atmosphere → atmosfera
1. Atmosphere is the column of air which is extending several hundred kilometers above the surface the Earth's surface. The density of this air decreases as you proceed up from the surface. The air in the atmosphere consists of 78 % nitrogen, 21 % oxygen, and 0.9 % argon. The remaining 0.1 % of the atmosphere consists of ozone, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, helium, and neon. The atmosphere is divided into different regions. The lowest two layers are the troposphere (the layer closest to the earth) and the stratosphere respectively. These two layers contain more than 99 % of the atmospheric molecules.
2. Standard atmosphere (atm) is an obsolete pressure and stress unit which should be discontinued. It is unit of pressure equal to the air pressure measured at mean sea level.
1 atm = 101 325 Pa
Technical atmosphere (at) is an obsolete MKpS pressure and sttress derived unit.
1 at = 98 066.5 Pa
1 atm = 1.033 227 453 at
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
Ostwald’s viscometer → Ostwaldov viskozimetar
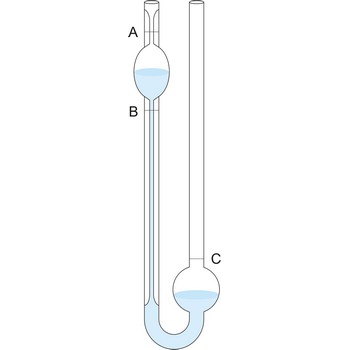
Ostwald viscometer, also known as U-tube viscometer or capillary viscometer is a device used to measure the viscosity of the liquid with a known density. The method of determining viscosity with this instrument consists of measuring the time for a known volume of the liquid (the volume contained between the marks A and B) to flow through the capillary under the influence of gravity. Ostwald viscometers named after the German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald (1853-1932).
The instrument must first be calibrated with materials of known viscosity such as pure (deionized) water. Knowing the value of viscosity of one liquid, one can calculate the viscosity of other liquid.
where η1 and η2 are viscosity coefficients of the liquid and water, and ρ1 and ρ2 are the densities of liquid and water, respectively.
picnometer → piknometar
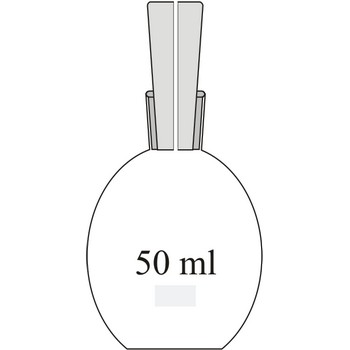
Picnometer is a special glass flask which is used for determining a relative density of liquids using the weight of a known volume. It usually has a glass faceted cork which is pierced in the centre like a thin capillary through which surplus of liquid runs out.
resonance → rezonancija
Resonance is a stabilising quality of certain molecules that can be represented by considering the electron distribution in an ion or molecule as a composite of two or more forms, in those cases where a single form is an inadequate representation; for example, benzene and the carbonate ion. A various canonical structures can be drawn to show how electron delocalisation will explain the discrepancy, the difference in electron density
seawater → more
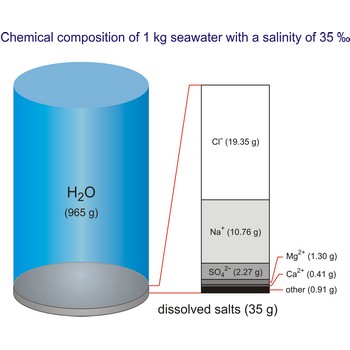
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
silver coulometer → srebrni kulometar
Silver coulometer consists of a platinum vessel which acts as a cathode and contains a solution of pure silver nitrate as an electrolyte (c(AgNO3) = 1 mol/L). A rod of pure silver enclosed in a porous pot acts as the anode. The current density at the anode should not exceed 0.2 Acm-2. After electrolysis, the electrolyte is taken out and the platinum vessel is washed, dried and weighed. The increase in the weight gives the amount of silver deposited (96500 C of electricity deposits 107.88 g of silver). From the mass of the silver deposited, the coulomb involved in the reaction can be calculated.
supercritical fluid → superkritični fluid
Supercritical fluid is any substance above its critical temperature and critical pressure (see phase diagram). It shows unique properties that are different from those of either gases or liquids under standard conditions. A supercritical fluid has both the gaseous property of being able to penetrate anything, and the liquid property of being able to dissolve materials into their components. Solublity increases with increasing density (i.e. with increasing pressure). An example of this is naphthalene which is practically insoluble in low pressure carbon dioxide. At 100 bar the solubility is 10 g/L and at 200 bar it is 50 g/L. Rapid expansion of supercritical solutions leads to precipitation of a finely divided solid.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Polietilen visoke gustoće." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table