catalytic hydrogenation → katalitičko hidrogeniranje
Catalytic hydrogenation is the infusing of unsaturated or impure hydrocarbons with hydrogen gas at controlled temperatures and pressures and in the presence of a catalyst for the purpose of obtaining saturated hydrocarbons and/or removing various impurities such as sulphur and nitrogen.
cation exchange → kationski izmjenjivač
Cation exchange is a cationic resin has positive ions built into its structure and therefore exchanges negative ions. In the cation exchange, the side groups are ionised acidic groups, such as (-SO3H, -COOH, -OH) to which cations H+ are attached. The exchange reaction is one in which different cations in the solution displace the H+ from the solid.
catalyst → katalizator
Catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change. Catalysts that have the same phase as the reactants are homogenous catalysts (e.g. enzymes in biochemical reactions). Those that have a different phase are heterogeneous catalyst (e.g. metals or oxides used in gas reactions).
The catalyst provides an alternative pathway by which the reaction can proceed, in which the activation energy is lower. In thus increases the rate at which the reaction comes to an equilibrium, although it does not alter the position of the equilibrium.
catalytic cracking → katalitčko krekiranje
Catalytic cracking is a petroleum refining process in which heavy-molecular weight hydrocarbons are broken up into light hydrocarbon molecules by the application of heat and pressure in the presence of a catalyst.
cathode → katoda
Cathode is a negative electrode of an electrolytic cell to which positively charged ions (cations) migrate when a current is passed as in electroplating baths.
In a primary or secondary cell (battery or accumulator) the cathode is the electrode that spontaneously becomes negative during discharge, and form which therefore electrons emerge.
In vacuum electronic devices electrons are emitted by the cathode and flow to the anode.
cathode ray → katodna zraka
Cathode ray is a negatively charged beam that emanates from the cathode of a discharge tube. Cathode rays are streams of electrons.
coal tar → ugljeni katran
Coal tar is a material obtained from the destructive distillation of coal in the production of coal gas. The crude tar contains a large number of organic compounds (e.g. benzene, naphthalene, methylbenzene, etc.), which can be separated by fractional distillation.
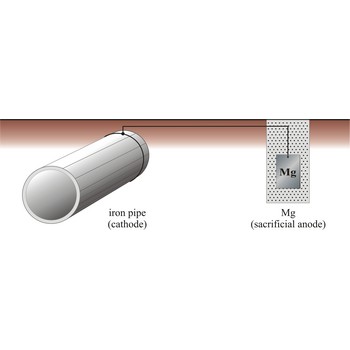
cathodic protection → katodna zaštita
Cathodic protection is a process in which a structural metal, such as iron, is protected from corrosion by connecting it to a metal that has a more negative reduction half-cell potential, which now corrodes instead of iron. There are two major variations of the cathodic method of corrosion protection. The first is called the impressed current method, and the other is called the sacrificial anode method.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kate greenaway." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table