thermodynamic laws → termodinamički zakoni
Thermodynamic laws are the foundation of the science of thermodynamics:
First law: The internal energy of an isolated system is constant; if energy is supplied to the system in the form of heat dq and work dw, then the change in energy dU = dq + dw.
Second law: No process is possible in which the only result is the transfer of heat from a reservoir and its complete conversion to work.
Third law: The entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero as the thermodynamic temperature approaches zero.
analytical balance → analitička vaga
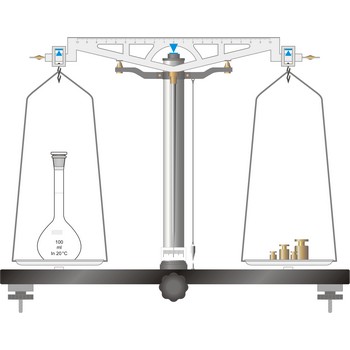
Analytical balances are instruments used for precise determining mass of matter. Analytical balances are sensitive and expensive instruments, and upon their accuracy and precision the accuracy of analysis result depends. The most widely used type of analytical balances are balances with a capacity of 100 g and a sensitivity of 0.1 mg. Not one quantitative chemical analysis is possible without usage of balances, because, regardless of which analytical method is being used, there is always a need for weighing a sample for analysis and the necessary quantity of reagents for solution preparation.
The working part of the balance is enclosed in a glass-fitted case. The baseplate is usually of black glass or black slate. The beam has agate knife-edges at its extremes, supporting stirrups from which balance pans are suspended. Another agate or steel knife-edge is fixed exactly in the middle of the beam on its bottom side. This knife-edge faces downwards and supports the beam. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
The principle of operation of a modern laboratory balance bears some resemblance to its predecessor - the equal arm balance. The older instrument opposed the torque exerted by an unknown mass on one side of a pivot to that of an adjustable known weight on the other side. When the pointer returned to the center position, the torques must be equal, and the weight was determined by the position of the moving weights.
Modern electronic laboratory balances work on the principle of magnetic force restoration. In this system, the force exerted by the object being weighed is lifted by an electromagnet. A detector measures the current required to oppose the downward motion of the weight in the magnetic field.
chemical reaction equation → jednadžba kemijske reakcije
Chemical reactions are symbolically shown with chemical equations. On the left side of the equation we write formulas or substance symbols which enter the chemical reaction, reactants. On the right side formulas or substance symbols which emerge from the chemical reaction, products, are writen.
Each chemical reaction leads to an equilibrium which is moved more or less to one side (left or right). Because of that, in reversible reactions instead of = sign two opposite arrows are put
In order to write down certain chemical reaction equation all reactants and all products and their stechiometric proportions must be known. (See Chemical reaction balancing)
harmonic motion → harmoničko gibanje
Harmonic motion is caused by restoring force, acting on a body that is displaced from its equilibrium position. This force tries to put the body back in equilibrium. Usual examples are the motion of a body attached to elastic spring (see: Hooke’s law) and the motion of mathematical pendulum. The body undergoes periodic motion around the equilibrium point.
equal-arm balance → vaga s jednakim krakovima
The simplest type of balance, the equal-arm balance, is an application of a first class lever. The beam of the balance is supported on a central knife-edge, usually of agate, which rests upon a plane agate plate. The point of support is called the fulcrum. Two pans of equal weight are suspended from the beam, one at each end, at points equidistant from the fulcrum. A long pointer attached at right angles to the beam at the fulcrum indicates zero on a scale when the beam is at rest parallel to a level surface.
To prevent the knife-edge from becoming dull under the weight of the beam and pans the balance is equipped with a special device called an arrest. The arrest is operated by means of milled knob underneath the base plate in the middle and in front of the balance (sometimes the arrest knob is at one side of the balance).
The object to be weighed is placed on one pan, and standard weights are added to the other until the balance of the beam is established again. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
stoichiometry → stehiometrija
Stoichiometry is the relative proportions elements from compounds or in which substances react. Every chemical reaction has its characteristic proportions. For example, when methane unites with oxygen in complete combustion, 1 mol of methane requires 2 mol of oxygen.
At the same time, 1 mol of carbon dioxide and 2 mol of water are formed as reaction products.
Alternatively, 16 g of methane and 64 g of oxygen produce 44 g of carbon dioxide and 36 g of water.
The stoichiometric relationship between the products and reactants can be used to in calculations.
absorbance → apsorbancija
Absorbance (A) is a logarithm of the ratio of incident radiant power (Po) to transmitted radiant power (P) through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls).
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
acid dissociation constant → konstanta disocijacije kiseline
Acid dissociation constant (Ka) is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of an acid HA through the reaction
The quantity pKa = -log Ka is often used to express the acid dissociation constant.
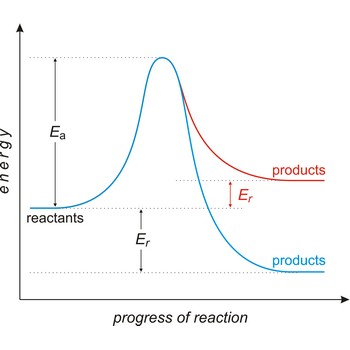
activation energy → energija aktivacije
Activation energy (Ea) is the energy that must be added to a system in order for a process to occur, even though the process may already be thermodynamically possible. In chemical kinetics, the activation energy is the height of the potential barrier separating the products and reactants. It determines the temperature dependence on the reaction rate.
Avogadro, Amadeo → Avogadro, Amadeo
Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856) is an Italian chemist and physicist that proposed a correct molecular explanation for Gay-Lussac’s law of combining volumes. His work provided a simple way to determine atomic weights and molecular weights of gases. He is published a theory about the movement of particles in gases that became known as Avogadro’s Law.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Zakon o kemijskoj ravnoteži." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table