diastereoisomer → dijastereoizomer
Diastereoisomers (diastereomers) are stereoisomers of a compound having two or more chiral centers that are not a mirror image of another stereoisomer of the same compound. For example, in the structure below, 1 and 2 are enantiomers and so are 3 and 4; 1 and 3 are diastereoisomers, as are 2 and 4. Unlike enantiomers, diastereoisomers need not have closely similar physical and chemical properties
ecological footprint → ekološki otisak
The Ecological Footprint is defined as the area of productive land and water ecosystems required to produce the resources that the population consumes (food, fiber, timber, energy, and space for infrastructure) and assimilate the wastes that the population produces (CO2 is the only waste product currently included), wherever on Earth the land and water is located. It compares actual throughput of renewable resources relative to what is annually renewed. Non-renewable resources are not assessed, as by definition their use is not sustainable.
Ecological footprints and biocapacity are expressed in global hectares (gha). Each unit corresponds to one hectare of biologically productive space with world average productivity. In U.S. Footprint results are often presented in global acres (ga). One U.S. acre is equal to 0.405 hectares.
Humanity is currently consuming renewable resources at a faster rate than ecosystems can regenerate them and continuing to release more CO2 than ecosystems can absorb. In 2007, humanity's Footprint was 18 billion gha, or 2.7 gha per person. However, the Earth's biocapacity was only 11.9 billion gha, or 1.8 gha per person. This represents an ecological overshoot of 50 per cent. Put another way, people used the equivalent of 1.5 planets to support their activities (more developed countries generally make higher demands on the Earth's ecosystems than poorer, less developed countries).
EDTA → EDTA
Ethyldiaminetetraacetic acid (C10H16N2O8) or shortened EDTA is a hexadentant ligand, and it forms chelates with both transition-metal ions and main-group ions. EDTA is used as a negative ion - EDTA4-. The diagram shows the structure of the ion with the important atoms picked out. The EDTA ion entirely wraps up a metal ion using all 6 of the positions. The co-ordination number is again 6 because of the 6 co-ordinate bonds being formed by the central metal ion.
EDTA is frequently used in soaps and detergents, because it forms a complexes with calcium and magnesium ions. These ions are in hard water and interfere with the cleaning action of soaps and detergents. EDTA is also used extensively as a stabilizing agent in the food industry and as an anticoagulant for stored blood in blood banks. EDTA is the most common reagent in complexometric titration.
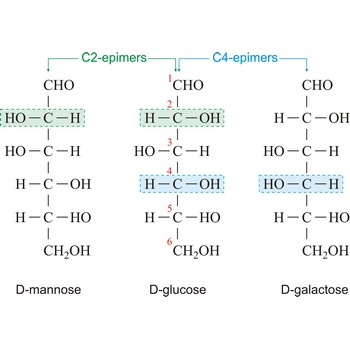
epimer → epimer
Epimers are diastereoisomers that have the opposite configuration at only one of two or more chiral centers present in the respective molecular entities. For example D-glucose and D-mannose, which differ only in the stereochemistry at C-2, are epimers, as are D-glucose and D-galactose (which differ at C-4).
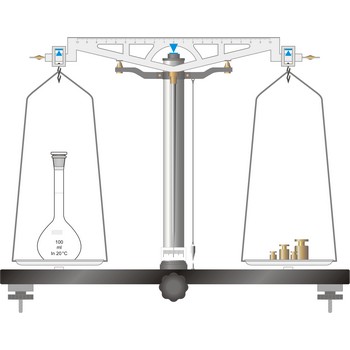
equal-arm balance → vaga s jednakim krakovima
The simplest type of balance, the equal-arm balance, is an application of a first class lever. The beam of the balance is supported on a central knife-edge, usually of agate, which rests upon a plane agate plate. The point of support is called the fulcrum. Two pans of equal weight are suspended from the beam, one at each end, at points equidistant from the fulcrum. A long pointer attached at right angles to the beam at the fulcrum indicates zero on a scale when the beam is at rest parallel to a level surface.
To prevent the knife-edge from becoming dull under the weight of the beam and pans the balance is equipped with a special device called an arrest. The arrest is operated by means of milled knob underneath the base plate in the middle and in front of the balance (sometimes the arrest knob is at one side of the balance).
The object to be weighed is placed on one pan, and standard weights are added to the other until the balance of the beam is established again. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
fuel cell → gorivi članak
Fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is different from a battery in that the energy conversion continues as long as fuel and oxidising agent are fed to the fuel cell; that is, in principle indefinitely. (A battery is manufactured with a limited amount of chemicals, and it is exhausted when all the chemicals have reacted.) It is a galvanic cell where spontaneous chemical reactions occur at the electrodes. The fuel is oxidised at the anode, and the oxidising agent (almost always oxygen or air) is reduced at the cathode. Presently, the most commonly used fuel is hydrogen. More conventional fuels (e.g., petrol or natural gas) must be converted (reformed) into hydrogen before they can be utilised in a fuel cell.
Some fuel cells employ an aqueous solution as electrolyte, that can be either acidic or basic (alkaline), or an ion-exchange membrane soaked in aqueous solution can act as the electrolyte. These fuel cells operate at relatively low temperatures (from room temperature to not much above the boiling point of water). Some fuel cells employ molten salts (especially carbonates) as electrolytes and have to operate at temperatures of several hundred degrees centigrade (Celsius). Others employ ionically conductive solids as electrolyte and must operate close to 1 000 °C.
gas washing bottle → boca ispiralica
Gas washing bottle or Drechsel bottle provide an inexpensive but effective method for washing or drying gases. The gas enters the bottle through the top of the central vertical tube, the lower end of which is below the surface of the washing medium. To maximize surface area contact of the gas to the liquid, a gas stream is slowly blown into the vessel through the fritted glass tip so that it breaks up the gas into many tiny bubbles. After bubbling through the medium, the gas rises to the top and exits through the side tube. It is named after the German chemist Edmund Drechsel (1843-1897).
galvanic celll → galvanski članak
Galvanic cell (voltaic cell) is a simple device with which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. Galvanic cells consist of two separate compartments called half cells containing electrolyte solutions and electrodes that can be connected in a circuit. Two dissimilar metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are immersed in an electrolyte. If the metals are connected by an external circuit, one metal is reduced (i.e., gains electrons) while the other metal is oxidized (i.e., loses electrons).
In the example above, copper is reduced and zinc is oxidized. The difference in the oxidation potentials of the two metals provides the electric power of the cell.
A voltaic cell can be diagrammed using some simple symbols. In the diagram the electrodes are on the outer side of the diagram and a vertical line (|) is used to separate the electrode from the electrolyte solution found in the compartment. A double vertical line (||) is used to separate the cell compartments and is symbolic of the salt bridge. Usually in a diagram the species oxidized is written to the left of the double slash. Here is an example of the Daniell cell:
The names refer to the 18th-century Italian scientists Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) and Luigi Galvani (1737-1798).
Geiger counter → Geigerov brojač
Geiger counter (Geiger-Muller counter) is a device used to detect and measure ionising radiation. It consists of a tube containing a low-pressure gas (usually argon or neon with methane) and a cylindrical hollow cathode through the centre of which runs a fine-wire anode. A potential difference of about 1 000 V is maintained between the electrodes. An ionising particle or photon passing through a window into the tube will cause an ion to be produced and the high potential will accelerate it towards its appropriate electrode, causing an avalanche of further ionisations by collision. The consequent current pulses can be counted in electronic circuits or simply amplified to work a small loudspeaker in the instrument. It was first devised in 1908 by the German physicist Hans Geiger (1882-1945). Geiger and W. Muller produced an improved design in 1928.
glutamic acid → glutaminska kiselina
Glutamic acid is an electrically charged amino acids. It is one of the two amino acids that contain a carboxylic acid group in its side chains. These acids play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Glutamic acid is commonly referred to as glutamate, because its carboxylic acid side chain will be deprotonated and thus negatively charged in its anionic form at physiological pH. Glutamic acid is referred to as a non-essential amino acid because a healthy human can synthesize all the glutamic acid needed for normal body function from other amino acids.
- Abbreviations: Glu, E
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopentanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO4
- Molecular weight: 147.13 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Centi." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table