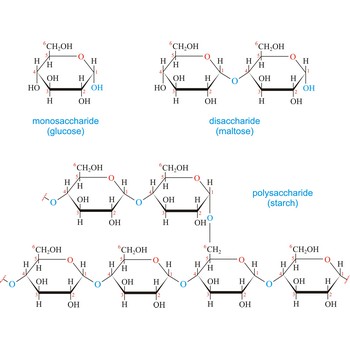
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
Carnot cycle → Carnotov kružni proces
Carnot cycle is the most efficient cycle of operations for a reversible heat engine. Published in 1824 by French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), it consists of four operations on the working substance in the engine:
1-2: Isothermal expansion at thermodynamic temperature T1 with heat QH taken in.
2-3: Adiabatic expansion with a fall of temperature to T2.
3-4: Isothermal compression at temperature T2 with heat QC given out.
4-1: Adiabatic compression at temperature back to T1.
According to the Carnot principle, the efficiency of any reversible heat engine depends only on the temperature range through which it works, rather than the properties of the working substances.
equal-arm balance → vaga s jednakim krakovima
The simplest type of balance, the equal-arm balance, is an application of a first class lever. The beam of the balance is supported on a central knife-edge, usually of agate, which rests upon a plane agate plate. The point of support is called the fulcrum. Two pans of equal weight are suspended from the beam, one at each end, at points equidistant from the fulcrum. A long pointer attached at right angles to the beam at the fulcrum indicates zero on a scale when the beam is at rest parallel to a level surface.
To prevent the knife-edge from becoming dull under the weight of the beam and pans the balance is equipped with a special device called an arrest. The arrest is operated by means of milled knob underneath the base plate in the middle and in front of the balance (sometimes the arrest knob is at one side of the balance).
The object to be weighed is placed on one pan, and standard weights are added to the other until the balance of the beam is established again. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
lead-acid battery → olovni akumulator
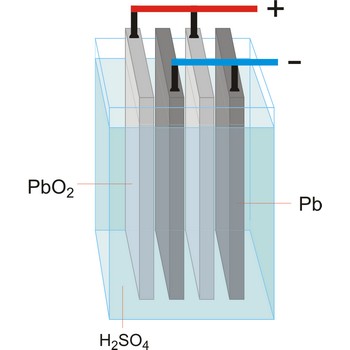
Lead-acid battery is a electrical storage device that uses a reversible chemical reaction to store energy. It was invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. Lead-acid batteries are composed of a lead(IV) oxide cathode, a sponge metallic lead anode and a sulphuric acid solution electrolyte.
In charging, the electrical energy supplied to the battery is changed to chemical energy and stored. The chemical reaction during recharge is normally written:
In discharging, the chemical energy stored in the battery is changed to electrical energy. During discharge, lead sulfate (PbSO4) is formed on both the positive and negative plates. The chemical reaction during discharge is normally written:
Lead acid batteries are low cost, robust, tolerant to abuse, tried and tested. For higher power applications with intermittent loads however, they are generally too big and heavy and they suffer from a shorter cycle life.
precision balance → tehnička vaga
Precision balances typically display results from three to one decimal places (0.001 g up to 0.1 g). The readability precision balances are reduced when compared to analytical balances but, precision balances accommodate higher capacities (up to several kilograms). In its traditional form, it consists of a pivoted horizontal lever of equal length arms, called the beam, with a weighing pan, also called scale, suspended from each arm.
In electronic top pan, or toploader balances, mass is determined not by mechanical deflection but by electronically controlled compensation of an electric force. The signal generated enables the mass to be read from a digital display. The mass of the empty container can be stored in the balance’s computer memory and automatically deducted from the mass of the container plus its contents.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sửa báo cáo khoản vay nước ngoài." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table