biochemistry → biokemija
Biochemistry is the study of the chemistry of living organisms, especially the structure and function of their chemical components (principally proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids).
activity coefficient → koeficijent aktiviteta
Activity coefficient (γ or f) is a fractional number which, when multiplied by the molar concentration of a substance in solution, yields the chemical activity. This term gives an idea of how much interaction exists between molecules at higher concentration.
In solutions of very low ionic strength, when m is less than 0.01, the Debye-Hückel limiting law can be used to calculate approximate activity coefficients
where γi = activity coefficient of the species i, zi = charge on the species i and μ = ionic strength of the solution.
Bronsted acid → Bronstedova kiselina
Brøsted acid is a material that gives up hydrogen ions in a chemical reaction.
Bronsted base → Bronstedova baza
Brønsted base is a material that accepts hydrogen ions in a chemical reaction.
chemical → kemikalija
Chemicals are a common name for all chemical products or substances prepared by means of chemical-technologic processes.
arginine → arginin
Arginine is an electrically charged amino acids with basic side chains. It is one of the least frequent amino acids. As a group the charged amino acids are important for making proteins soluble. These residues are generally located on the surface of the protein. Arginine is well designed to bind the phosphate anion, and is often found in the active centers of proteins that bind phosphorylated substrates. As a cation, arginine, as well as lysine, plays a role in maintaining the overall charge balance of a protein. Although arginine is considered an essential amino acid (it must be obtained through the diet), this is true only during the juvenile period in humans.
- Abbreviations: Arg, R
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H14N4O2
- Molecular weight: 174.20 g/mol
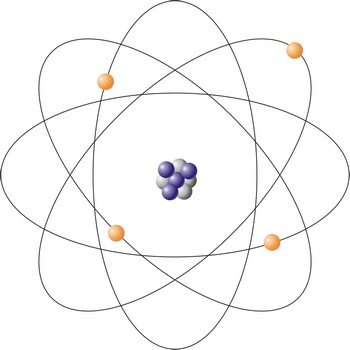
atom → atom
Atom is an atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of the element. Rutherford-Bohr’s model represents the atom as a positively charged core of a size around 10-14 m composed of protons (positive particles) and neutrons (neutral particles) around which negatively charged electrons circle. The number of protons and electrons are equal, so the atom is an electrically a neutral particle. Diameter of the atom is about 10-10 m.
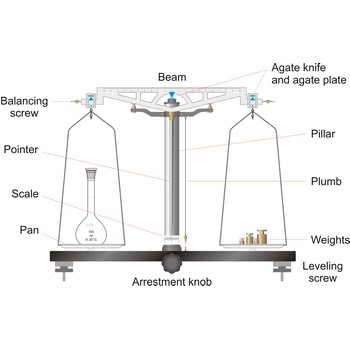
balance → vaga
Balance is an instrument to measure the mass (or weight) of a body. Balance beam type scales are the oldest type and measure weight using a fulcrum or pivot and a lever with the unknown weight placed on one end of the lever, and a counterweight applied to the other end. When the lever is balanced, the unknown weight and the counterweight are equal. The equal-arm balance consists of two identical pans hung from either end of a centrally suspended beam. The unequal-arm balance is made with one arm of the balance much longer than the other.
More modern substitution balances use the substitution principle. In this calibrated weights are removed from the single lever arm to bring the single pan suspended from it into equilibrium with a fixed counter weight. The substitution balance is more accurate than the two-pan device and enables weighing to be carried out more rapidly.
Electromagnetic force restoration balances also use a lever system but a magnetic field is used to generate the force on the opposite end of the lever and balance out the unknown mass. The current used to drive the magnetic coil is proportional to the mass of the object placed on the platform.
chemical compound → kemijski spoj
Some substance is a compound only if it can be decomposed into two or more different substances by means of a chemical reaction. If two or more substances react, thus creating a new substance, that new substance is called a chemical compound.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Zakon o kemijskoj ravnoteži." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table