acetal → acetal
Acetals are organic compounds having the structure R2C(OR’)2 (R’ ≠ H). They are organic compounds formed by addition of alcohol molecules to aldehyde or ketone molecules. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H ). Mixed acetals have different R’ groups. The formation of acetals is reversible; acetals can be hydrolysed back to aldehydes (ketone) in acidic solutions.
Acetal, 1,1-diethoxyethane (CH3CH(OC2H5)2), is an organic compound, pleasant smelling, formed by addition of ethyl alcohol to ethanal (acetaldehyde). It is used as a solvent and in synthetic organic chemistry.
cellulose → celuloza
Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n, is a polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by (1→4)-β-glycoside bonds. Nature uses cellulose primarily as a structural material to impart strength and rigidity to plants. Leaves, grasses, and cotton are primarily cellulose. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc. Cellulose also serves as raw material for the manufacture of cellulose acetate, known commercially as acetate rayon, and cellulose nitrate, known as guncotton. Gunncotton is the major ingredient in smokeless powder, the explosive propellant used in artillery shells and in ammunition for firearms.
weak electrolyte → slabi elektrolit
Weak electrolytes are those electrolytes which in water solutions dissociate only partially, giving ions and which are in equilibrium with undissociated molecules. Their water solutions conduct electric current weakly. For example, acetic acid partially dissociates into acetate ions and hydrogen ions, so that an acetic acid solution contains both molecules and ions.
acid → kiselina
Acid is a type of compound that contains hydrogen and dissociates in water to produce positive hydrogen ions. The reaction for an acid HA is commonly written:
In fact, the hydrogen ion (the proton) is solvated, and the complete reaction is:
This definition of acids comes from the Arrhenius theory. Such acids tend to be corrosive substances with a sharp taste, which turn litmus red and produce colour changes with other indicators. They are referred to as protonic acids and are classified into strong acids, which are almost completely dissociated in water, (e.g. sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid), and weak acids, which are only partially dissociated (e.g. acetic acid and hydrogen sulphide). The strength of an acid depends on the extent to which it dissociates, and is measured by its dissociation constant.
In the Lowry-Brønsted theory of acids and bases (1923), the definition was extended to one in which an acid is a proton donor (a Brønsted acid), and a base is a proton acceptor (a Brønsted base). An important feature of the Lowry-Brønsted concept is that when an acid gives up a proton, a conjugate base is formed that is capable of accepting a proton.
Similarly, every base produces its conjugate acid as a result of accepting a proton.
For example, acetate ion is the conjugate base of acetic acid, and ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of ammonia.
As the acid of a conjugate acid/base pair becomes weaker, its conjugate base becomes stronger and vice versa.
A further extension of the idea of acids and bases was made in the Lewis theory. In this, a G. N. Lewis acid is a compound or atom that can accept a pair of electrons and a Lewis base is one that can donate an electron pair. This definition encompasses "traditional" acid-base reactions, but it also includes reactions that do not involve ions, e.g.
in which NH3 is the base (donor) and BCl3 the acid (acceptor).
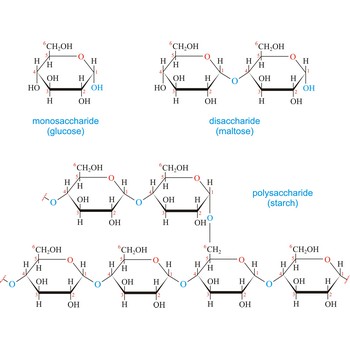
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
hemiacetal → poluacetal
Hemiacetals are organic compounds having the general formula R2C(OH)OR’ (R’ ≠ H), derived from aldehydes or ketones by formal addition of an alcohol to the carbonyl group. Hemiacetals are generally unstable compounds. In some cases however, stable cyclic hemiacetals can be readily formed, especially when 5- and 6-membered rings are possible. In this case an intramolecular OH group reacts with the carbonyl group. Glucose and many other aldoses exist as cyclic hemiacetals whereas fructose and similar ketoses exist as cyclic hemiketals. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H).
ketal → ketal
Ketals are organic compounds formed by addition of an alcohol to a ketone. If one molecule of ketone (RR’CO) reacts with one molecule of alcohol (R"OH) then a hemiketal is formed. The rings of ketose sugars are hemiketals. Further reaction produces a full ketal (RR’C(OR")2). This term, once abandoned, has been reinstated as a subclass of acetals.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Acetat." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table