effective nuclear charge → efektivni naboj jezgre
Effective nuclear charge. (Zeff) is the nuclear charge experienced by an electron when other electrons are shielding the nucleus.
size of the nucleus → veličina jezgre
Size of the nucleus was measured by Lord Rutherford using the scattering patterns of alpha particles passing through a gold foil. It is 10-15 m.
charge number → nabojni broj
Charge number represents ion charge of an atom or a group. It is denoted as a right superscript (Fe2+ or SO42-).
activity → aktivitet
Activity (a) is a thermodynamic function used in place of concentration in equilibrium constants for reactions involving nonideal gases and solutions. For the species i activity is defined as
where ai is the activity of the species i, ci is its molar concentration, and fi is a dimensionless quantity called the activity coefficient.
alpha particle → alfa-čestica
Alpha particle is a helium nucleus emitted spontaneously from radioactive elements, both natural and manufactured. Its energy is in range 4-8 MeV and is dissipated in a very short path, i.e. a few centimetres of air or less than 0.005 mm of aluminium. As helium nucleus consists of two protons and two neutrons bound together as a stable entity the loss of an alpha particle involves a decrease in nucleon number of 4 and decrease of 2 in the atomic number, e.g.
A stream of alpha particles is known as an alpha ray or alpha-radiation.
chemical element → kemijski element
Chemical element is a type of matter of which elementary matter is composed. Chemical element is composed of atoms with the same core charge.
lanthanides contraction → kontrakcija lantanoida
Lanthanides contraction is a reduction of metal and ion diameters from lanthanum to lutetium and it is caused by a core charge growth inside the same shell. Elements which in the periodic system of elements come after lanthanides have, because of lanthanides contraction, smaller diameter than they should have according to their position in the periodic system of elements.
electron → elektron
The electron is an elementary particle with a negative electric charge of (1.602 189 2±0.000 004 6)×10-19 C and a mass of 1/1837 that of a proton, equivalent to (9.109 534±0.000 047)×10-31 kg.
In 1897 the British physicist Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson (1856-1940) discovered the electron in a series of experiments designed to study the nature of electric discharge in a high-vacuum cathode-ray tube. Thomson interpreted the deflection of the rays by electrically charged plates and magnets as evidence of bodies much smaller than atoms that he calculated as having a very large value for the charge to mass ratio. Later he estimated the value of the charge itself.
Electrons are arranged in from one to seven shells around the nucleus; the maximum number of electrons in each shell is strictly limited by the laws of physics (2n2). The outer shells are not always filled: sodium has two electrons in the first shell (2×12 = 2), eight in the second (2×22 = 8), and only one in the third (2×32 = 18). A single electron in the outer shell may be attracted into an incomplete shell of another element, leaving the original atom with a net positive charge. Valence electrons are those that can be captured by or shared with another atom.
Electrons can be removed from the atoms by heat, light, electric energy, or bombardment with high-energy particles. Decaying radioactive nuclei spontaneously emit free electrons, called β particles.
proton → proton
Proton is a stable elementary particle of unit positive charge and spin 1/2. Protons and neutrons, which are collectively called nucleons, are the constituents of the nucleus.
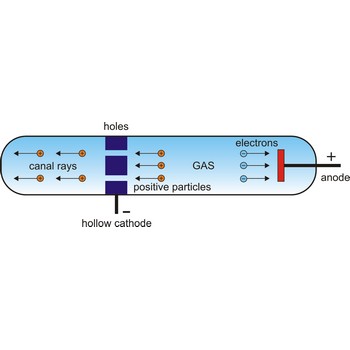
In 1886, German physicist Eugene Goldstein (1850-1930) discovered positive particles by using a modified Crookes tube with holes in the cathode in an evacuated tube. When cathode rays were given off in one direction toward the anode, other rays found their way through the holes in the cathode and sped off in the opposite direction. Since these other rays traveled in the direction opposite to the negatively charged cathode rays, it seemed that they must be composed of positively charged particles. Rutherford suggested that this fundamental positive particle be called the proton.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Efektivni naboj jezgre." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table