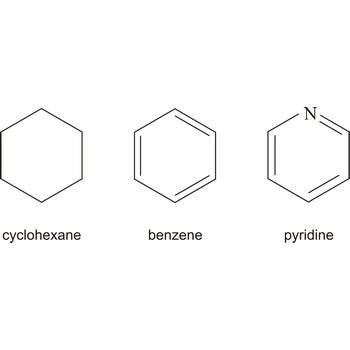
cyclic compound → ciklički spoj
Cyclic describing a compound that has a ring of atoms in its molecules. In homocyclic compounds all the atoms in the ring are of the same type, e.g. benzene (C6H6) and cyclohexane (C6H12). These two examples are also examples of carbocyclic compounds; i.e. the rings are made of carbon atoms. If different atoms occur in the ring, as in pyridine (C5H5N), the compound is said to be heterocyclic.
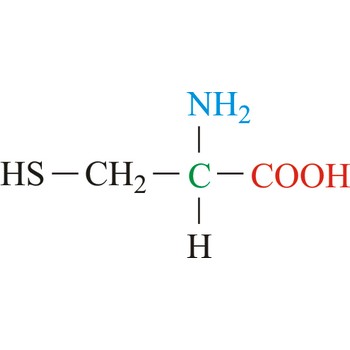
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
decay series → raspadni niz
Decay series is a series of decay in which radioactive element is decomposed in different elements until it produces one stable atom.
Daniell cell → Daniellov članak
In 1836 the British chemist John Frederic Daniell (1790-1845) proposed an improved electric cell that supplied an even current during continuous operation. Daniell cell consisted of a glass jar containing copper and zinc electrodes, each immersed in their respective acidic sulphate solutions. The two solutions were separated by a porous clay cylinder separator. It was a galvanic cell in which the spontaneous electrodissolution of zinc and electroplating of copper provided the electrical current.
Zn(s) |
→ | Zn2+ + 2e- |
+0.763 V |
Cu2+ + 2e- |
→ | Cu(s) |
+0.337 V |
Zn(s) + Cu2+ |
→← | Zn2+ + Cu(s) |
+1.100 V |
deoxyribonucleic acid → dezoksiribonukleinska kiselina
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid with 2-deoxy-D-ribose as the sugar in its nucleotides. DNA contains encoded genetic information, specifically templates for the synthesis of all of an organism’s proteins and enzymes.
DNA was first identified in the 1869 by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895). In 1953, American biologist James Dewey Watson (1928-) and English physicist Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916–2004) had discovered that DNA occurs in the cell as a double helix, with two long strands of the molecule wound around each other, and further that the chemical structure of the molecule dictates that adenine (A) always aligns or pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). It is this base pairing that allows DNA in a cell to copy itself, and transfer its information to a new cell. The diameter of the helix is 2.0 nm and there is a residue on each chain every 0.34 nm in the z direction. The angle between each residue on the same strand is 36°, so that the structure repeats after 10 residues (3.4 nm) on each strand.
desiccator → eksikator
Desiccator is a glass container with dry atmosphere due to the presence of some dehydrating agent. It is used for protecting the samples, reagents or precipitates from humidity. As dehydrating agent usually waterless calcium chloride (CaCl2) is used.
Dewar flask → Dewarova posuda
Dewar flask or vacuum bottle is a container for storing hot or cold substances. It consists of two flasks, one placed inside the other, with a vacuum between. The vacuum prevents the conduction of heat from one flask to the other. For greater efficiency the flasks are silvered to reflect heat. The substance to be kept hot or cold, e.g., liquid air, is contained in the inner flask. The flask is named after British chemist and physicist Sir James Dewar (1842-1923). Dewar invented the Dewar flask in 1892 to aid him in his work with liquid gases. The common thermos bottle is an adaptation of the Dewar flask.
dialysis → dijaliza
Dialysis is a method by which large molecules (such as starch or protein) and small molecules (such as glucose or amino acids) may be separated in a solution by selective diffusion through a semipermeable membrane. Through this kind of membrane dissolved particles pass and colloid dimension particles fall behind. For example, if a mixed solution of starch and glucose is placed in a closed container made of a semipermeable substance (such as cellophane), which is then immersed in a beaker of water, the smaller glucose molecules will pass trough the membrane into the water, while the starch molecules remain behind.
diamond → dijamant
Diamond is the hardest known mineral (with a hardness of 10 on Mohs’ scale). It is an allotropic form of pure carbon that has crystallised in the cubic system, usually as octahedral or cubes, under great pressure. Diamond crystals my be colourless and transparent or yellow, brown or black. They are highly prized as gemstones, but also have extensive uses in industry, mainly for cutting and grinding tools. Diamonds occur in ancient volcanic pipes of kimberlite, or in river deposits that have been derived from weathered kimberlite. Industrial diamonds are being increasingly synthetically produced.
diastereoisomer → dijastereoizomer
Diastereoisomers (diastereomers) are stereoisomers of a compound having two or more chiral centers that are not a mirror image of another stereoisomer of the same compound. For example, in the structure below, 1 and 2 are enantiomers and so are 3 and 4; 1 and 3 are diastereoisomers, as are 2 and 4. Unlike enantiomers, diastereoisomers need not have closely similar physical and chemical properties
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Visoko fruktozni kukuruzni sirup." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table