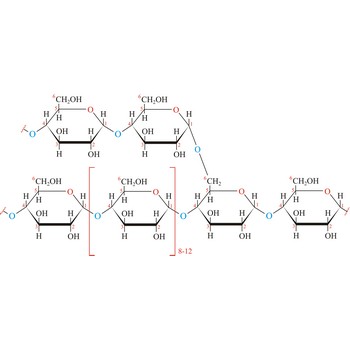
glycogen → glikogen
Glycogen (animal starch) is a polysaccharide that serves the same energy storage function in animals that starch serves in plants. Dietary carbohydrates not needed for immediate energy are converted by the body to glycogen for long term storage (principally in muscle and liver cells). Like amylopectin found in starch, glycogen is a polymer of α(1→4)-linked subunits of glucose, with α(1→6)-linked branches. Glycogen molecules are larger than those of amylopectin (up to 100 000 glucose units) and contain even more branches. Branch points occur about every 10 residues in glycogen and about every 25 residues in amylopectin. The branching also creates lots of ends for enzyme attack and provides for rapid release of glucose when it is needed.
high fructose corn syrup → visoko fruktozni kukuruzni sirup
High fructose corn syrup (HFCS) is commonly used in place of sugar in foods and drinks. Corn starch is hydrolyzed to glucose, which is then treated with glucose isomerase to produce a fructose-rich mixture. HFCS is available in a number of forms, named according to the percentage of fructose they contain, HFCS-55 for instance contains 55 % fructose and 45 % glucose. The enhanced sweetness, low cost and ease of use are the main reasons why manufacturers now prefer to use high fructose corn syrup instead of sugar.
lactose → laktoza
Lactose (milk sugar) is a disaccharide comprising one glucose molecule linked to a galactose molecule by an β(1→4)-glycosidic linkage. Lactose has a beta acetal. Lactose is manufactured by the mammary gland and occurs only in milk (from 4 % to 7 %). Lactose intolerance is a common medical condition that results in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and flatulence and is caused by reduced or absent activity of enzyme lactase.
Like cellobiose and maltose, lactose is a reducing sugar. All reducing sugar undergo mutarotation in aqueous solution. The equilibrium mixture at 20 °C is composed of 62.7 % β-lactose (β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranose) and 37.3 % α-lactose (β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-α-D-glucopyranose).
protelysis → proteoliza
Proteolysis is hydrolytic decomposition of proteins with enzymes, for example trypsin.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Enzim." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table