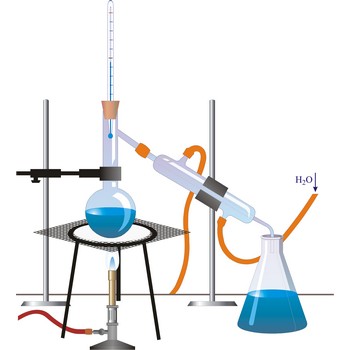
distillation → destilacija
Distillation is a process of boiling a liquid and condensing and collecting the vapour. The liquid collected is the distillate. The usual purpose of distillation is purification or separation of the components of a mixture. This is possible because the composition of the vapour is usually different from that of liquid mixture from which it is obtained. Petrol, kerosene, fuel oil, and lubricating oil are produced from petroleum by distillation.
Earth’s crust → Zemljina kora
Crust is outer layer of the solid earth, above the Mohorovicic discontinuity. Its thickness averages about 35 km on the continents and about 7 km below the ocean floor, and has the approximate chemical composition:
| Element | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| oxygen | 47 |
| silicon | 28 |
| aluminium | 8 |
| iron | 4.5 |
| calcium | 3.5 |
| sodium | 2.5 |
| potassium | 2.5 |
| magnesium | 2.2 |
Einstein, Albert → Einstein, Albert
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) is a German born American physicist, who took Swiss nationality in 1901. A year later he went to work in the Bern patent office. In 1905. he published five enormously influential papers, one on Brownian movement, one on the photoelectric effect, one on the special theory of relativity, and one on energy and inertia (which included the famous expression E = mc2). In 1915 he published the general theory of relativity, concerned mainly with gravitation. In 1921 he was awarded the Nobel Prize. In 1933, as a Jew, Einstein decided to remain in the USA (where he was lecturing), as Hitler had come to power. For the remainder of his life he sought a unified field theory. In 1939 he informed president Roosevelt that an atom bomb was feasible and that. Germany might be able to make one.
regeneration → regeneracija
Regeneration is the process of restoring an ion exchange medium to a usable state after exhaustion. The cation exchanger is normally regenerated with hydrochloric acid and the anion exchanger with sodium hydroxide.
resolution → rezolucija
Resolution is a process by which a racemic mixture is separated into its two pure enantiomers.
reverse osmosis → reverzna osmoza
Reverse osmosis is the method used for obtaining freshwater from saltwater. The process uses a semi-permeable membrane through which pure water and not the salts will pass. The saltwater must be pressurised to approximately 25 bar, which makes it operationally expensive to produce large quantities of fresh water by this method.
saponification → saponifikacija
Saponification is a proces of hydrolysis of esters using hot sodium hydroxide solution to produce the salt of a carboxylic acid. Saponification usually refers to the hydrolysis of esters of fatty acids to manufacture soaps.
electric field → električno polje
If a small amount of charge experience a force, there is an electric field in the vicinity. Electric field E is defined in terms of electrostatic force F that would be exerted on positive test charge qp placed in the field:
SI unit for electric field is N C-1, or V m-1.
The electric field due to a point charge q at distance r from it given by:
where ε0 is permittivity constant, and is εo=8.85×10-12 C2 N-1 m-2.
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Born-Haberov kružni proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table