ligand → ligand
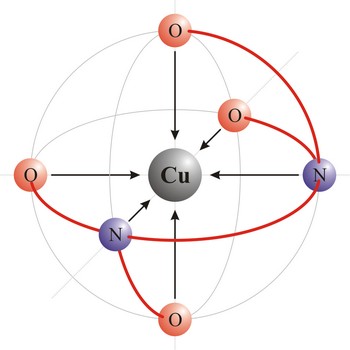
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
mass spectrometry → masena spectrometrija
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique in which ions are separated according to the mass/charge (m/e) ratio and detected by a suitable detector.
In a mass spectrometer a sample is ionised and the positive ions produced are accelerated into a high-vacuum region containing electric and magnetic fields. These fields deflect and focus the ions onto a detector. A mass spectrum is thus obtained, consisting of a series of peaks of variable intensity to which m/e values can be assigned. Different molecules can be identified by their characteristic pattern of lines.
metal → metal
Metals are materials in which the highest occupied energy band (conduction band) is only partially filled with electrons.
Their physical properties generally include:
- They are good conductors of heat and electricity. The electrical conductivity of metals generally decreases with temperature.
- They are malleable and ductile in their solid state.
- They show metallic lustre.
- They are opaque.
- They have high density.
- They are solids (except mercury)
- They have a crystal structure in which each atom is surrounded by eight to twelve near neighbours
Their chemical properties generally are:
- They have one to four valence electrons.
- They have low ionisation potentials; they readily lose electrons.
- They are good reducing agents.
- They have hydroxides which are bases or amphoteric.
- They are electropositive.
Metallic characteristics of the elements decrease and non-metallic characteristics increase with the increase of valence electrons. Also metallic characteristics increase with the number of electron shells. Therefore, there is no sharp dividing line between the metals and non-metals.
Of the 114 elements now known, only 17 show primarily non-metallic characteristics, 7 others are metalloids, and 89 may be classed as metals.
photomultiplier → fotomultiplikator
Photomultiplier (photomultiplier tube or PMT) is a very versatile and sensitive detector of radiant energy in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. A typical photomultiplier tube consists of a photoemissive cathode (photocathode) followed by focusing electrodes, an electron multiplier (dynode) and an electron collector (anode) in a vacuum tube.
polarogram → polarogram
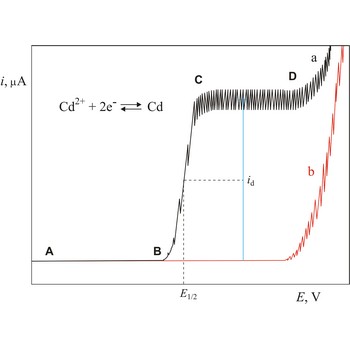
Polarogram is a graph of current versus potential in a polarographic analysis. The position of a polarographic wave in a polarogram along the x axis (E1/2) provides an identity of the substance while the magnitude of the limiting diffusion current (id) provides the concentration of this substance.
resistance → električni otpor
Electrical resistance (R) of a given object is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that object. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm, represented by the Greek letter omega (Ω). Resistance is the electric potential difference divided by the current when there is no electromotive force in the conductor. This definition applies to direct current. For a conductor of uniform cross section with area A and length L, and whose resistivity is ρ, the resistance is given by
Schrodinger equation → Schrodingerova jednadžba
Schrödinger equation is the basic equation of wave mechanics which, for systems not dependent on time, takes the form:
where Ψ is the wavefunction, V is the potential energy expressed as a function of the spatial coordinates, E its total energy, ![]() 2 is the Laplacian operator, h is Planck’s constant, and m is the mass.
2 is the Laplacian operator, h is Planck’s constant, and m is the mass.
solar cell → sunčeva ćelija
Solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is a device that captures sunlight and transforms it directly to electricity. All solar cells make use of photovoltaic effect, so often they are called photovoltaic cells. Almost all solar cells are built from solid-state semiconducting materials, and in the vast majority of these the semiconductor is silicon.
The photovoltaic effect involves the generation of mobile charge carriers-electrons and positively charged holes-by the absorption of a photon of light. This pair of charge carriers is produced when an electron in the highest filled electronic band of a semiconductor (the valence band) absorbs a photon of sufficient energy to promote it into the empty energy band (the conduction band). The excitation process can be induced only by a photon with an energy corresponding to the width of the energy gap that separates the valence and the conduction band. The creation of an electron-hole pair can be converted into the generation of an electrical current in a semiconductor junction device, wherein a layer of semiconducting material lies back to back with a layer of either a different semiconductor or a metal. In most photovoltaic cells, the junction is p-n junction, in which p-doped and n-doped semiconductors are married together. At the interface of the two, the predominance of positively charged carriers (holes) in the p-doped material and of negatively charged carriers (electrons) in the n-doped material sets up an electric field, which falls off to either side of the junction across a space-charge region. When absorption of a photon in this region generates an electron-hole pair, these charge carriers are driven in opposite directions by the electric field, i.e. away from the interface and toward the top and bottom of the two-layer structure, where metal electrodes on these faces collect the current. The electrode on the top layer (through which light is absorbed) is divided into strips so as not to obscure the semiconducting layers below. In most widely used commercial solar cells, the p-doped and n-doped semiconductive layers are formed within a monolithic piece of crystalline silicon. Silicon is able to absorb sunlight at those wavelengths at which it is most intense-from the near-infrared region (wavelengths of around 1200 nm) to the violet (around 350 nm).
superfluid helium → superfluidni helij
Superfluidity in helium-4 was discovered in 1938 by the Soviet physicist Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa. Helium-4 exhibits superfluidity when it is cooled below 2.18 K (-270.97 C), which is called the lambda (λ) point. At these temperatures, helium-4 exhibits the characteristics of two distinct fluids, one of which appears to flow without friction. An extensive series of experiments showed that in this state of helium, called helium II (He II), there is an apparent enormous rise in heat conductivity, at an increase rate of about three million. Another unusual property of He II is its mobile, rapid flow through capillaries or over the rim of its containment vessel as a thin film that exhibits no measurable viscosity and appears unaffected by the forces of gravity or evaporation and condensation.
tear gas → suzavac
Tear gases is the common name for substances which, in low concentrations, cause pain in the eyes, flow of tears and difficulty in keeping the eyes open. Tear gases are used mainly in military exercises and in riot control, etc., but have also been used as a method of warfare. Irritating gases have been used in war since ancient times but it was not until after the Second World War that a more systematic search for effective substances was started. Among a long series of substances, three have become of greater importance than the others. These substances are chloroacetophenone (codename CN), orto-chlorobenzylidene-malononitrile (CS) and dibenz(b,f)-1,4-oxazepine (CR).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Electrode potential series." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table