computational chemistry → kompjutacijska kemija
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry concerned with the prediction or simulation of chemical properties, structures, or processes using numerical techniques.
benzene → benzen
Benzene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon, C6H6, b.p. 80 °C. It is now made from petroleum by catalytic reforming (formerly obtained from coal tar). Benzene is the archetypal aromatic compound. It has an unsaturated molecule, yet will not readily undergo addition reactions. On the other hand, it does undergo substitution reactions in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or groups.
In 1865, Friedrich August Kekulé purposed the benzene molecule structure as a hexagonal ring which consists of six carbon atoms with alternate carbon-carbon single and carbon-carbon double bond. But such a structure should be highly reactive, and so didn't account for the unreactive nature of benzene. We now know that the best representation for the structure of benzene is indeed, hexagonal, with each C-C bond distance being identical and intermediate between those for a single and double bond. The π-orbitals from each neighbouring carbon atom overlap to form a delocalised molecular orbital which extends around the ring, giving added stability and with it, decreased reactivity. That is the reason the structural formula of benzene represents as a hexagon with a circle in the center which represents the delocalized electrons.
beta-glucan → beta-glukan
Beta-glucans are are naturally occurring polysaccharides that contain only glucose as structural components, and are linked with β-glycosidic bonds. They is the most known powerful immune stimulant. The most active forms of β-glucans are those comprising D-glucose units with β(1→3) links and with short side-chains of D-glucose attached at the β(1→6) position. These are referred to as beta-1,3/1,6 glucan. They are a major component of soluble dietary fiber, which can be found in cereal grains (oats, barley, wheat), yeast, and certain mushrooms (shiitake, maitake).
body-centered cubic lattice → prostorno centrirana kubična rešetka
Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc or cubic-I), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus an additional points at the center of the cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the bcc structures the spheres fill 68 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is two (8 × 1/8 + 1 = 2). There are 23 metals that have the bcc lattice.
borane → borani
Borane is any of the group of compounds of boron and hydrogen (B2H6, B4H10, B5H9, B5H11...), many of which can be prepared by action of acid on magnesium boride (Mg3B2). Boranes are a remarkable group of compounds in that their structures cannot be described using the conventional two-electron covalent bond model.
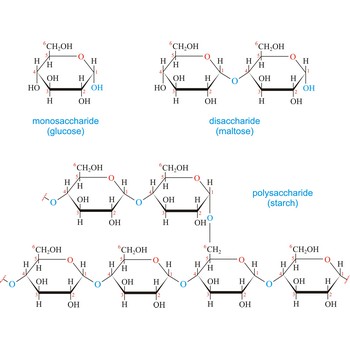
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
conjugated protein → konjugirani protein
Conjugated proteins are proteins which have a prostetic group as a part of their structure which is bonded with one or more amino acids of the same protein.
crystal → kristal
Crystal is a solid with a regular geometric shape, having a characteristic internal structure and enclosed by symmetrically arranged plane surfaces, intersecting at definite and characteristic angles. In crystals the particles (atoms, ions, or molecules) have a regular three-dimensional repeating arrangement in space. This is called the crystal structure. The crystal lattice is the arrangement of points in space at which the particles are positioned.
crystallography → kristalografija
Crystallography is a science that studies structure, shapes, crystalline properties and laws of their creation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Lewis structure." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table