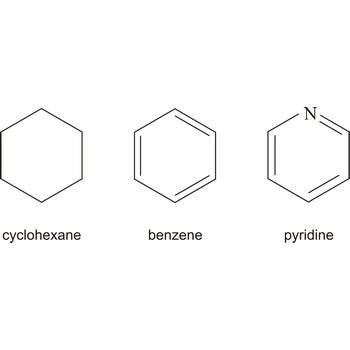
ringlike structure → prstenasta struktura
The ringlike structure is a structure by which the cycloalcanes and aromates are shown.
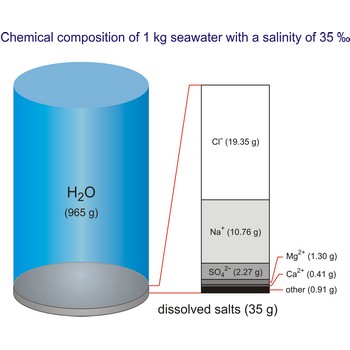
seawater → more
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
ribonucleic acid → ribonukleinska kiselina
Ribonucleic acid is a complex organic compound in living cells that is concerned with protein synthesis. Plays an intermediary role in converting the information contained in DNA into proteins. RNA carries the genetic information from DNA to those parts of the cell where proteins are made. Some viruses store their genetic information as RNA not as DNA.
Ribonucleic acid is a similar molecule to DNA but with a slightly different structure.
The structural difference with DNA is that RNA contains a -OH group both at the 2' and 3' position of the ribose ring, whereas DNA (which stands, in fact, for deoxy-RNA) lacks such a hydroxy group at the 2' position of the ribose. The same bases can be attached to the ribose group in RNA as occur in DNA, with the exception that in RNA thymine does not occur, and is replaced by uracil, which has an H-group instead of a methyl group at the C-5 position of the pyrimidine. Unlike the double-stranded DNA molecule, RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
The three main functionally distinct varieties of RNA molecules are: (1) messenger RNA (mRNA) which is involved in the transmission of DNA information, (2) ribosomal RNa (rRNA) which makes up the physical machinery of the synthetic process, and (3) transfer RNA (tRNA) which also constitutes another functional part of the machinery of protein synthesis.
silver → srebro
Silver has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word argentum meaning silver. It is silvery-ductile and malleable metal. Stable in water and oxygen. Reacts with sulfur compounds to form black sulfides. Silver is found in ores called argentite (AgS), light ruby silver (Ag3AsS3), dark ruby silver (Ag3SbS3) and brittle silver. Used in alloys for jewellery and in other compounds for photography. It is also a good conductor, but expensive.
sodium → natrij
Sodium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word natrium meaning sodium carbonate. It is soft silvery-white metal. Fresh surfaces oxidize rapidly. Reacts vigorously, even violently with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame. Sodium is obtained by electrolysis of melted sodium chloride (salt), borax and cryolite. Metallic sodium is vital in the manufacture of organic compounds. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is table salt. Liquid sodium is used to cool nuclear reactors.
solubility product constant → konstanta produkta topljivosti
Solubility product constant (Ksp) (or the solubility product) is the product of the molar concentrations of the constituent ions, each raised to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient in the equilibrium equation. For instance, if a compound AaBb is in equilibrium with its solution
the solubility product is given by
Soxhlet extractor → Soxhletov ekstraktor
Soxhlet extractor is a laboratory apparatus designed to extract substances with a low solubility in the extracting solvent. The method described by the German chemist Franz von Soxhlet (1848-1926) in 1879 is the most commonly used example of a semi-continuous method applied to extraction of lipids from foods. In the Soxhlet extractor, the sample soaks in hot solvent that is periodically siphoned off, distilled and returned to the sample. During each cycle, a portion of the non-volatile compound dissolves in the solvent. After many cycles the desired compound is concentrated in the distillation flask. The solvent in the flask is then evaporated and the mass of the remaining lipid is measured.
spectrophotometer → spektrofotometar
Spectrophotometer is an instrument for measuring the amount of light absorbed by a sample.
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
stereoisomer → stereoizomer
Stereoisomers are compounds that have identical chemical constitution, but differ as regards the arrangement of the atoms or groups in space. Stereoisomers fall into two broad classes: optical isomers (enantiomers) and geometric isomers (cis-trans).
stoichiometric coefficient → stehiometrijski koeficijent
Stoichiometric coefficient (ν) is the number appearing before the symbol for each compound in the equation for a chemical reaction. By convention, it is negative for reactants and positive for products.
Stoichiometric coefficients describe the stoichiometry of the chemical reaction.
In this equation, a, b, c and d are called as Stoichiometric coefficients of the A, B, C and D respectively.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Oxo compound." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table