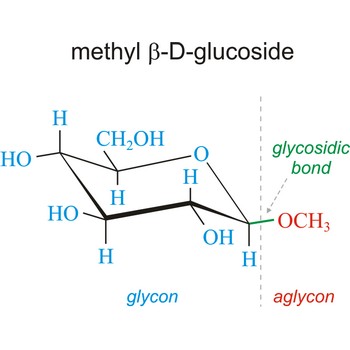
glycoside → glikozid
Glycoside is one of a group of organic compounds in which a sugar group is bonded through its anomeric carbon to another group via a glycosidic bond. The sugar group is known as the glycon and the non-sugar group as the aglycon. According to the IUPAC definition, all disaccharides and polysaccharides are glycosides where the aglycone is another sugar.
In the free hemiacetal form, sugars will spontaneously equilibrate between the α and β anomers. However, once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Therefore, the alpha and beta glycosides are chemically distinct. They will have different chemical, physical, and biological properties. Many glycosides occur abundantly in plants, especially as flower and fruit pigments.
The term glycoside was later extended to cover not only compounds in which the anomeric hydroxy group is replaced by a group -OR, but also those in which the replacing group is -SR (thioglycosides), -SeR (selenoglycosides), -NR1R2 (N-glycosides), or even -CR1R2R3 (C-glycosides). Thioglycoside and selenoglycoside are legitimate generic terms; however the use of N-glycoside, although widespread in biochemical literature, is improper and not recommended here (glycosylamine is a perfectly acceptable term). C-Glycoside is even less acceptable. All other glycosides are hydrolysable; the C-C bond of C-glycosides is usually not. The use and propagation of names based on C-glycoside terminology is therefore strongly discouraged.
glycosidic bond → glikozidna veza
Glycosidic bond ia a bond between the glycosyl group, the structure obtained by removing the hydroxy group from the hemiacetal function of a monosaccharide, and the -OR group (which itself may be derived from a saccharide and chalcogen replacements thereof (RS–, RSe–). The terms N-glycosides and C-glycosides are misnomers and should not be used. The glycosidic bond can be α or β in orientation, depending on whether the anomeric hydroxyl group was α or β before the glycosidic bond was formed and on the specificity of the enzymatic reaction catalyzing their formation. Once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Specific glycosidic bonds therefore may be designated α(1→4), β(1→4), α(1→6), and so on. Cellulose is formed of glucose molecules linked by β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds, whereas starch is composed of α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds.
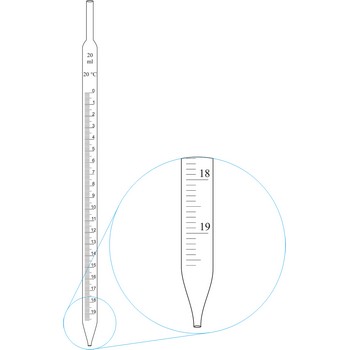
graduated pipette → graduirana pipeta
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark 0. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely.
graphite → grafit
Graphite is an allotrope of carbon. The atoms are arranged in layers as a series of flat, hexagonal rings. Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity. The layers cleave easily, making graphite useful as a solid lubricant. A process to make pure synthetic graphite was invented by the American chemist Edward Goodrich Acheson (1856–1931). The process consists of heating a mixture of clay (aluminum silicate) and powdered coke (carbon) in an iron bowl. The reaction involves the production of silicon carbide, which loses silicon at 4150 °C to leave graphite.
Gratzel solar cell → Gratzelova sunčeva ćelija
Grätzel solar cell is photoelectrochemical cell, developed by Michael Grätzel and collaborators, simulates some characteristics of the natural solar cell, which enables photosynthesis take place. In natural solar cell the chlorophyll molecules absorb light (most strongly in the red and blue parts of the spectrum, leaving the green light to be reflected). The absorbed energy is sufficient to knock an electron from the excited chlorophyll. In the further transport of electron, other molecules are involved, which take the electron away from chlorophyll. In Grätzel cell, the tasks of charge-carrier generation and transport are also assigned to different species.
His device consists of an array of nanometre-sized crystallites of the semiconductor titanium dioxide, welded together and coated with light-sensitive molecules that can transfer electrons to the semiconductor particles when they absorb photons. So, light-sensitive molecules play a role equivalent to chlorophyll in photosynthesis. In Grätzel cell, the light-sensitive molecule is a ruthenium ion bound to organic bipyridine molecules, which absorb light strongly in the visible range; titanium dioxide nanocrystals carry the received photoexcited electrons away from electron donors. On the other hand, a donor molecule must get back an electron, so that it can absorb another photon. So, this assembly is immersed in a liquid electrolyte containing molecular species (dissolved iodine molecules) that can pick up an electron from an electrode immersed in the solution and ferry it to the donor molecule. These cells can convert sunlight with efficiency of 10 % in direct sunlight and they are even more efficient in diffuse daylight.
half-cell → polučlanak
Half-cell is a part of galvanic cell in which oxidations or reduction of an element in contact with water or water solution one of its compounds.
half-wave potential → poluvalni potencijal
Half-wave potential (E1/2) is a potential at which polarographic wave current is equal to one half of diffusion current (id). In a given supporting electrolyte, the half-wave potential is unique for each element and its different valence states and chemical forms. Observation of a current peak at a specific half-wave potential therefore identifies the chemical species producing the current.
halogens → halogeni elementi
Halogens are the elements fluorine (F) chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). They are non-metals, and make up part of the 17 group in the periodic table. Compounds of these elements are called halogenides or halides.
The halogens all have a strong unpleasant odour and will burn flesh. They do not dissolve well in water. The five elements are strongly electronegative. They are oxidising agents, with fluorine being the strongest and astatine being the weakest. They react with most metals and many non-metals.
Halogens form molecules which consist of atoms covalently bonded. With increasing atomic weight there is a gradation in physical properties. For example: Fluorine is a pale green gas of low density. Chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas 1.892 times as dense as fluorine. Bromine is a deep reddish-brown liquid which is three times as dense as water. Iodine is a grayish-black crystalline solid with a metallic appearance. And astatine is a solid with properties which indicate that it is somewhat metallic in character.
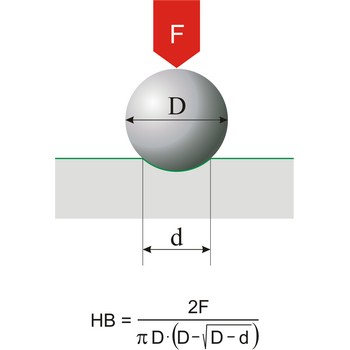
hardness → tvrdoća
Hardness is the resistance of a material to deformation of an indenter of specific size and shape under a known load. This definition applies to all types of hardness scales except Mohs scale, which is a based on the concept of scratch hardness and is used chiefly for minerals. The most generally used hardness scales are Brinell (for cast iron), Rockwell (for sheet metal and heat-treated steel), Knoop (for metals).
hemiacetal → poluacetal
Hemiacetals are organic compounds having the general formula R2C(OH)OR’ (R’ ≠ H), derived from aldehydes or ketones by formal addition of an alcohol to the carbonyl group. Hemiacetals are generally unstable compounds. In some cases however, stable cyclic hemiacetals can be readily formed, especially when 5- and 6-membered rings are possible. In this case an intramolecular OH group reacts with the carbonyl group. Glucose and many other aldoses exist as cyclic hemiacetals whereas fructose and similar ketoses exist as cyclic hemiketals. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Perioda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table