absorption coefficient → apsorpcijski koeficijent
Absorption coefficient (a) is the relative decrease in the intensity of a collimated beam of electromagnetic radiation, as a result of absorption by a medium, during traversal of an infinitesimal layer of the medium, divided by the length traversed.
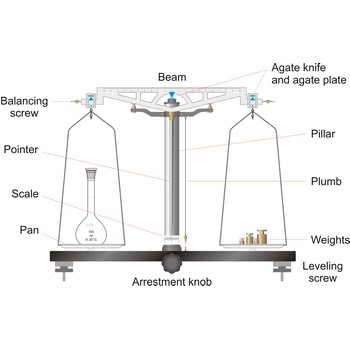
analytical balance → analitička vaga
Analytical balances are instruments used for precise determining mass of matter. Analytical balances are sensitive and expensive instruments, and upon their accuracy and precision the accuracy of analysis result depends. The most widely used type of analytical balances are balances with a capacity of 100 g and a sensitivity of 0.1 mg. Not one quantitative chemical analysis is possible without usage of balances, because, regardless of which analytical method is being used, there is always a need for weighing a sample for analysis and the necessary quantity of reagents for solution preparation.
The working part of the balance is enclosed in a glass-fitted case. The baseplate is usually of black glass or black slate. The beam has agate knife-edges at its extremes, supporting stirrups from which balance pans are suspended. Another agate or steel knife-edge is fixed exactly in the middle of the beam on its bottom side. This knife-edge faces downwards and supports the beam. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
The principle of operation of a modern laboratory balance bears some resemblance to its predecessor - the equal arm balance. The older instrument opposed the torque exerted by an unknown mass on one side of a pivot to that of an adjustable known weight on the other side. When the pointer returned to the center position, the torques must be equal, and the weight was determined by the position of the moving weights.
Modern electronic laboratory balances work on the principle of magnetic force restoration. In this system, the force exerted by the object being weighed is lifted by an electromagnet. A detector measures the current required to oppose the downward motion of the weight in the magnetic field.
holography → holografija
Holography is a technique for creating a three-dimensional image of an object by recording the interference pattern between a light beam diffracted from the object and a reference beam. The image can be reconstructed from this pattern by a suitable optical system.
nucleophile → nukleofil
Nucleophiles are negatively charged or bear a partial negative charge. Examples are lone pairs or a hydroxide ion.
radiography → radiografija
Radiography is nondestructive method of internal examination in which metal objects are exposed to a beam of X-ray or gamma radiation. Differences in thickness, density, or absorption caused by internal defects or inclusions are apparent in the shadow image produced on a fluorescent screen or photographic film placed behind the object.
balance → vaga
Balance is an instrument to measure the mass (or weight) of a body. Balance beam type scales are the oldest type and measure weight using a fulcrum or pivot and a lever with the unknown weight placed on one end of the lever, and a counterweight applied to the other end. When the lever is balanced, the unknown weight and the counterweight are equal. The equal-arm balance consists of two identical pans hung from either end of a centrally suspended beam. The unequal-arm balance is made with one arm of the balance much longer than the other.
More modern substitution balances use the substitution principle. In this calibrated weights are removed from the single lever arm to bring the single pan suspended from it into equilibrium with a fixed counter weight. The substitution balance is more accurate than the two-pan device and enables weighing to be carried out more rapidly.
Electromagnetic force restoration balances also use a lever system but a magnetic field is used to generate the force on the opposite end of the lever and balance out the unknown mass. The current used to drive the magnetic coil is proportional to the mass of the object placed on the platform.
Beer’s law → Beerov zakon
Beer’s law (or Beer-Lambert law) is the functional relationship between the quantity measured in an absorption method (A) and the quantity sought, the analyte concentration (c). As a consequence of interactions between the photons and absorbing particles, the power of the beam is attenuated from Po to P. Beer’s law can be written
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
Tyndall’s effect → Tyndallov efekt
Tyndall’s effect occurs when light disperses on colloid particles. This phenomenon can be seen when a ray of light enters in dark room through a small hole. In the beam some dust particles of colloid dimensions can be seen sparkling.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Bead snowflakes." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table