electroplating → galvaniziranje
Electroplating (also called electrodeposition) is the deposition of a metallic coating onto an object by putting a negative charge onto the object and immersing it into a solution which contains a salt of the metal to be deposited. The metallic ions of the salt carry a positive charge and are attracted to the part. When they reach it, the negatively charged part provides the electrons to reduce the positively charged ions to metallic form.
Typically, a brass or nickel object is coated with a layer of silver by making use of electrolysis of a silver solution, using the object to be coated as the cathode. The anode consist of pure silver, and the cathode is the object to be plated. The electrolyte is a mixure of silver nitrate with potassium cyanide. The reactions are:
The cyanide ensures a low concentration of silver ions, a condition for providing the best plating results.
enzyme → enzim
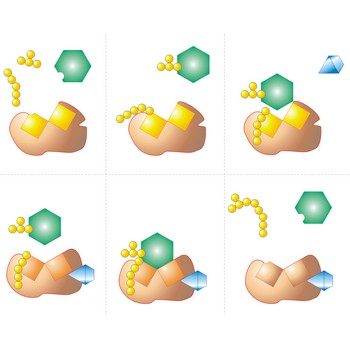
Enzyme is a protein that acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions. Each enzyme is specific to a particular reaction or a group of similar reactions. Many require the association of certain nonprotein cofactors in order to function. The molecule undergoing a reaction (the substrate) binds to a specific active site on the enzyme molecule to form a short-lived intermediate: this greatly increases (by a factor of up to 1020) the rate at which the reaction proceeds to form the product.
europium → europij
Europium was discovered by Eugene Demarcay (France) in 1896. Named for the continent of Europe. It is soft, silvery-white metal. Extremely reactive with oxygen and water. Europium is obtained from monazite sand, which is a mixture of phosphates of calcium, thorium, cerium and most other rare earths. Used with yttrium oxide to make red phosphors for colour televisions.
Fischer-Tropsch process → Fischer-Tropschov postupak
Fischer-Tropsch process is an industrial method of making hydrocarbon fuels from carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The process was introduced in 1933. and used by Germany in World War II. to produce motor fuel. Hydrogen and carbon monoxide are mixed in the ratio 2:1 (water gas was used with added hydrogen) and passed at 200 °C over a nickel or cobalt catalyst. The resulting hydrocarbon mixture can be separated into a higher-boiling fraction for Diesel engines and a lower-boiling petrol fraction. The petrol fraction contains a high proportion of straight-chain hydrocarbons and has to be reformed for use in motor fuel. Alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones are also present. The process is also used in the manufacture of SNG from coal. It is named after the German chemist Franz Fischer (1852-1932) and the Czech Hans Tropsch (1839-1935).
fuel cell → gorivi članak
Fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is different from a battery in that the energy conversion continues as long as fuel and oxidising agent are fed to the fuel cell; that is, in principle indefinitely. (A battery is manufactured with a limited amount of chemicals, and it is exhausted when all the chemicals have reacted.) It is a galvanic cell where spontaneous chemical reactions occur at the electrodes. The fuel is oxidised at the anode, and the oxidising agent (almost always oxygen or air) is reduced at the cathode. Presently, the most commonly used fuel is hydrogen. More conventional fuels (e.g., petrol or natural gas) must be converted (reformed) into hydrogen before they can be utilised in a fuel cell.
Some fuel cells employ an aqueous solution as electrolyte, that can be either acidic or basic (alkaline), or an ion-exchange membrane soaked in aqueous solution can act as the electrolyte. These fuel cells operate at relatively low temperatures (from room temperature to not much above the boiling point of water). Some fuel cells employ molten salts (especially carbonates) as electrolytes and have to operate at temperatures of several hundred degrees centigrade (Celsius). Others employ ionically conductive solids as electrolyte and must operate close to 1 000 °C.
gadolinium → gadolinij
Gadolinium was discovered by Jean de Marignac (France) in 1880. Named after the mineral gadolinite, named for J. Gadolin, a Finnish chemist and mineralogist. It is soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. Reacts slowly with water and oxygen. Dissolves in acids. Metal ignites and burns readily. Gadolinium is found with other rare earths in gadolinite and monazite sand. Used in steel alloying agents and the manufacture of electronic components.
Geiger counter → Geigerov brojač
Geiger counter (Geiger-Muller counter) is a device used to detect and measure ionising radiation. It consists of a tube containing a low-pressure gas (usually argon or neon with methane) and a cylindrical hollow cathode through the centre of which runs a fine-wire anode. A potential difference of about 1 000 V is maintained between the electrodes. An ionising particle or photon passing through a window into the tube will cause an ion to be produced and the high potential will accelerate it towards its appropriate electrode, causing an avalanche of further ionisations by collision. The consequent current pulses can be counted in electronic circuits or simply amplified to work a small loudspeaker in the instrument. It was first devised in 1908 by the German physicist Hans Geiger (1882-1945). Geiger and W. Muller produced an improved design in 1928.
global warming → globalno zatopljenje
Global warming or greenhouse effect is an effect occurring in the atmosphere because of the presence of certain gases (greenhouse gases) that absorb infrared radiation. Light and ultraviolet radiation from the sun is able to penetrate the atmosphere and warm the Earth’s surface. This energy is re-radiated as infrared radiation which because of its longer wavelength, is absorbed by such substances as carbon dioxide. The overall effect is that the average temperature of the Earth and its atmosphere is increasing (so-called global Warming). The effect is similar to that occurring in a greenhouse, where light and long-wavelength ultraviolet radiation can pass through the glass into greenhouse but the infrared radiation is absorbed by the glass and part of it is re-radiated into the greenhouse.
The greenhouse effect is seen as a major environmental hazard. Average increases in temperature could change weather patterns and agricultural output. It might also lead to melting of the polar ice caps and a corresponding rise in sea level. Carbon dioxide, from fossil-fuel power stations and car exhausts, is the main greenhouse gas. Other contributory pollutants are nitrogen oxides, ozone, methane, and chloroflourocarbons.
Haber process → Haberov proces
Haber process is an industrial process for producing ammonia by reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen:
The reaction is reversible and exothermic, so that a high yield of ammonia is favoured by low temperature. However, the rate of reaction would be too slow for equilibrium to be reached at normal temperatures, so an optimum temperature of about 450 °C is used, with a catalyst of iron containing potassium aluminium oxide promoters. The higher the pressure the greater the yield, although there are technical difficulties in using very high pressures. A pressure of about 250 atmospheres is commonly employed. The removal of ammonia from the batch as soon as it is formed ensures that an equilibrium favouring product formation is maintained. The nitrogen is obtained from air. Formerly, the hydrogen was from water gas and the water-gas shift reaction (the Bosch process) but now the raw material (called synthesis gas) is obtained by steam reforming natural gas.
The process is of immense importance for the fixation of nitrogen for fertilisers and explosives. It was developed in 1908 by German chemist Fritz Haber (1868-1934) and was developed for industrial use by Carl Bosch (1874-1940), hence the alternative name Haber-Bosch process.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kate greenaway." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table