solar cell → sunčeva ćelija
Solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is a device that captures sunlight and transforms it directly to electricity. All solar cells make use of photovoltaic effect, so often they are called photovoltaic cells. Almost all solar cells are built from solid-state semiconducting materials, and in the vast majority of these the semiconductor is silicon.
The photovoltaic effect involves the generation of mobile charge carriers-electrons and positively charged holes-by the absorption of a photon of light. This pair of charge carriers is produced when an electron in the highest filled electronic band of a semiconductor (the valence band) absorbs a photon of sufficient energy to promote it into the empty energy band (the conduction band). The excitation process can be induced only by a photon with an energy corresponding to the width of the energy gap that separates the valence and the conduction band. The creation of an electron-hole pair can be converted into the generation of an electrical current in a semiconductor junction device, wherein a layer of semiconducting material lies back to back with a layer of either a different semiconductor or a metal. In most photovoltaic cells, the junction is p-n junction, in which p-doped and n-doped semiconductors are married together. At the interface of the two, the predominance of positively charged carriers (holes) in the p-doped material and of negatively charged carriers (electrons) in the n-doped material sets up an electric field, which falls off to either side of the junction across a space-charge region. When absorption of a photon in this region generates an electron-hole pair, these charge carriers are driven in opposite directions by the electric field, i.e. away from the interface and toward the top and bottom of the two-layer structure, where metal electrodes on these faces collect the current. The electrode on the top layer (through which light is absorbed) is divided into strips so as not to obscure the semiconducting layers below. In most widely used commercial solar cells, the p-doped and n-doped semiconductive layers are formed within a monolithic piece of crystalline silicon. Silicon is able to absorb sunlight at those wavelengths at which it is most intense-from the near-infrared region (wavelengths of around 1200 nm) to the violet (around 350 nm).
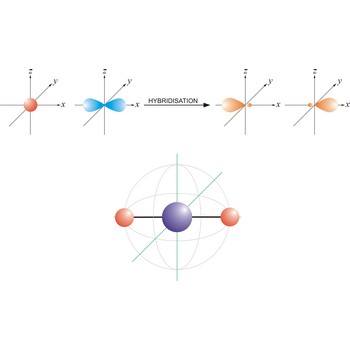
sp hybrid orbital → sp hibridna orbitala
An sp hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and one p orbital of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The two sp hybrid orbitals are aligned in a straight line in opposite direction (bond angles are 180°). The remaining two p orbitals are at right angles to one another and to the line formed by the two sp orbitals.
sp3 hybrid orbital → sp3 hibridna orbitala
An sp3 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and three p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The four sp3 hybrid orbitals point toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron with the bond angle of 109.5°.
square planar molecular geometry → kvadratna planarna geometrija molekule
Square planar is a molecular shape that results when there are four bonds and two lone pairs on the central atom in the molecule. An example of a square planar molecule is xenon tetrafluoride (XeF4). This molecule is made up of six equally spaced sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybrid orbitals arranged at 90° angles. The shape of the orbitals is octahedral. Two orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons on opposite sides of the central atom. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
square pyramidal molecular geometry → kvadratna piramidalna geometrija molekule
Square pyramidal is a molecular shape that results when there are five bonds and one lone pair on the central atom in the molecule. Bromine pentafluoride (BrF5) has the geometry of a square pyramid, with fluorine atoms occupying five vertices, one of which is above the plane of the other four. This molecule is made up of six equally spaced sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybrid orbitals arranged at 90° angles. The shape of the orbitals is octahedral. Because of the high symmetry of the octahedral arrangement, all six positions are equivalent, so it does not matter in which position in the drawing we put the lone pair. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
structural formula → strukturna formula
Structural formula is a two dimensional representations of the arrangement of the atoms in molecules. Atoms are represented by their element symbols and covalent bonds are represented by lines. The symbol for carbon is often not drawn.
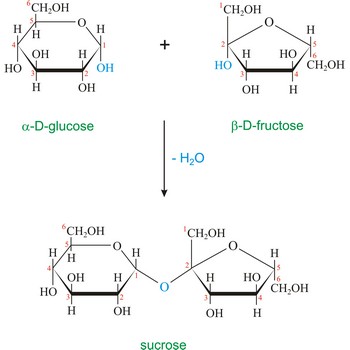
sucrose → saharoza
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
T-shaped molecular geometry → T-oblik geometrije molekule
T-shape is a molecular geometry that results when there are 3 bonds and 2 lone pairs around the central atom in the molecule. The atoms bonded to the central atom lie at the ends of a T with 90° angles between them. Molecules with an trigonal bipyramidal electron pair geometries have sp3d (or dsp3) hybridization at the central atom. ICl3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry.
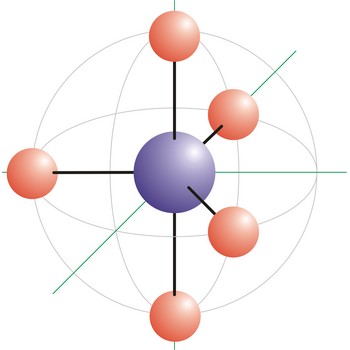
tetrahedral molecular geometry → tetraedarska geometrija molekule
Tetrahedral is a molecular shape that results when there are four bonds and no lone pairs around the central atom in the molecule. The atoms bonded to the central atom lie at the corners of a tetrahedron with 109.5° angles between them. Molecules with an tetrahedral electron pair geometries have sp3 hybridization at the central atom. The ammonium ion (NH4+) and methane (CH4) have a tetrahedral molecular geometry.
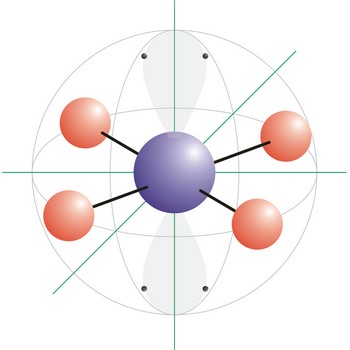
trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry → trigonska bipiramidalna geometrija molekule
Trigonal bipyramidal (trigonal bipyramidal shape) is a molecular geometry that results when there are five bonds and no lone pairs on the central atom in the molecule. Three of the bonds are arranged along the atom’s equator, with 120° angles between them; the other two are placed at the atom’s axis. Axial bonds are at right angles to the equatorial bonds. Molecules with an trigonal bipyramidal electron pair geometries have sp3d (or dsp3) hybridization at the central atom. The PCl5 molecule has a trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Valence bond theory." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table