potentiometric titration → potenciometrijska titracija
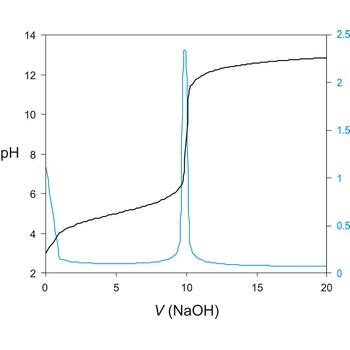
Potentiometric titration is a volumetric method in which the potential between two electrodes is measured (referent and indicator electrode) as a function of the added reagent volume. Types of potentiometric titrations for the determination of analytes in photoprocessing solutions include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric.
Potentiometric titrations are preferred to manual titrations, since they are more accurate and precise. They are also more easily adapted to automation, where automated titration systems can process larger volumes of samples with minimal analyst involvement.
A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The part of the curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalence point of the titration. The first derivative, ΔE/ΔV, is the slope of the curve, and the endpoint occurs at the volume, V', where ΔE/ΔV has the maximum value.
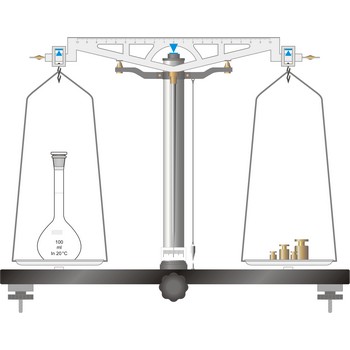
precision balance → tehnička vaga
Precision balances typically display results from three to one decimal places (0.001 g up to 0.1 g). The readability precision balances are reduced when compared to analytical balances but, precision balances accommodate higher capacities (up to several kilograms). In its traditional form, it consists of a pivoted horizontal lever of equal length arms, called the beam, with a weighing pan, also called scale, suspended from each arm.
In electronic top pan, or toploader balances, mass is determined not by mechanical deflection but by electronically controlled compensation of an electric force. The signal generated enables the mass to be read from a digital display. The mass of the empty container can be stored in the balance’s computer memory and automatically deducted from the mass of the container plus its contents.
proline → prolin
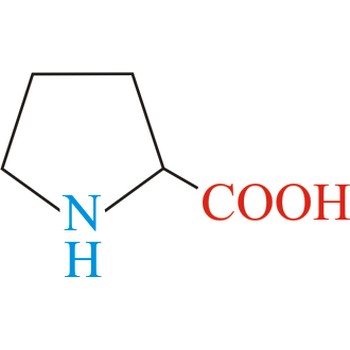
Proline has an aliphatic side chain with a distinctive cyclic structure. It is unusual because it is conformationally restricted. The secondary amino (imino) group of proline residues is held in a rigid conformation that reduces the structural flexibility of polypeptide regions containing proline. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it.
- Abbreviations: Pro, P
- IUPAC name: pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO2
- Molecular weight: 115.13 g/mol
protactinium → protaktinij
Protactinium was discovered by Otto Hahn (Germany) and Lise Meitner (Austria) in 1917. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word protos meaning first. It is very rare, silvery-white, extremely radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; reacts with oxygen and acids. Attacked by steam. Highly radiotoxic. Protactinium is extremely toxic and must be handled with great care. Protactinium does not occur in nature. Found among fission products of uranium, thorium and plutonium.
proton → proton
Proton is a stable elementary particle of unit positive charge and spin 1/2. Protons and neutrons, which are collectively called nucleons, are the constituents of the nucleus.
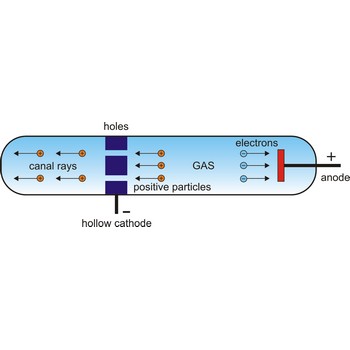
In 1886, German physicist Eugene Goldstein (1850-1930) discovered positive particles by using a modified Crookes tube with holes in the cathode in an evacuated tube. When cathode rays were given off in one direction toward the anode, other rays found their way through the holes in the cathode and sped off in the opposite direction. Since these other rays traveled in the direction opposite to the negatively charged cathode rays, it seemed that they must be composed of positively charged particles. Rutherford suggested that this fundamental positive particle be called the proton.
qualitative analysis → kvalitativna analiza
Qualitative analysis involves determining the nature of a pure unknown compound or the compounds present in a mixture. Qualitative inorganic analysis is used to separate and detect cations and anions in a sample substance. According to their properties, cations are usually classified into six groups. Each group has a common reagent which can be used to separate them from the solution.
radioactive series → radioaktivni niz
Radioactive series is a sequence of nuclides formed by successive radioactive decays until a stable decay product, the end product, is formed. A famous example of a radioactive series is the decay of uranium, which through a series of steps decays into stable lead.
radium → radij
Radium was discovered by Marie and Pierre Curie (France) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word radius meaning ray. It is silvery-white radioactive metal. Reacts with oxygen and water. Highly radiotoxic. Carcinogen by inhalation, ingestion, or exposure. Radium is found in uranium ores at 1 part per 3 million parts uranium. Used in treating cancer because of the gamma rays it gives off.
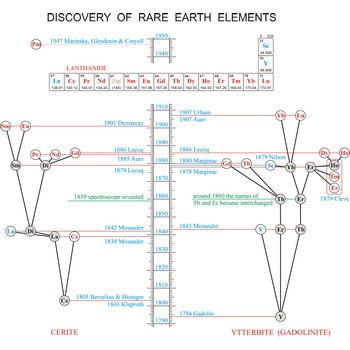
rare earth elements → elementi rijetkih zemalja
Rare earth elements (metals) are the elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), and the lanthanides (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu). These elements got their name from the fact that chemists first isolated them in their oxide forms. These oxides somewhat resemble calcium, magnesium and aluminium oxides, sometimes called common earths. Do you want to know more?
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Visoka peÃâ¡." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table