atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
base → baza
Historically, base is a substance that yields an OH - ion when it dissociates in solution, resulting in a pH>7. In the Brønsted definition, a base is a substance capable of accepting a proton in any type of reaction. The more general definition, due to G.N. Lewis, classifies any chemical species capable of donating an electron pair as a base. Typically, bases are metal oxides, hydroxides, or compounds (such as ammonia) that give hydroxide ions in aqueous solution.
benzene → benzen
Benzene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon, C6H6, b.p. 80 °C. It is now made from petroleum by catalytic reforming (formerly obtained from coal tar). Benzene is the archetypal aromatic compound. It has an unsaturated molecule, yet will not readily undergo addition reactions. On the other hand, it does undergo substitution reactions in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or groups.
In 1865, Friedrich August Kekulé purposed the benzene molecule structure as a hexagonal ring which consists of six carbon atoms with alternate carbon-carbon single and carbon-carbon double bond. But such a structure should be highly reactive, and so didn't account for the unreactive nature of benzene. We now know that the best representation for the structure of benzene is indeed, hexagonal, with each C-C bond distance being identical and intermediate between those for a single and double bond. The π-orbitals from each neighbouring carbon atom overlap to form a delocalised molecular orbital which extends around the ring, giving added stability and with it, decreased reactivity. That is the reason the structural formula of benzene represents as a hexagon with a circle in the center which represents the delocalized electrons.
chemisorption → kemisorpcija
Chemisorption is a binding of a liquid or gas on the surface or in the interior of a solid by chemical bonds or forces.
beta-glucan → beta-glukan
Beta-glucans are are naturally occurring polysaccharides that contain only glucose as structural components, and are linked with β-glycosidic bonds. They is the most known powerful immune stimulant. The most active forms of β-glucans are those comprising D-glucose units with β(1→3) links and with short side-chains of D-glucose attached at the β(1→6) position. These are referred to as beta-1,3/1,6 glucan. They are a major component of soluble dietary fiber, which can be found in cereal grains (oats, barley, wheat), yeast, and certain mushrooms (shiitake, maitake).
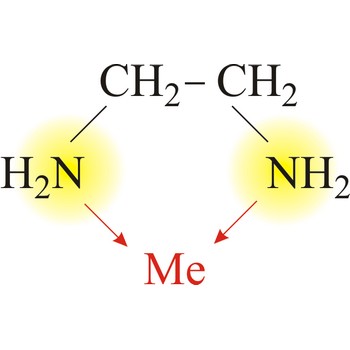
bidentate ligand → bidentatni ligand
Bidentate ligand is a ligand that has two "teeth" or atoms that coordinate directly to the central atom in a complex. An example of a bidentate ligand is ethylenediamine. A single molecule of ethylenediamine can form two bonds to a metal ion. The bonds form between the metal ion and the nitrogen atoms of ethylenediamine.
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
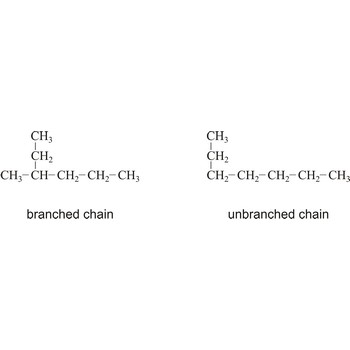
branched chain → razgranati lanac
Branched chain is an open chain of atoms with one or more side chains attached to it.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Teorija valentne veze." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table