plain salt → jednostavna sol
Plain salt is a salt that contains only metal ions (or ammonium ions) and acid radical. It is created when all ions of hydrogen in an acid are replaced with ions of metal (or ammonium ions).
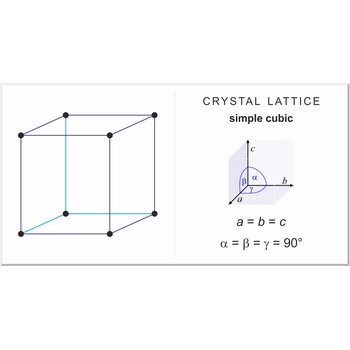
simple cubic lattice → jednostavna kubična rešetka
Simple or primitive cubic lattice (sc or cubic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angels α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the sc structures the spheres fill 52 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is one (8×1/8 = 1). This is only one metal (α-polonium) that have the sc lattice.
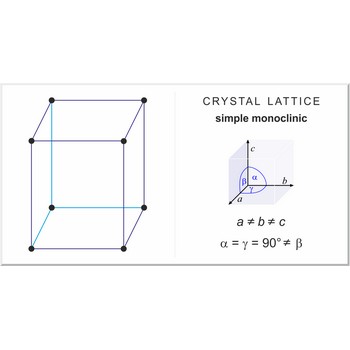
simple monoclinic lattice → jednostavna monoklinska rešetka
Simple or primitive monoclinic lattice (monoclinic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=γ=90°≠β.
simple orthorhombic lattice → jednostavna ortorompska rešetka
Simple or primitive orthorhombic lattice (orthorhombic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
simple tetragonal lattice → jednostavna tetragonska rešetka
Simple or primitive tetragonal lattice (tetragonal-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
actinium → aktinij
Actinium was discovered by André Debierne (France) in 1899. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word aktinos meaning ray. It is heavy, silvery-white, very radioactive metal. Reacts with water. Glows in the dark. Actinium is extremely rare, found in all uranium ores. Usually obtained by treating radium with neutrons in a reactor.
Bravais lattice → Bravaisova rešetka
Bravais lattice is a set of points constructed by translating a single point in discrete steps by a set of basis vectors. The French crystallographer Auguste Bravais (1811-1863) established that in three-dimensional space only fourteen different lattices may be constructed. All crystalline materials recognised till now fit in one of these arrangements. The fourteen three-dimensional lattices, classified by crystal system, are shown to the bottom.
|
Crystal system
|
Bravais lattices
|
|||
|
cubic a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
simple cubic
|
body-centered cubic
|
face-centered cubic
|
|
|
tetragonal a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple tetragonal
|
body-centered tetragonal
|
||
|
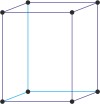
orthorhombic a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
simple orthorhombic
|
base-centered orthorhombic
|
body-centered orthorhombic
|
face-centered orthorhombic
|
|
monoclinic a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple monoclinic
|
base-centered monoclinic
|
||
|
hexagonal a=b≠c α=β=90° γ=120° |
 |
|||
|
|
hexagonal
|
|||
|
rhombohedral a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
|
rhombohedral
|
|||
|
triclinic a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
triclinic
|
||||
elementary substance → elementarna tvar
Elementary substance is a simple and pure substance which can not be, by chemistry methods, decomposed further into simpler substances.
fermentation → fermentacija
Fermentation is a class of biochemical reactions that break down complex organic molecules (such as carbohydrates) into simpler materials (such as ethanol, carbon dioxide, and water). Fermentation reactions are catalyzed by enzymes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Jednostavna sol." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table