glycine → glicin
Glycine is the smallest amino acid and is unique because it lacks a side chain. This gives it more conformational freedom than any other amino acid. Glycine is often found in turns and loops where other amino acids would be sterically unacceptable. Although it is formally nonpolar, it’s very small side chain makes no real contribution to hydrophobic interactions. Glycine is not essential to the human diet, as it is biosynthesized in the body from the amino acid serine.
- Abbreviations: Gly, G
- IUPAC name: 2-aminoacetic acid
- Molecular formula: C2H5NO2
- Molecular weight: 75.07 g/mol
glycoside → glikozid
Glycoside is one of a group of organic compounds in which a sugar group is bonded through its anomeric carbon to another group via a glycosidic bond. The sugar group is known as the glycon and the non-sugar group as the aglycon. According to the IUPAC definition, all disaccharides and polysaccharides are glycosides where the aglycone is another sugar.
In the free hemiacetal form, sugars will spontaneously equilibrate between the α and β anomers. However, once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Therefore, the alpha and beta glycosides are chemically distinct. They will have different chemical, physical, and biological properties. Many glycosides occur abundantly in plants, especially as flower and fruit pigments.
The term glycoside was later extended to cover not only compounds in which the anomeric hydroxy group is replaced by a group -OR, but also those in which the replacing group is -SR (thioglycosides), -SeR (selenoglycosides), -NR1R2 (N-glycosides), or even -CR1R2R3 (C-glycosides). Thioglycoside and selenoglycoside are legitimate generic terms; however the use of N-glycoside, although widespread in biochemical literature, is improper and not recommended here (glycosylamine is a perfectly acceptable term). C-Glycoside is even less acceptable. All other glycosides are hydrolysable; the C-C bond of C-glycosides is usually not. The use and propagation of names based on C-glycoside terminology is therefore strongly discouraged.
histidine → histidin
Histidine is an electrically charged amino acids with basic side chains. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Histidine is perhaps the most common and versatile catalytic residue in proteins. The imidazole sidechain of histidine has a pKa of approximately 6.0. This means that, at physiologically relevant pH values, relatively small shifts in pH will change its average charge. The unprotonated imidazole is nucleophilic and can serve as a general base, while the protonated form can serve as a general acid. In addition, it is often a ligand for transition metal ions such as iron and zinc.
- Abbreviations: His, H
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H9N3O2
- Molecular weight: 155.15 g/mol
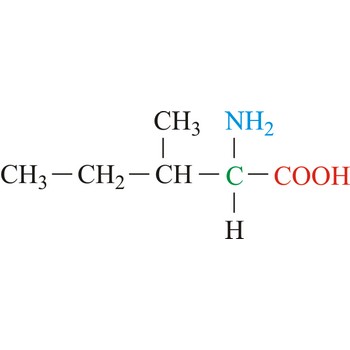
isoleucine → izoleucin
Isoleucine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is one of the three amino acids having branched hydrocarbon side chains. The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive but, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. Isoleucine is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Ile, I
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular weight: 131.12 g/mol
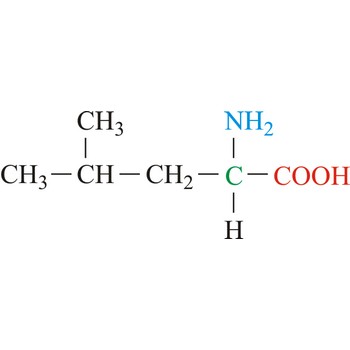
leucine → leucin
Leucine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It has one additional methylene group in its side chain compared with valine. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Leucine is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Leu, L
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular weight: 131.17 g/mol
lysine → lizin
Lysine is an electrically charged amino acids with basic side chains. Lysine is a base, as are arginine and histidine. The amino group is highly reactive and often participates in reactions at the active centers of enzymes. Lysine plays an important role in coordinating negatively charged ligands. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Lys, K
- IUPAC name: 2,6-diaminohexanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H14N2O2
- Molecular weight: 146.19 g/mol
methionine → metionin
Methionine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of the two sulfur-containing amino acids. Methionine is a fairly hydrophobic amino acid and typically found buried within the interior of a protein. It can form stacking interactions with the aromatic moieties of tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Met, M
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2S
- Molecular weight: 149.21 g/mol
normal conditions → normalni uvjeti
Gas is under normal (or standard) conditions when: p0 = 105 Pa and T0 = 273.15 K (0 °C). IUPAC recommends that the former use of the pressure of 1 atm as standard pressure (equivalent to 101 325 Pa) should be discontinued. At these conditions, the molar volume of gas Vm0 is 0.022 711 m3 (22.711 L).
phenylalanine → fenilalanin
Phenylalanine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. It is quite hydrophobic and even the free amino acid is not very soluble in water. Phenylalanine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Phe, F
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 165.19 g/mol
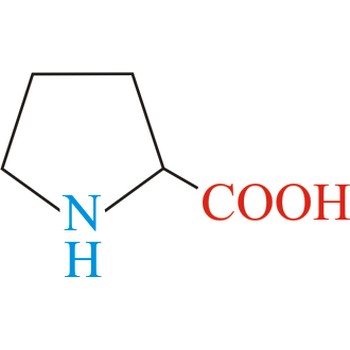
proline → prolin
Proline has an aliphatic side chain with a distinctive cyclic structure. It is unusual because it is conformationally restricted. The secondary amino (imino) group of proline residues is held in a rigid conformation that reduces the structural flexibility of polypeptide regions containing proline. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it.
- Abbreviations: Pro, P
- IUPAC name: pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO2
- Molecular weight: 115.13 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "IUPAC." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table