battery acid → baterijska kiselina
Battery acid is a solution of approximately 6 mol L-1 sulphuric acid used in the lead storage battery
chemiluminescence → kemiluminiscencija
Chemiluminescence is energy release in form of electromagnetic radiation during a chemical reaction.
coagulation → koaguliranje
Coagulation is a process of colloid particles merging into bigger ones. By removing the charge form a colloid ion, by increasing the temperature or by increasing electrolyte concentration, colloid particles will gather into bigger groups precipitate will emerge. Precipitate that is formed in this way (coagulate) is amorphic and considerably polluted with adsorbed pollutants.
analytical balance → analitička vaga
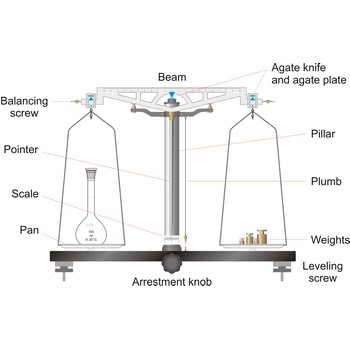
Analytical balances are instruments used for precise determining mass of matter. Analytical balances are sensitive and expensive instruments, and upon their accuracy and precision the accuracy of analysis result depends. The most widely used type of analytical balances are balances with a capacity of 100 g and a sensitivity of 0.1 mg. Not one quantitative chemical analysis is possible without usage of balances, because, regardless of which analytical method is being used, there is always a need for weighing a sample for analysis and the necessary quantity of reagents for solution preparation.
The working part of the balance is enclosed in a glass-fitted case. The baseplate is usually of black glass or black slate. The beam has agate knife-edges at its extremes, supporting stirrups from which balance pans are suspended. Another agate or steel knife-edge is fixed exactly in the middle of the beam on its bottom side. This knife-edge faces downwards and supports the beam. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
The principle of operation of a modern laboratory balance bears some resemblance to its predecessor - the equal arm balance. The older instrument opposed the torque exerted by an unknown mass on one side of a pivot to that of an adjustable known weight on the other side. When the pointer returned to the center position, the torques must be equal, and the weight was determined by the position of the moving weights.
Modern electronic laboratory balances work on the principle of magnetic force restoration. In this system, the force exerted by the object being weighed is lifted by an electromagnet. A detector measures the current required to oppose the downward motion of the weight in the magnetic field.
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
complete ionic equation → potpuna ionska jednadžba
Complete ionic equation is a balanced equation that describes a reaction occurring in a solution, in which all strong electrolytes are written as dissociated ions.
conjugated bond → konjugirana veza
Conjugated bonds describe the alternating pattern of double and single bonds, or triple bonds and single bonds, in a molecule. In such molecules, there is some delocalisation of electrons into the pi orbitals of the carbon atoms linked by the single bond.
balance → vaga
Balance is an instrument to measure the mass (or weight) of a body. Balance beam type scales are the oldest type and measure weight using a fulcrum or pivot and a lever with the unknown weight placed on one end of the lever, and a counterweight applied to the other end. When the lever is balanced, the unknown weight and the counterweight are equal. The equal-arm balance consists of two identical pans hung from either end of a centrally suspended beam. The unequal-arm balance is made with one arm of the balance much longer than the other.
More modern substitution balances use the substitution principle. In this calibrated weights are removed from the single lever arm to bring the single pan suspended from it into equilibrium with a fixed counter weight. The substitution balance is more accurate than the two-pan device and enables weighing to be carried out more rapidly.
Electromagnetic force restoration balances also use a lever system but a magnetic field is used to generate the force on the opposite end of the lever and balance out the unknown mass. The current used to drive the magnetic coil is proportional to the mass of the object placed on the platform.
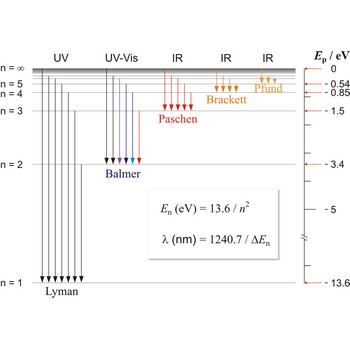
Balmer series → Balmerova serija
Balmer series, Balmer lines is a series of lines in the emission spectrum of hydrogen that involve transitions to the n=2 state from states with n>2.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Elektron." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table