cosmic rays → kozmičke zrake
Cosmic rays are high energy (1015 eV- 1017 eV) nuclear particles, electrons, and photons, originating mostly outside the solar system, which continually bombard the Earth’s atmosphere.
angular velocity → kutna brzina
A point-like object that undergoes circular motion changes its angular position from initial Θi to final Θf, relative to a fixed axis, specified in a coordinate system with an origin that coincides the centre of the circular path of object. The change in its angular position is called angular displacement ΔΘ = Θf - Θi. Also, a rigid body that rotates about a specified rotation axis, changing its angular position from initial Θi to final Θf, undergoes an angular displacement ΔΘ.
The average angular velocity, ωav, is the ratio of the angular displacement and the time interval Δt=tf-ti, in which that displacement occurs.
Θf and Θi are the initial and final angular position, respectively.
The instantaneous angular velocity ω is the limit of the average angular velocity, as Δt is made to approach zero.
ωav and ω are positive for the counterclockwise rotation (in direction of increasing Θ) and negative for the clockwise rotation (in direction of decreasing Θ).
SI unit for angular velocity is s-1.The measure for the angle Θ is radian. The relationship between radians and degrees is:
For example, the angular velocity of the minute hand of a clock is:
cumulated double bond → kumulirana dvostruka veza
Cumulated double bond in organic compounds is a system of two double bonds on the same atom of carbon (C=C=C)
decomposition potential → potencijal razlaganja
Decomposition potential of some system is the smallest voltage which should be applied so that electrolysis occurs.
dehydrogenation → dehidrogenacija
Dehydrogenation is a chemical reaction in which hydrogen is removed from a compound. Dehydrogenation of organic compounds converts single carbon-carbon bonds into double bonds. It is usually affected by means of a metal catalyst or in biological systems by enzyme dehydrogenases.
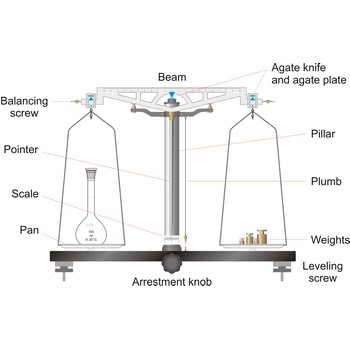
balance → vaga
Balance is an instrument to measure the mass (or weight) of a body. Balance beam type scales are the oldest type and measure weight using a fulcrum or pivot and a lever with the unknown weight placed on one end of the lever, and a counterweight applied to the other end. When the lever is balanced, the unknown weight and the counterweight are equal. The equal-arm balance consists of two identical pans hung from either end of a centrally suspended beam. The unequal-arm balance is made with one arm of the balance much longer than the other.
More modern substitution balances use the substitution principle. In this calibrated weights are removed from the single lever arm to bring the single pan suspended from it into equilibrium with a fixed counter weight. The substitution balance is more accurate than the two-pan device and enables weighing to be carried out more rapidly.
Electromagnetic force restoration balances also use a lever system but a magnetic field is used to generate the force on the opposite end of the lever and balance out the unknown mass. The current used to drive the magnetic coil is proportional to the mass of the object placed on the platform.
benzene → benzen
Benzene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon, C6H6, b.p. 80 °C. It is now made from petroleum by catalytic reforming (formerly obtained from coal tar). Benzene is the archetypal aromatic compound. It has an unsaturated molecule, yet will not readily undergo addition reactions. On the other hand, it does undergo substitution reactions in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or groups.
In 1865, Friedrich August Kekulé purposed the benzene molecule structure as a hexagonal ring which consists of six carbon atoms with alternate carbon-carbon single and carbon-carbon double bond. But such a structure should be highly reactive, and so didn't account for the unreactive nature of benzene. We now know that the best representation for the structure of benzene is indeed, hexagonal, with each C-C bond distance being identical and intermediate between those for a single and double bond. The π-orbitals from each neighbouring carbon atom overlap to form a delocalised molecular orbital which extends around the ring, giving added stability and with it, decreased reactivity. That is the reason the structural formula of benzene represents as a hexagon with a circle in the center which represents the delocalized electrons.
dynamic equilibrium → dinamička ravnoteža
Dynamic equilibrium is established when two opposing processes are occurring at precisely the same rate, so that there is no apparent change in the system over long periods of time.
beryllium → berilij
Beryllium was discovered by Friedrich Wöhler (Germany) and independently by A. B. Bussy (France) in 1828. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word beryllos meaning mineral beryl; also called glucinium from the Greek word glykys meaning sweet. It is steel-grey metal. It resists attack by concentrated nitric acid, has excellent thermal conductivity and is nonmagnetic. At ordinary temperatures, it resists oxidation in air. Beryllium and its salts are toxic and should be handled with the greatest of care. Beryllium is found mostly in minerals like beryl [AlBe3(Si6O18)] and chrysoberyl (Al2BeO4). Pure beryllium is obtained by chemically reducing beryl mineral. Also by electrolysis of beryllium chloride. Its ability to absorb large amounts of heat makes it useful in spacecraft, missiles, aircraft, etc. Emeralds are beryl crystals with chromium traces giving them their green colour.
body-centered cubic lattice → prostorno centrirana kubična rešetka
Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc or cubic-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the bcc structures the spheres fill 68 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is two (8 × 1/8 + 1 = 2). There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Hexagonal_crystal_system." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table