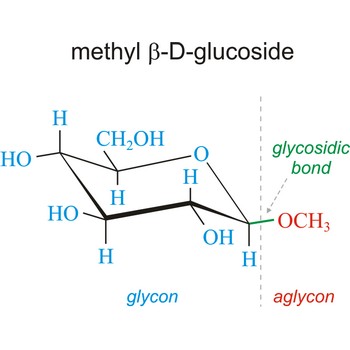
glycosidic bond → glikozidna veza
Glycosidic bond ia a bond between the glycosyl group, the structure obtained by removing the hydroxy group from the hemiacetal function of a monosaccharide, and the -OR group (which itself may be derived from a saccharide and chalcogen replacements thereof (RS–, RSe–). The terms N-glycosides and C-glycosides are misnomers and should not be used. The glycosidic bond can be α or β in orientation, depending on whether the anomeric hydroxyl group was α or β before the glycosidic bond was formed and on the specificity of the enzymatic reaction catalyzing their formation. Once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Specific glycosidic bonds therefore may be designated α(1→4), β(1→4), α(1→6), and so on. Cellulose is formed of glucose molecules linked by β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds, whereas starch is composed of α(1→4)-glycosidic bonds.
Gratzel solar cell → Gratzelova sunčeva ćelija
Grätzel solar cell is photoelectrochemical cell, developed by Michael Grätzel and collaborators, simulates some characteristics of the natural solar cell, which enables photosynthesis take place. In natural solar cell the chlorophyll molecules absorb light (most strongly in the red and blue parts of the spectrum, leaving the green light to be reflected). The absorbed energy is sufficient to knock an electron from the excited chlorophyll. In the further transport of electron, other molecules are involved, which take the electron away from chlorophyll. In Grätzel cell, the tasks of charge-carrier generation and transport are also assigned to different species.
His device consists of an array of nanometre-sized crystallites of the semiconductor titanium dioxide, welded together and coated with light-sensitive molecules that can transfer electrons to the semiconductor particles when they absorb photons. So, light-sensitive molecules play a role equivalent to chlorophyll in photosynthesis. In Grätzel cell, the light-sensitive molecule is a ruthenium ion bound to organic bipyridine molecules, which absorb light strongly in the visible range; titanium dioxide nanocrystals carry the received photoexcited electrons away from electron donors. On the other hand, a donor molecule must get back an electron, so that it can absorb another photon. So, this assembly is immersed in a liquid electrolyte containing molecular species (dissolved iodine molecules) that can pick up an electron from an electrode immersed in the solution and ferry it to the donor molecule. These cells can convert sunlight with efficiency of 10 % in direct sunlight and they are even more efficient in diffuse daylight.
halogens → halogeni elementi
Halogens are the elements fluorine (F) chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). They are non-metals, and make up part of the 17 group in the periodic table. Compounds of these elements are called halogenides or halides.
The halogens all have a strong unpleasant odour and will burn flesh. They do not dissolve well in water. The five elements are strongly electronegative. They are oxidising agents, with fluorine being the strongest and astatine being the weakest. They react with most metals and many non-metals.
Halogens form molecules which consist of atoms covalently bonded. With increasing atomic weight there is a gradation in physical properties. For example: Fluorine is a pale green gas of low density. Chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas 1.892 times as dense as fluorine. Bromine is a deep reddish-brown liquid which is three times as dense as water. Iodine is a grayish-black crystalline solid with a metallic appearance. And astatine is a solid with properties which indicate that it is somewhat metallic in character.
heavy water → teška voda
Water molecules are composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (H2O). If the hydrogen atoms of a water molecule are replaced by deuterium atoms, the result is heavy water (D2O). Deuterium differs from hydrogen by having one neutron in the nucleus of the atom. There is approx. one part in 5000 D2O in normal water and it can be concentrated by electrolysis. Heavy water has a higher boiling point (101.4 °C) and melts at 3.6 °C. Heavy water is 20/18=1.11 times heavier than ordinary water.
hemiacetal → poluacetal
Hemiacetals are organic compounds having the general formula R2C(OH)OR’ (R’ ≠ H), derived from aldehydes or ketones by formal addition of an alcohol to the carbonyl group. Hemiacetals are generally unstable compounds. In some cases however, stable cyclic hemiacetals can be readily formed, especially when 5- and 6-membered rings are possible. In this case an intramolecular OH group reacts with the carbonyl group. Glucose and many other aldoses exist as cyclic hemiacetals whereas fructose and similar ketoses exist as cyclic hemiketals. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H).
histidine → histidin
Histidine is an electrically charged amino acids with basic side chains. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Histidine is perhaps the most common and versatile catalytic residue in proteins. The imidazole sidechain of histidine has a pKa of approximately 6.0. This means that, at physiologically relevant pH values, relatively small shifts in pH will change its average charge. The unprotonated imidazole is nucleophilic and can serve as a general base, while the protonated form can serve as a general acid. In addition, it is often a ligand for transition metal ions such as iron and zinc.
- Abbreviations: His, H
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H9N3O2
- Molecular weight: 155.15 g/mol
hydration → hidratacija
Hydration is addition of water or the elements of water (i.e. H and OH) to a molecular entity. The term is also used in a more restricted sense for the process:
hydrogen bond → vodikova veza
Hydrogen is a bond formed by a hydrogen atom to an electronegative atom, and is denoted by dashed lines H-X---H-B. A hydrogen atom covalently bound to an oxygen (electronegative atom) has a significant positive charge and can form a weak bond to another electronegative atom.
hydrolysis → hidroliza
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which water reacts with another substance to form two or more new substances. This involves ionisation of the water molecule, as well as splitting of the compound hydrolysed, e.g.
Examples are conversion of starch to glucose by water in the presence of suitable catalysts and a reaction of the ions of a dissolved salt to form various products, such as acids, complex ions, etc.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Trigonska planarna geometrija molekule." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table