Results 1–10 of 10 for eksperiment
experiment → eksperiment
Experiment is direct observation under controlled conditions. Most experiments involve carefully changing one variable and observing the effect on another variable (for example, changing temperature of a water sample and recording the change volume that results).
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
electrogravimetry → electrogravimetrija
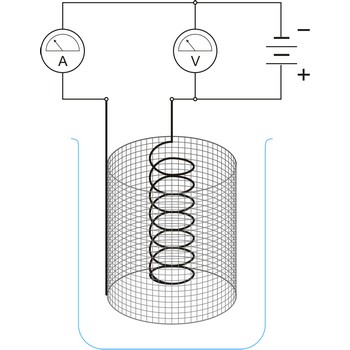
Electrogravimetry is an electroanalytical technique in which the substance to be determined (usually a metal) is deposited out on an electrode which is weighed before and after the experiment. The potential of the electrode must be carefully chosen to ensure that only the metal do be determined will deposit.
heat transfer → prijenos topline
From observations and experiments it has been found that heat energy can be transferred from one position to another through three different modes: conduction, convection and radiation.
laboratory → laboratorij
Laboratory is a specially equipped room used for conducting experiments, analysis, measurements and scientific research.
viscosity → viskozitet
Viscosity. (η) (coefficient of viscosity) is the resistance a liquid exhibits to flow. Experimentally, the frictional force between two liquid layers moving past each other is proportional to the area of the layers and the difference in flow speed between them.
wave-particle duality → valno-čestična dualnost
Wave-particle duality is an observation that electrons, photons, and other very small entities behave like particles in some experiments and like waves in others.
Hesse’s law → Hessov zakon
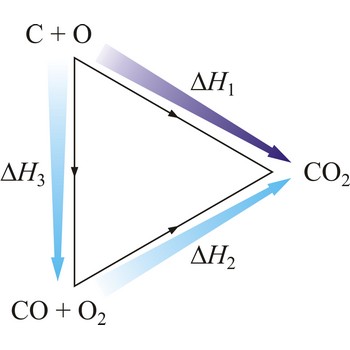
Hesse’s law says that reaction heat of some chemical change does not depend on the way in which the reaction is conducted, but only on starting and ending system state. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. The law was first put forward in 1840 by the Swiss-born Russian chemist Germain Henri Hess (1802-1850).
Hesse’s law can be used to obtain thermodynamic data that cannot be measured directly. For example, it is very difficult to control the oxidation of graphite to give pure CO. However, enthalpy for the oxidation of graphite to CO2 can easily be measured. So can the enthalpy of oxidation of CO to CO2. The application of Hess’s law enables us to estimate the enthalpy of formation of CO.
| C(s) + O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH1 = -393 kJ mol-1 |
| CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH2 = -283 kJ mol-1 |
| C(s) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO(g) | ΔrH3 = -110 kJ mol-1 |
The equation shows the standard enthalpy of formation of CO to be -110 kJ/mol.
Kohlrausch’s law → Kohlrauschov zakon
Kohlrausch’s law states that the equivalent conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is equal to the sum of the conductances of the anions and cations. If a salt is dissolved in water, the conductivity of the solution is the sum of the conductances of the anions and cations. The law, which depends on the independent migration of ions, was deduced experimentally by the German chemist Friedrich Kohlrausch (1840-1910).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Eksperiment." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table