allotrope → alotrop
Allotropes are the elements which exist in two or more different forms in the same physical state. Allotropes generally differ in physical properties and may also differ in chemical activity.
Diamond, graphite and fullerenes are three allotropes of the element carbon. Graphite is a soft, black, slippery substance; by contrast, diamond is one of the hardest substances known. The different properties of the allotropes arise from their chemical structures. Diamonds typically crystallize in the cubic crystal system and consist of tetrahedrally bonded carbon atoms. Graphite crystallizes in the hexagonal system. In the fullerenes, the carbon atoms taking the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, or tube.
In some cases, the allotropes are stable over a temperature range, with a definite transition point at which one changes into the other. For instance, tin has two allotropes: white (metallic) tin stable above 13.2 °C and grey (nonmetallic) tin stable below 13.2 °C.
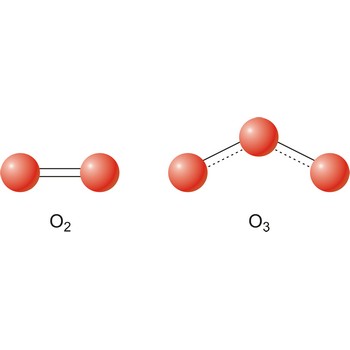
The term allotropes may also be used to refer to the molecular forms of an element. Ozone is a chemically active triatomic allotrope of the element oxygen.
allotropic modification → alotropska modifikacija
Different substances of the same elementary system are called allotropes or allotropic modifications. In the case of oxygen, there are two allotropic modifications: "normal" dioxygen (O2) and trioxygen (O3) or ozone.
geometrical optics → geometrijska optika
In most cases light can be described as an electromagnetic wave. Geometrical optics is an approximation in which the waves can be represented as straight-line rays. This approximation is valid if the light waves do not meet obstacles comparable in size to the wavelength of radiation.
allotropy → alotropija
Allotropy (Gr. allos, other, and tropos, manner) is the phenomenon of an element existing in two or more physical forms in the same physical state. The difference between the forms involves either crystaline structure (white, red and black phosphorus), the number of atoms in the molecule of a gas (diatomic oxygen and triatomic ozone), or the molecular structure of a liquid (liquid helium an helium II).
In some cases, the allotropes are stable over a temperature range, with a definite transition point at which one changes into the other. For instance, tin has two allotropes: white (metallic) tin stable above 13.2 °C and grey (nonmetallic) tin stable below 13.2 °C. This form allotropy is called enantiotropy. Form of allotropy, in which there is no transition temperature at which the two are in equilibrium, is called monotropy.
Allotropy does not apply to the substance existing in different physical states as, for example, when ice melts and changes from solid ice to liquid water.
Allotropy is generally restricted to describing polymorphic behaviour in elements, while polymorphism may refer to any material having multiple crystal structures.
angular momentum → moment količine gibanja
Angular momentum is a physical quantity defined for rotating motion (in analogy to momentum that is defined for linear motion). If a body rotates around a specified axis, its angular momentum equals
Where I is the rotational inertia concerning that axis and ω is the angular velocity of the body.
Angular momentum can also be defined for a point-like body concerning a specified origin (in that case, it is not necessary that the point-like body undergoes circular motion). Rotational inertia of the point-like body, concerning that origin equals:
Where m is the mass of the body and r is its distance from the origin.
ball mill → kuglični mlin
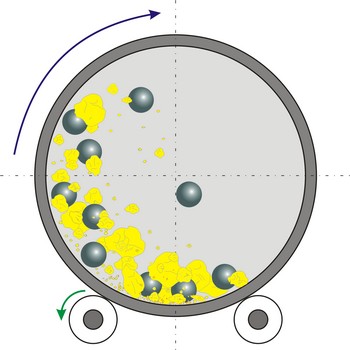
Ball mill is a grinder for reducing hard materials to powder. The grinding is carried out by the pounding and rolling of a charge of steel or ceramic balls carried within the cylinder. The cylinder rotates at a relatively slow speed, allowing the balls to cascade through the mill base, thus grinding or dispersing the materials.
Type of ball mills, centrifugal and planetary mills, are devices used to rapidly grind materials to colloidal fineness (approximately 1 μm and below) by developing high grinding energy via centrifugal and/or planetary action.
analytical balance → analitička vaga
Analytical balances are instruments used for precise determining mass of matter. Analytical balances are sensitive and expensive instruments, and upon their accuracy and precision the accuracy of analysis result depends. The most widely used type of analytical balances are balances with a capacity of 100 g and a sensitivity of 0.1 mg. Not one quantitative chemical analysis is possible without usage of balances, because, regardless of which analytical method is being used, there is always a need for weighing a sample for analysis and the necessary quantity of reagents for solution preparation.
The working part of the balance is enclosed in a glass-fitted case. The baseplate is usually of black glass or black slate. The beam has agate knife-edges at its extremes, supporting stirrups from which balance pans are suspended. Another agate or steel knife-edge is fixed exactly in the middle of the beam on its bottom side. This knife-edge faces downwards and supports the beam. When not in use and during loading or unloading of the pans, the balance should be arrested.
The principle of operation of a modern laboratory balance bears some resemblance to its predecessor - the equal arm balance. The older instrument opposed the torque exerted by an unknown mass on one side of a pivot to that of an adjustable known weight on the other side. When the pointer returned to the center position, the torques must be equal, and the weight was determined by the position of the moving weights.
Modern electronic laboratory balances work on the principle of magnetic force restoration. In this system, the force exerted by the object being weighed is lifted by an electromagnet. A detector measures the current required to oppose the downward motion of the weight in the magnetic field.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ventas de casa en la ciudadela orellana guayaquil." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table