solid state → čvrsto agregatno stanje
Solid state is characterised by a constant shape and volume. Particles are placed very close to one another and have efect one on another with great attraction forces. Solid bodies do not assume the shape of the container in which they are put.
solar cell → sunčeva ćelija
Solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is a device that captures sunlight and transforms it directly to electricity. All solar cells make use of photovoltaic effect, so often they are called photovoltaic cells. Almost all solar cells are built from solid-state semiconducting materials, and in the vast majority of these the semiconductor is silicon.
The photovoltaic effect involves the generation of mobile charge carriers-electrons and positively charged holes-by the absorption of a photon of light. This pair of charge carriers is produced when an electron in the highest filled electronic band of a semiconductor (the valence band) absorbs a photon of sufficient energy to promote it into the empty energy band (the conduction band). The excitation process can be induced only by a photon with an energy corresponding to the width of the energy gap that separates the valence and the conduction band. The creation of an electron-hole pair can be converted into the generation of an electrical current in a semiconductor junction device, wherein a layer of semiconducting material lies back to back with a layer of either a different semiconductor or a metal. In most photovoltaic cells, the junction is p-n junction, in which p-doped and n-doped semiconductors are married together. At the interface of the two, the predominance of positively charged carriers (holes) in the p-doped material and of negatively charged carriers (electrons) in the n-doped material sets up an electric field, which falls off to either side of the junction across a space-charge region. When absorption of a photon in this region generates an electron-hole pair, these charge carriers are driven in opposite directions by the electric field, i.e. away from the interface and toward the top and bottom of the two-layer structure, where metal electrodes on these faces collect the current. The electrode on the top layer (through which light is absorbed) is divided into strips so as not to obscure the semiconducting layers below. In most widely used commercial solar cells, the p-doped and n-doped semiconductive layers are formed within a monolithic piece of crystalline silicon. Silicon is able to absorb sunlight at those wavelengths at which it is most intense-from the near-infrared region (wavelengths of around 1200 nm) to the violet (around 350 nm).
Soxhlet extractor → Soxhletov ekstraktor
Soxhlet extractor is a laboratory apparatus designed to extract substances with a low solubility in the extracting solvent. The method described by the German chemist Franz von Soxhlet (1848-1926) in 1879 is the most commonly used example of a semi-continuous method applied to extraction of lipids from foods. In the Soxhlet extractor, the sample soaks in hot solvent that is periodically siphoned off, distilled and returned to the sample. During each cycle, a portion of the non-volatile compound dissolves in the solvent. After many cycles the desired compound is concentrated in the distillation flask. The solvent in the flask is then evaporated and the mass of the remaining lipid is measured.
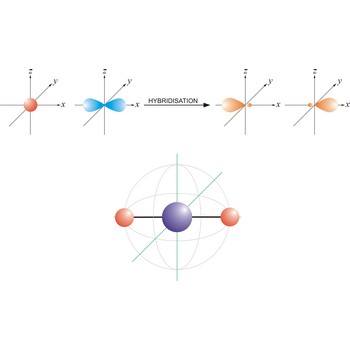
sp hybrid orbital → sp hibridna orbitala
An sp hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and one p orbital of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The two sp hybrid orbitals are aligned in a straight line in opposite direction (bond angles are 180°). The remaining two p orbitals are at right angles to one another and to the line formed by the two sp orbitals.
sp2 hybrid orbital → sp2 hibridna orbitala
An sp2 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and two p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals lie in a plane with angle of 120°. The remaining p orbital remains unchanged and is perpendicular to the plane of the three sp2 orbitals.
sp3 hybrid orbital → sp3 hibridna orbitala
An sp3 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and three p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The four sp3 hybrid orbitals point toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron with the bond angle of 109.5°.
spectrophotometer → spektrofotometar
Spectrophotometer is an instrument for measuring the amount of light absorbed by a sample.
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
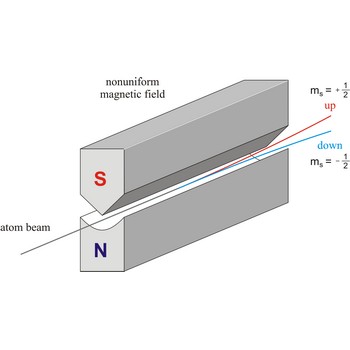
spin → spin
Spin is the intrinsic angular momentum of an elementary particle, or system of particles such as nucleus, that is also responsible for the magnetic moment; or, a particle or nucleus possessing such a spin. The spins of nuclei have characteristic fixed values. Pairs of neutrons and protons align to cancel out their spins, so that nuclei with an odd number of neutrons and/or protons will have a net non-zero rotational component characterized by a non-zero quantum nuclear spin number.
Stern-Gerlach experiment: a beam of silver atoms is split into two beams when it traverses a nonuniform magnetic field. Atoms with spin quantum number ms=+1/2 follow one trajectory, and those with ms=+1/2 follow another.
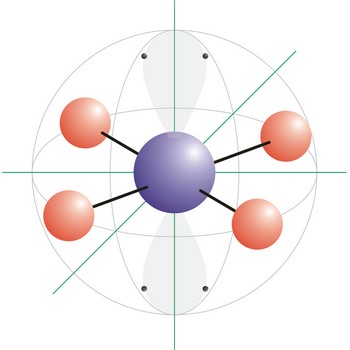
square planar molecular geometry → kvadratna planarna geometrija molekule
Square planar is a molecular shape that results when there are four bonds and two lone pairs on the central atom in the molecule. An example of a square planar molecule is xenon tetrafluoride (XeF4). This molecule is made up of six equally spaced sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybrid orbitals arranged at 90° angles. The shape of the orbitals is octahedral. Two orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons on opposite sides of the central atom. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
square pyramidal molecular geometry → kvadratna piramidalna geometrija molekule
Square pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are five bonds and one lone pair on the central atom in the molecule. Bromine pentafluoride (BrF5) has the geometry of a square pyramid, with fluorine atoms occupying five vertices, one of which is above the plane of the other four. This molecule is made up of six equally spaced sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybrid orbitals arranged at 90° angles. The shape of the orbitals is octahedral. Because of the high symmetry of the octahedral arrangement, all six positions are equivalent, so it does not matter in which position in the drawing we put the lone pair. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Perioda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table