plasma → plazma
Plasma is a highly ionised gas in which the charge of the electrons is balanced by the charge of the positive ions, so that the system as a whole is electrically neutral. Plasmas are created by exposing gases at low pressure to an electric or electromagnetic field. In semiconductor processing, plasmas are used for etching and thin film deposition (the excited state of the gas makes it very reactive). In everyday life plasmas are used to give light in fluorescent light bulbs, neon lamps, and blue insect traps.
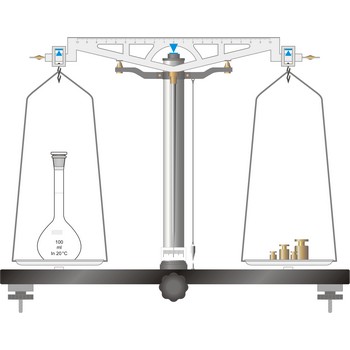
precision balance → tehnička vaga
Precision balances typically display results from three to one decimal places (0.001 g up to 0.1 g). The readability precision balances are reduced when compared to analytical balances but, precision balances accommodate higher capacities (up to several kilograms). In its traditional form, it consists of a pivoted horizontal lever of equal length arms, called the beam, with a weighing pan, also called scale, suspended from each arm.
In electronic top pan, or toploader balances, mass is determined not by mechanical deflection but by electronically controlled compensation of an electric force. The signal generated enables the mass to be read from a digital display. The mass of the empty container can be stored in the balance’s computer memory and automatically deducted from the mass of the container plus its contents.
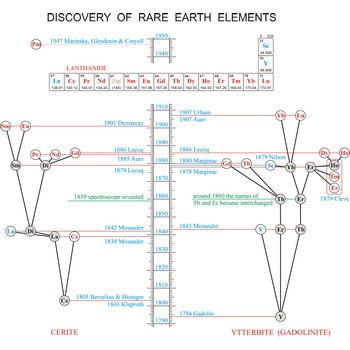
rare earth elements → elementi rijetkih zemalja
Rare earth elements (metals) are the elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), and the lanthanides (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu). These elements got their name from the fact that chemists first isolated them in their oxide forms. These oxides somewhat resemble calcium, magnesium and aluminium oxides, sometimes called common earths. Do you want to know more?
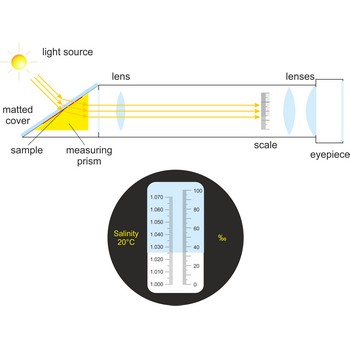
refractometer → refraktometar
Refractometer is an optical device used from measurement of refractive index. A refractometer takes advantage of the fact that light bends as it passes through different materials. It can be used to measure the salinity of water or the amount of sugar in fresh grapes. Refractometers are available with or without automatic temperature compensation (ATC).
When using a conventional saltwater refractometer, a sample is placed on an optical prism in the sample window. As light shines through the sample, it is bent according to the salinity of the water, and casts a shadow on the scale that is visible through the eyepiece. Salinity is read directly through the eyepiece.
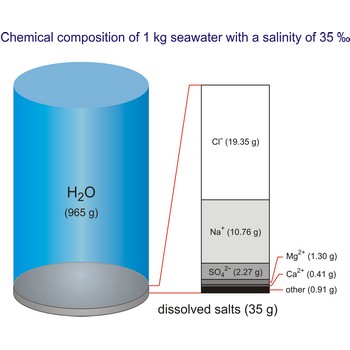
salt water → slana voda
Salt water is the water of the sea and the ocean. This water contains a relatively high percentage of dissolved salt (about 35 g of salt per 1 000 g of sea water.). About 90 % of that salt would be sodium chloride, or ordinary table salt.
The salinity of ocean water varies. It is affected by such factors as melting of ice, inflow of river water, evaporation, rain, etc.
ribonucleic acid → ribonukleinska kiselina
Ribonucleic acid is a complex organic compound in living cells that is concerned with protein synthesis. Plays an intermediary role in converting the information contained in DNA into proteins. RNA carries the genetic information from DNA to those parts of the cell where proteins are made. Some viruses store their genetic information as RNA not as DNA.
Ribonucleic acid is a similar molecule to DNA but with a slightly different structure.
The structural difference with DNA is that RNA contains a -OH group both at the 2' and 3' position of the ribose ring, whereas DNA (which stands, in fact, for deoxy-RNA) lacks such a hydroxy group at the 2' position of the ribose. The same bases can be attached to the ribose group in RNA as occur in DNA, with the exception that in RNA thymine does not occur, and is replaced by uracil, which has an H-group instead of a methyl group at the C-5 position of the pyrimidine. Unlike the double-stranded DNA molecule, RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
The three main functionally distinct varieties of RNA molecules are: (1) messenger RNA (mRNA) which is involved in the transmission of DNA information, (2) ribosomal RNa (rRNA) which makes up the physical machinery of the synthetic process, and (3) transfer RNA (tRNA) which also constitutes another functional part of the machinery of protein synthesis.
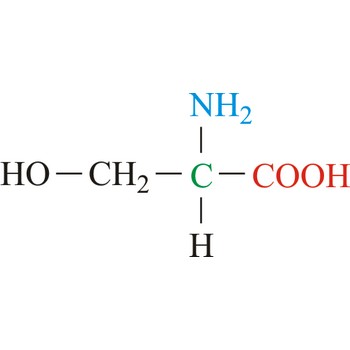
serine → serin
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
solar cell → sunčeva ćelija
Solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is a device that captures sunlight and transforms it directly to electricity. All solar cells make use of photovoltaic effect, so often they are called photovoltaic cells. Almost all solar cells are built from solid-state semiconducting materials, and in the vast majority of these the semiconductor is silicon.
The photovoltaic effect involves the generation of mobile charge carriers-electrons and positively charged holes-by the absorption of a photon of light. This pair of charge carriers is produced when an electron in the highest filled electronic band of a semiconductor (the valence band) absorbs a photon of sufficient energy to promote it into the empty energy band (the conduction band). The excitation process can be induced only by a photon with an energy corresponding to the width of the energy gap that separates the valence and the conduction band. The creation of an electron-hole pair can be converted into the generation of an electrical current in a semiconductor junction device, wherein a layer of semiconducting material lies back to back with a layer of either a different semiconductor or a metal. In most photovoltaic cells, the junction is p-n junction, in which p-doped and n-doped semiconductors are married together. At the interface of the two, the predominance of positively charged carriers (holes) in the p-doped material and of negatively charged carriers (electrons) in the n-doped material sets up an electric field, which falls off to either side of the junction across a space-charge region. When absorption of a photon in this region generates an electron-hole pair, these charge carriers are driven in opposite directions by the electric field, i.e. away from the interface and toward the top and bottom of the two-layer structure, where metal electrodes on these faces collect the current. The electrode on the top layer (through which light is absorbed) is divided into strips so as not to obscure the semiconducting layers below. In most widely used commercial solar cells, the p-doped and n-doped semiconductive layers are formed within a monolithic piece of crystalline silicon. Silicon is able to absorb sunlight at those wavelengths at which it is most intense-from the near-infrared region (wavelengths of around 1200 nm) to the violet (around 350 nm).
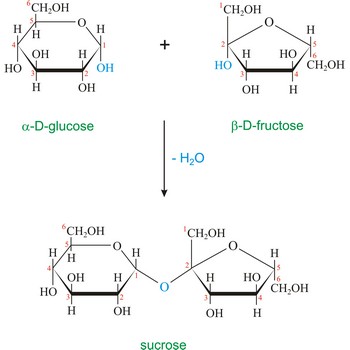
sucrose → saharoza
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
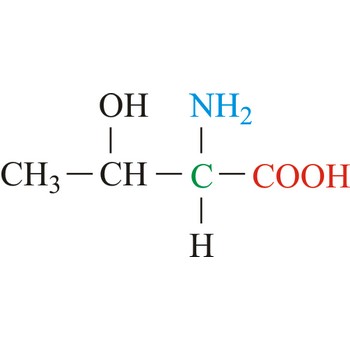
threonine → treonin
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Neutral face meme." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table