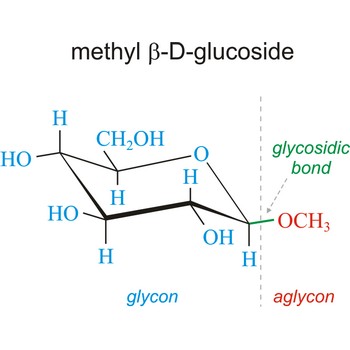
Glycosidic bond ia a bond between the glycosyl group, the structure obtained by removing the hydroxy group from the hemiacetal function of a monosaccharide, and the -OR group (which itself may be derived from a saccharide and chalcogen replacements thereof (RS–, RSe–). The terms N-glycosides and C-glycosides are misnomers and should not be used. The glycosidic bond can be α or β in orientation, depending on whether the anomeric hydroxyl group was α or β before the glycosidic bond was formed and on the specificity of the enzymatic reaction catalyzing their formation. Once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Specific glycosidic bonds therefore may be designated α(1→4), β(1→4), α(1→6), and so on. Cellulose is formed of glucose molecules linked by β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds, whereas starch is composed of α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Glycosidic bond." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table