nucleic acid → nukleinska kiselina
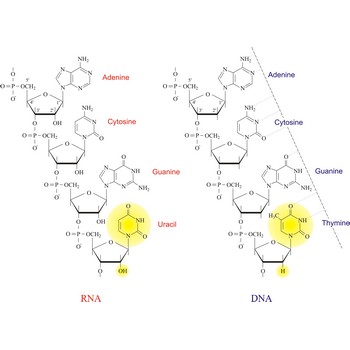
Nucleic acids are a complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecules composed of nucleotide chains that convey genetic information. The most common nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Each nucleic acid chain is composed of subunits called nucleotides, each containing a sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. DNA was first discovered in 1869 by the Swiss biochemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895).
Both DNA and RNA contain the two major purine bases adenine (A) and guanine (G) and one of the major pyrimidines, cytosine (C). Of the other two pyrimidines, thymine (T) is found in DNA and uracil (U) is found in RNA. There are two major pentoses in nucleic acids:2'-deoxy-D-ribose in DNA and D-ribose in RNA.
Nucleotides are linked together in both DNA and RNA in a polymeric fashion via covalent bonds. These bonds exist through phosphate-group bridges in which the 5' hydroxyl group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3' hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide. RNA is usually a single-stranded molecule, whereas DNA is usually double-stranded.
plasma → plazma
Plasma is a highly ionised gas in which the charge of the electrons is balanced by the charge of the positive ions, so that the system as a whole is electrically neutral. Plasmas are created by exposing gases at low pressure to an electric or electromagnetic field. In semiconductor processing, plasmas are used for etching and thin film deposition (the excited state of the gas makes it very reactive). In everyday life plasmas are used to give light in fluorescent light bulbs, neon lamps, and blue insect traps.
polar molecule → polarna molekula
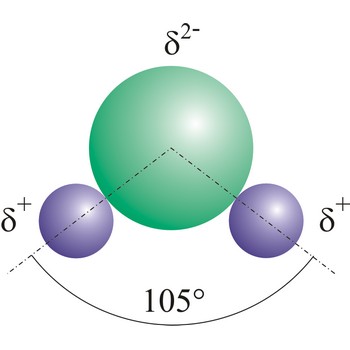
Polar molecules are molecules at which centres of gravity of positive and negative charge are not in the same point.
rutherfordium → ruthefordij
Rutherfordium was discovered by workers at the Nuclear Institute at Dubna (USSR) and by workers at the University of California, Berkeley (USA) in 1964. Name in honour of Lord Rutherford, the physicist and chemist from New Zealand. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Rutherfordium was made by bombarding californium-249 with beams of carbon-12 and 13. Six isotopes of rutherfordium have so far been identified. Rutherfordium-261, the longest-lived, has a half-life of 62 seconds.
ribonucleic acid → ribonukleinska kiselina
Ribonucleic acid is a complex organic compound in living cells that is concerned with protein synthesis. Plays an intermediary role in converting the information contained in DNA into proteins. RNA carries the genetic information from DNA to those parts of the cell where proteins are made. Some viruses store their genetic information as RNA not as DNA.
Ribonucleic acid is a similar molecule to DNA but with a slightly different structure.
The structural difference with DNA is that RNA contains a -OH group both at the 2' and 3' position of the ribose ring, whereas DNA (which stands, in fact, for deoxy-RNA) lacks such a hydroxy group at the 2' position of the ribose. The same bases can be attached to the ribose group in RNA as occur in DNA, with the exception that in RNA thymine does not occur, and is replaced by uracil, which has an H-group instead of a methyl group at the C-5 position of the pyrimidine. Unlike the double-stranded DNA molecule, RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
The three main functionally distinct varieties of RNA molecules are: (1) messenger RNA (mRNA) which is involved in the transmission of DNA information, (2) ribosomal RNa (rRNA) which makes up the physical machinery of the synthetic process, and (3) transfer RNA (tRNA) which also constitutes another functional part of the machinery of protein synthesis.
spin → spin
Spin is the intrinsic angular momentum of an elementary particle, or system of particles such as nucleus, that is also responsible for the magnetic moment; or, a particle or nucleus possessing such a spin. The spins of nuclei have characteristic fixed values. Pairs of neutrons and protons align to cancel out their spins, so that nuclei with an odd number of neutrons and/or protons will have a net non-zero rotational component characterized by a non-zero quantum nuclear spin number.
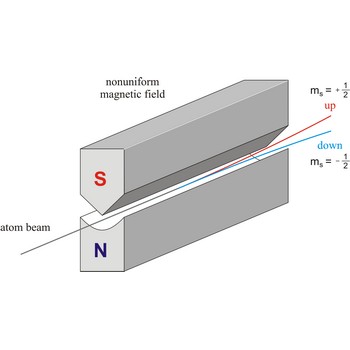
Stern-Gerlach experiment: a beam of silver atoms is split into two beams when it traverses a nonuniform magnetic field. Atoms with spin quantum number ms=+1/2 follow one trajectory, and those with ms=+1/2 follow another.
solar cell → sunčeva ćelija
Solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is a device that captures sunlight and transforms it directly to electricity. All solar cells make use of photovoltaic effect, so often they are called photovoltaic cells. Almost all solar cells are built from solid-state semiconducting materials, and in the vast majority of these the semiconductor is silicon.
The photovoltaic effect involves the generation of mobile charge carriers-electrons and positively charged holes-by the absorption of a photon of light. This pair of charge carriers is produced when an electron in the highest filled electronic band of a semiconductor (the valence band) absorbs a photon of sufficient energy to promote it into the empty energy band (the conduction band). The excitation process can be induced only by a photon with an energy corresponding to the width of the energy gap that separates the valence and the conduction band. The creation of an electron-hole pair can be converted into the generation of an electrical current in a semiconductor junction device, wherein a layer of semiconducting material lies back to back with a layer of either a different semiconductor or a metal. In most photovoltaic cells, the junction is p-n junction, in which p-doped and n-doped semiconductors are married together. At the interface of the two, the predominance of positively charged carriers (holes) in the p-doped material and of negatively charged carriers (electrons) in the n-doped material sets up an electric field, which falls off to either side of the junction across a space-charge region. When absorption of a photon in this region generates an electron-hole pair, these charge carriers are driven in opposite directions by the electric field, i.e. away from the interface and toward the top and bottom of the two-layer structure, where metal electrodes on these faces collect the current. The electrode on the top layer (through which light is absorbed) is divided into strips so as not to obscure the semiconducting layers below. In most widely used commercial solar cells, the p-doped and n-doped semiconductive layers are formed within a monolithic piece of crystalline silicon. Silicon is able to absorb sunlight at those wavelengths at which it is most intense-from the near-infrared region (wavelengths of around 1200 nm) to the violet (around 350 nm).
ununbium → ununbij
Ununbium was discovered by S. Hofmann et al. collaboration at the Heavy Ion Research Laboratory (Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany in February 1996. The new element has not yet been officially named, but it is known as ununbium, according to the system designated by the IUPAC for naming new elements. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Using the electromagnetic velocity filter SHIP, fusion-like residues of the reaction of 70Zn with enriched 208Pb targets were measured. Two chains of localized alpha-emitters were identified as originating with 277112 + 1n.
unununium → unununij
Unununium was discovered by S. Hofmann et al. collaboration at the Heavy Ion Research Laboratory (Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany in December 1994. The new element has not yet been officially named, but it is known as unununium, according to the system designated by the IUPAC for naming new elements. It is synthetic radioactive metal. In bombardments of 209Bi targets with 64Ni using the velocity selector SHIP facility to discriminate in favor of the fused product, 272111 + 1n, three sets of localized alpha-decay chains were observed with position-sensitive detectors.
Volta, Alessandro → Volta, Alessandro
The Italian physicist Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (1745-1827) was the inventor of the voltaic pile, the first electric battery (1800). In 1775 he invented the electrophorus, a device that, once electrically charged by having been rubbed, could transfer charge to other objects. Between 1776 and 1778, Volta discovered and isolated methane gas (CH4). The electrical unit known as the volt was named in his honor.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Efektivni naboj jezgre." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table