antifreeze → antifriz
Antifreeze is a substance added to the liquid (usually water) in the cooling systems of internal-combustion engines to lower its freezing point so that it does not solidify at sub-zero temperatures. The commonest antifreeze is ethane- 1.2-diol (ethylene glycol).
antioxidant → antioksidans
Antioxidants are compounds that slow down oxidation processes that degrade foods, fuels, rubber, plastic, and other materials. Antioxidants like butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), are added to food to prevent fats from becoming rancid and to minimize decomposition of vitamins and essential fatty acids; they work by scavenging destructive free radicals from the food.
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
blanching → blanširanje
1. Blanching is a heat treatment of foodstuffs to partially or completely inactivate the naturally occurring enzymes prior to freezing.
2. Blanching is a washing process for coins cleaning. The black surface layer of cupric oxide is removing by dipping the coins in hot dilute sulphuric acid (w(H2SO4) = 10 %).
Bravais lattice → Bravaisova rešetka
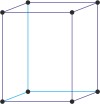
Bravais lattice is a set of points constructed by translating a single point in discrete steps by a set of basis vectors. The French crystallographer Auguste Bravais (1811-1863) established that in three-dimensional space only fourteen different lattices may be constructed. All crystalline materials recognised till now fit in one of these arrangements. The fourteen three-dimensional lattices, classified by crystal system, are shown to the bottom.
|
Crystal system
|
Bravais lattices
|
|||
|
cubic a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
simple cubic
|
body-centered cubic
|
face-centered cubic
|
|
|
tetragonal a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple tetragonal
|
body-centered tetragonal
|
||
|
orthorhombic a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
simple orthorhombic
|
base-centered orthorhombic
|
body-centered orthorhombic
|
face-centered orthorhombic
|
|
monoclinic a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple monoclinic
|
base-centered monoclinic
|
||
|
hexagonal a=b≠c α=β=90° γ=120° |
 |
|||
|
|
hexagonal
|
|||
|
rhombohedral a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
|
rhombohedral
|
|||
|
triclinic a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
triclinic
|
||||
Celsius → Celzijev stupanj
Celsius (°C) is a common but non-SI unit of temperature, defined by assigning temperatures of 0 °C and 100 °C to the freezing and boiling points of water, respectively.
bismuth → bizmut
Bismuth was discovered by Claude Geoffroy (France) in 1753. The origin of the name comes from the German words Weisse Masse meaning white mass; now spelled wismut and bisemutum. It is hard, brittle, steel-grey metal with a pink tint. Stable in oxygen and water. Dissolves in concentrated nitric acid. Bismuth can be found free in nature and in minerals like bismuthine (Bi2S3) and in bismuth ochre (Bi2O3) Main use is in pharmaceuticals and low melting point alloys used as fuses.
brass → mjed
Brasses are alloys of copper and zinc (generally 5 % to 40 %). Brass has been known to man since prehistoric times, long before zinc itself was discovered. It was produced by melting copper together with calamine, a zinc ore. Its ductility reaches a maximum with about 30 % zinc and its tensile strength with 45 % although this property varies greatly with the mechanical and heat treatment of the alloy. Typical applications included gears, plumbing ware fittings, adapters, valves and screw machine products. The French horn is a valved brass wind instrument.
Brass may contain small amounts of other alloying elements, such as aluminum, lead, tin, or nickel. Lead can be added as an alloying element resulting in a brass that can be rapidly machined and produces minimal tool wear. Additions of aluminium, iron and manganese to brass improve strength, whilst silicon additions improve wear resistance. Brass containing tin (< 2 % ) is less liable to corrosion in seawater; it is sometimes called naval brass and is used in naval construction.

Celsius temperature scale → Celsiusova temperaturna skala
For value of zero in Celsius temperature scale the freezing point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 101 325 Pa is taken as another reference point. This range is divided into 100 equal parts, and each part is an equivalent to 1 °C. Units of Celsius temperature scale (°C) and thermodynamic temperature scale (K) are identical
1 °C = 1 K.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Google translate freee." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table


