Hirsch funnel → Hirschov lijevak
Hirsch funnels are essentially smaller Büchner funnels and primarily used to collect a desired solid from a relatively small volume of liquid (1-10 mL). The main difference is that the plate is much smaller, while the walls of the funnel angle outward instead of being vertical. It is named after the German chemist Robert Hirsch (1856-1913).
Joule-Thomson coefficient → Joule-Thompsonov koeficijent
Joule-Thomson coefficient (μ) is a parameter which describes the temperature change when a gas expands adiabatically through a nozzle from a high pressure to a low pressure region. It is defined by
where H is enthalpy.
Knudsen burette → Knudsenova bireta
Knudsen's automatic bulb-burette, developed by the Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949), is designed in a way that even routine field analysis in a boat laboratory would provide highly accurate measurements. The burette is filled with a mixture of silver nitrate from reservoir R, located above the burette, by opening the A valve. When the solution crosses the three-way C valve the A valve is closed preventing further solution flow in to the burette. Any extra solution is caught in the W bowl. Turn the C valve, which marks the zero on the scale, in order to allow atmospheric air to enter the burette. Since most open-ocean samples lie in a relatively small chlorinity range, the burette is designed so that much of its capacity is in the bulb (B). This allows the titration to be quick (by quickly releasing contents from the B area) and reduces the error that occurs from the slow drainage along the inner wall of the burette.
Each millimeter is divided in to twenty parts (double millimeter division of the Knudsen burette) which allows for highly accurate measurements (the scale is read up to a precision of 0.005 mL). From 0 to 16 the burette isn't divided, that usually starts from 16 and goes until 20.5 or 21.5. A single double millimeter on a Knudsen burette scale corresponds to one permille of chloride in the seawater sample. This burette can be used for titration of water from all of the oceans and seas, with the exemptions being areas with very low salinity (e.g. the Baltic Sea) and river estuaries which require the use of normal burettes.
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
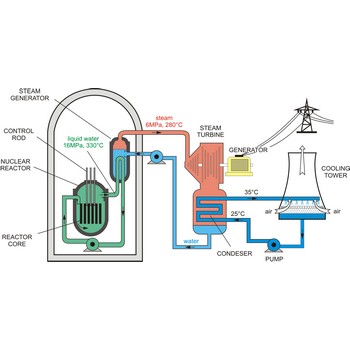
nuclear reactor → nuklearni reaktor
Nuclear reactor is an assembly of fissionable material (uranium-235 or plutonium-239) designed to produce a sustained and controllable chain reaction for the generation of electric power.
The essential components of a nuclear reactor are:
- The core, metal rods containing enough fissionable material to maintain a chain reaction at the necessary power level (as much as 50 t of uranium may be required).
- A source of neutrons to initiate the reaction (such as a mixture of polonium and beryllium)
- A moderator to reduce the energy of fast neutrons for more efficient fission (material such as graphite, beryllium, heavy water, and light water are used)
- A coolant to remove the fission-generated heat (water, sodium, helium, and nitrogen may be used)
- A control system such as rods of boron or cadmium that have high capture cross sections (to absorb neutrons)
- Adequate shielding, remote-control equipment, and appropriate instrumentation are essential for personnel safety and efficient operation.
monosaccharide → monosaharid
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates, with the general formula Cn(H2O)n, that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrates by hydrolysis.
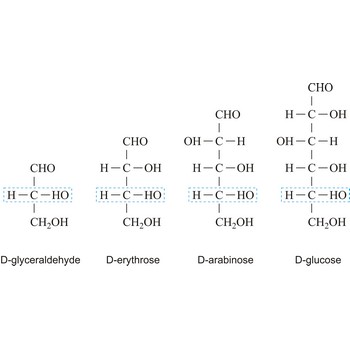
Depending on whether the molecule contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) or a ketone group (-CO-) monosaccharide can be a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose). These aldehyde and ketone groups confer reduction properties on monosaccharides. They are also classified according to the number of carbon atoms they contain: trioses have three carbon atoms, tetroses four, pentoses five, hexoses six, heptoses seven, etc. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, a six-carbon polyhydroxy aldehyde such as D-glucose is an aldohexose, whereas a six-carbon polyhydroxy ketone such as D-fructose is a ketohexose.
The notations D and L are used to describe the configurations of carbohydrates. In Fischer projections of monosaccharides, the carbonyl group is always placed on top (in the case of aldoses) or as close to the top as possible (in the case of ketoses). If the OH group attached to the bottom-most asymmetric carbon (the carbon that is second from the bottom) is on the right, then the compound is a D-sugar. If the OH group is on the left, then the compound is an L-sugar. Almost all sugars found in nature are D-sugars.
Monosaccharides can exist as either straight-chain or ring-shaped molecules. During the conversion from straight-chain form to cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon, becomes a chiral center with two possible configurations (anomers), α and β. When the stereochemistry of the first carbon matches the stereochemistry of the last stereogenic center the sugar is the α-anomer when they are opposite the sugar is the β-anomer.
octahedral molecular geometry → oktaedarska geometrija molekule
Octahedral molecular geometry (square bipyramidal shape) describes the shape of compounds where six atoms or ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom. The sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), with six bonding pairs, is predicted and found to be a regular octahedron. Four of the attachments are positioned in a square plane with 90° bond angles. The remaining two attachments are positioned perpendicular (90°) to the square plane at opposite ends of the central atom. Molecules with an octahedral electron pair geometries have sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybridization at the central atom.
Onsager relations → Onsagerove relacije
Onsager relations are an important set of equations in the thermodynamics of irreversible processes. They express the symmetry between the transport coefficients describing reciprocal processes in systems with a linear dependence of flux (Ji) on driving forces (Xj).
In Onsager’s theory the coupling coefficients are equal, Lij = Lji. This is known as reciprocal relations. The theory was developed by the Norwegian chemist Lars Onsager (1903-1976) in 1931.
pipette → pipeta
Pipettes are glass tubes which are tapers towards at both ends into narrow opened tubes. According to their design two types of pipettes can be distinguished:
Volumetric pipettes
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette
Graduated pipettes
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. They are filled in the same way as volumetric ones and liquid can be gradually released.
poison → otrov
Poisons are substance, which upon contact or being introduced into an organism, impair or prevent normal metabolic processes from taking place, thus altering the normal functioning of organs or tissues.
Poisons are molecules or material that tends to collect on a catalyst surface, blocking access to active sites or destroying their activities.
Poisons are substance that can reduce a nuclear reaction by absorbing neutrons, thereby preventing more fission. If enough poisons are present in a reactor core, the chain reaction will die out.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "What are desi folks." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table