toxic chemical → bojni otrov
Toxic chemical means any chemical which through its chemical action on life processes can cause death, temporary incapacitation, or permanent harm to humans or animals. This includes all such chemicals, regardless of their origin or of their method of production, and regardless of whether they are produced in facilities, in munitions or elsewhere.
dissociation constant → konstanta disocijacije
Dissociation constant is a constant whose numerical value depends on the equilibrium between the undissociated and dissociated forms of a molecule. A higher value indicates greater dissociation.
The term dissociation is also applied to ionisation reactions of acids and bases in water. For example
which is often regarded as a straightforward dissociation into ions
The equilibrium constant of such a dissociation is called the acid dissociation constant or acidity constant, given by
The concentration of water [H2O] can be taken as constant.
Similarly, for a base, the equilibrium
is also a dissociation; with the base dissociation constant or basicity constant, given by
Ka (Kb) is a measure of the strength of the acid (base).
dysprosium → disprozij
Dysprosium was discovered by Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran (France) in 1886. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word dysprositos meaning hard to obtain. It is soft, lustrous, silvery metal. Reacts with oxygen. Reacts rapidly with water; dissolves in acids. Metal ignites and burns readily. Reductant. Dysprosium usually found with erbium, holmium and other rare earths in some minerals such as monazite sand. Dysprosium uses are limited to the experimental and esoteric. Some isotopes of dysprosium are effective absorbers of thermal neutrons and are being considered for use in the control rods in nuclear reactors.
weak electrolyte → slabi elektrolit
Weak electrolytes are those electrolytes which in water solutions dissociate only partially, giving ions and which are in equilibrium with undissociated molecules. Their water solutions conduct electric current weakly. For example, acetic acid partially dissociates into acetate ions and hydrogen ions, so that an acetic acid solution contains both molecules and ions.
ecological footprint → ekološki otisak
The Ecological Footprint is defined as the area of productive land and water ecosystems required to produce the resources that the population consumes (food, fiber, timber, energy, and space for infrastructure) and assimilate the wastes that the population produces (CO2 is the only waste product currently included), wherever on Earth the land and water is located. It compares actual throughput of renewable resources relative to what is annually renewed. Non-renewable resources are not assessed, as by definition their use is not sustainable.
Ecological footprints and biocapacity are expressed in global hectares (gha). Each unit corresponds to one hectare of biologically productive space with world average productivity. In U.S. Footprint results are often presented in global acres (ga). One U.S. acre is equal to 0.405 hectares.
Humanity is currently consuming renewable resources at a faster rate than ecosystems can regenerate them and continuing to release more CO2 than ecosystems can absorb. In 2007, humanity's Footprint was 18 billion gha, or 2.7 gha per person. However, the Earth's biocapacity was only 11.9 billion gha, or 1.8 gha per person. This represents an ecological overshoot of 50 per cent. Put another way, people used the equivalent of 1.5 planets to support their activities (more developed countries generally make higher demands on the Earth's ecosystems than poorer, less developed countries).
EDTA → EDTA
Ethyldiaminetetraacetic acid (C10H16N2O8) or shortened EDTA is a hexadentant ligand, and it forms chelates with both transition-metal ions and main-group ions. EDTA is used as a negative ion - EDTA4-. The diagram shows the structure of the ion with the important atoms picked out. The EDTA ion entirely wraps up a metal ion using all 6 of the positions. The co-ordination number is again 6 because of the 6 co-ordinate bonds being formed by the central metal ion.
EDTA is frequently used in soaps and detergents, because it forms a complexes with calcium and magnesium ions. These ions are in hard water and interfere with the cleaning action of soaps and detergents. EDTA is also used extensively as a stabilizing agent in the food industry and as an anticoagulant for stored blood in blood banks. EDTA is the most common reagent in complexometric titration.
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
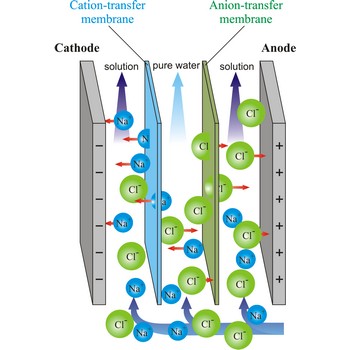
electrodialysis → elektrodijaliza
Electrodialysis is a procedure of dialysis accelerated with an electric field. Dialyser is divided into three sections. Solution flows through the middle section, between two semipermeable membranes alternately to positive ions and negative ions. An electrodes are placed in the neighbouring sections. Under the influence of electric field, positive ions will travel towards the cathode (the negative electrode), and negative ions towards the anode (the positive electrode), whereby travelling of ions through the membrane is accelerated. In this way, the feed water is separated into two streams: one of pure water and the other of more concentrated solution.
electrolytes → elektroliti
Electrolytes are substances which, when melted or dissolved in water, conduct electric current. By melting or dissolving they are dissociated into electrically charged particles (ions) which are able to conduct electric current. By passing of electric current the transfer of matter occurs. Positively charged particles (cations) travel towards the negative pole (the cathode) and negatively charged particles (the anions) travel towards the positive pole (the anode). Liquid metals, in which the conduction is by free electrons, are not usually regarded as electrolytes. Solid conductors of ions, as in the sodium-sulphur cell, are also known as electrolytes. Depending upon how it conducts electric current, matter can be divided into strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes and nonconductors.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Permanent hardness in water." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table