atomic orbital → atomska orbitala
Atomic orbital is a wave function that describes the behaviour of an electron in an atom.
degenerate orbitals → degenerirane orbitale
Degenerate orbitals are orbitals with the same energy. This degeneracy can sometimes be "lifted" by external electric or magnetic fields.
hybrid orbital → hibridne orbitale
Hybrid orbital is an orbital created by mixing together atomic orbitals to form an equal number of new hybrid atomic orbitals. For example, a common hybridization is sp3 where s orbital combine with a three p orbitals to form four new orbitals. After hybridization, all hybrid orbitals have the same energy, lower than p orbitals, but higher than s orbitals.
orbital → orbitala
Orbital is the area in space about an atom or molecule in which the probability of finding an electron is greatest.
The possible atomic orbitals correspond to subshells of the atom. Thus there is one s-orbital for each shell (orbital quantum number l = 0). There are three p-orbitals (corresponding to the three values of l) and five d-orbitals. The shapes of orbitals depend on the value of l.
sp hybrid orbital → sp hibridna orbitala
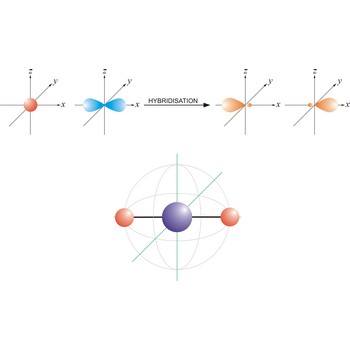
An sp hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and one p orbital of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The two sp hybrid orbitals are aligned in a straight line in opposite direction (bond angles are 180°). The remaining two p orbitals are at right angles to one another and to the line formed by the two sp orbitals.
sp2 hybrid orbital → sp2 hibridna orbitala
An sp2 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and two p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals lie in a plane with angle of 120°. The remaining p orbital remains unchanged and is perpendicular to the plane of the three sp2 orbitals.
sp3 hybrid orbital → sp3 hibridna orbitala
An sp3 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and three p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The four sp3 hybrid orbitals point toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron with the bond angle of 109.5°.
aromatic compounds → aromatski ugljikovodici
Aromatic compounds are a major group of unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons containing one or more rings, typified by benzene, which has a 6-carbon ring containing three double bonds. All the bonds in benzene (C6H6) are the same length intermediate between double and single C-C bonds. The properties arise because the electrons in the p-orbitals are delocalised over the ring, giving extra stabilization energy of 150 kJ/mol over the energy of Kekulé structure. Aromatic compounds are unsaturated compounds, yet they do not easily partake in addition reactions.
Historical use of the term implies a ring containing only carbon (e.g., benzene, naphthalene), but it is often generalized to include heterocyclic structures such as pyridine and thiophene.
benzene → benzen
Benzene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon, C6H6, b.p. 80 °C. It is now made from petroleum by catalytic reforming (formerly obtained from coal tar). Benzene is the archetypal aromatic compound. It has an unsaturated molecule, yet will not readily undergo addition reactions. On the other hand, it does undergo substitution reactions in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or groups.
In 1865, Friedrich August Kekulé purposed the benzene molecule structure as a hexagonal ring which consists of six carbon atoms with alternate carbon-carbon single and carbon-carbon double bond. But such a structure should be highly reactive, and so didn't account for the unreactive nature of benzene. We now know that the best representation for the structure of benzene is indeed, hexagonal, with each C-C bond distance being identical and intermediate between those for a single and double bond. The π-orbitals from each neighbouring carbon atom overlap to form a delocalised molecular orbital which extends around the ring, giving added stability and with it, decreased reactivity. That is the reason the structural formula of benzene represents as a hexagon with a circle in the center which represents the delocalized electrons.
Bohr atom → Bohrov atom
Bohr atom is a model of the atom that explains emission and absorption of radiation as transitions between stationary electronic states in which the electron orbits the nucleus at a definite distance. The Bohr model violates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle since it postulates definite paths and moment for electrons as they move around the nucleus. Modern theories usually use atomic orbitals to describe the behaviour of electrons in atoms.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sp2 hibridna orbitala." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table