depression of freezing point → snižavanje ledišta
Depression of freezing point of a pure solvent is observed when substances are dissolved in it. The amount by which the freezing point is depressed is proportional to the number of molecules of solute and independent of their nature.
free energy → slobodna energija
Free energy is an energy that is actually available to do useful work. A decrease in free energy accompanies any spontaneous process. Free energy does not change for systems that are at equilibrium.
freezing → smrzavanje
Freezing is the change of a liquid into a solid state as the temperature decreases. For water, the freezing point is 0 °C (or 273.16 K).
freezing point → ledište
Freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid at normal atmospheric pressure.
See Melting point
Helmholz free energy → Helmholzova slobodna energija
Helmholz free energy (A) is a thermodynamic function defined by A = U - TS, where U is the internal energy, S the entropy, and T the thermodynamic temperature. For a reversible isothermal process ΔA represents the useful work available.
mean free path → srednji slobodni put
Mean free path is the average distance a gas molecule travels between collisions.
free radical → slobodni radikal
Free radical is a molecular fragment having one or more unpaired electrons, usually short-lived and highly reactive. They can be produced by photolysis or pyrolysis in which a bond is broken without forming ions. In formulas, a free radical is conventionally indicated by a dot (·CH3, ·SnH3, ·Cl). Free radicals are known to be formed by ionising radiation and thus play a part in deleterious degradation effects that occur in irradiated tissue. They also act as initiators or intermediates in oxidation, combustion, photolysis, and polymerisation.
Gibbs free energy → Gibbsova slobodna energija
Gibbs free energy (G) is an important function in chemical thermodynamics, defined by
where H is the enthalpy, S the entropy, and T the thermodynamic temperature. Gibbs free energy is the energy liberated or absorbed in a reversible process at constant pressure and constant temperature. Sometimes called Gibbs energy and, in older literature, simply free energy.
Changes in Gibbs free energy, ΔG, are useful in indicating the conditions under which a chemical reaction will occur. If ΔG is negative the reaction will proceed spontaneously to equilibrium. In equilibrium position ΔG = 0.
abundance of elements → rasprostranjenost elemenata
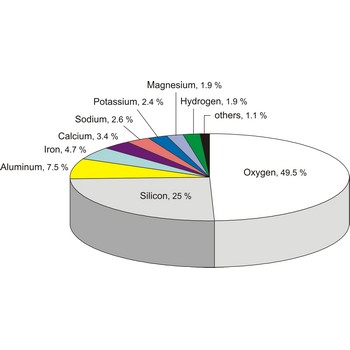
Elements in nature are mostly found in different compounds and, rarely, in the free (elementary) state. In Earth’s crust the most abundant of all elements is oxygen (with 49.5 %), then silicon (25 %), aluminium (7.5 %), iron (4.7 %), calcium (3.4 %), sodium (2.6 %), potassium (2.4 %), magnesium (1.9 %) and hydrogen (1.9 %). These nine elements make up almost 99 % of the Earth’s composition.
aluminium → aluminij
Aluminium was discovered by Friedrich Wöhler (Germany) in 1827. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word alumen meaning alum. It is soft, lightweight, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces quickly form protective oxide coating. Metal reacts violently with oxidants. Third most abundant element in the earth’s crust. Aluminium is the most abundant metal to be found in the earth’s crust, but is never found free in nature. Aluminium is obtained by electrolysis from bauxite. Used for many purposes from airplanes to beverage cans. Too soft in its pure form so less than 1 % of silicon or iron is added, which hardens and strengthens it.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Google translate freee." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table