valence bond theory → teorija valentne veze
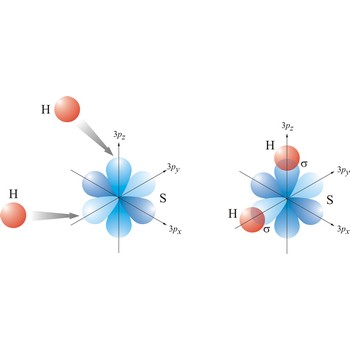
Valence bond theory is a theory that explains the shapes of molecules in terms of overlaps between half-filled atomic orbitals, or half filled hybridised orbitals.
valence bond → valentna veza
In the valence bond theory, a valence bond is a chemical bond formed by overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals on two different atoms.
sigma bond → sigma veza
Most single bonds are sigma bonds (σ-bond). In the valence bond theory, a sigma bond is a valence bond that is symmetrical around the imaginary line between the bonded atoms.
triple bond → trostruka veza
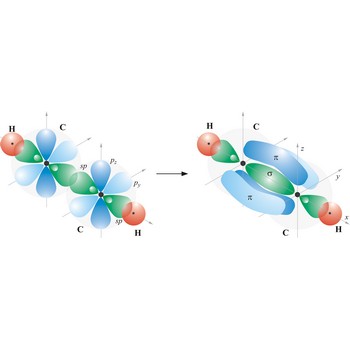
Triple bond. (≡) is a covalent bond that involves 3 bonding pairs. In the valence bond theory, one of the bonds in a triple bond is a sigma bond and the other two are pi bonds. For example, the central bond in acetylene is a triple bond: H-C≡C-H.
collision theory → teorija sudara
Collision theory is theory that explains how chemical reactions take place and why rates of reaction alter. For a reaction to occur the reactant particles must collide. Only a certain fraction of the total collisions cause chemical change; these are called successful collisions. The successful collisions have sufficient energy (activation energy) at the moment of impact to break the existing bonds and form new bonds, resulting in the products of the reaction. Increasing the concentration of the reactants and raising the temperature bring about more collisions and therefore more successful collisions, increasing the rate of reaction.
metallic bond → metalna veza
Metallic bond is a electrostatic attraction binding the positive ions of a solid metal together by means of a "sea" of delocalised valence electrons
Bronsted-Lowry’s acid-base theory → Bronsted-Lowryeva teorija kiselina i lužina
Brønsted-Lowry’s acid-base theory: Acid is a substance which gives a proton (protondonor) and base is a substance which accepts a proton (protonacceptor).
conjugated bond → konjugirana veza
Conjugated bonds describe the alternating pattern of double and single bonds, or triple bonds and single bonds, in a molecule. In such molecules, there is some delocalisation of electrons into the pi orbitals of the carbon atoms linked by the single bond.
conjugated double bond → konjugirana dvostruka veza
Conjugated double bond in organic compounds is a system of double bonds between atoms which are separated by one single bond (1,3-butene, H2C=CH-CH=CH2).
cumulated double bond → kumulirana dvostruka veza
Cumulated double bond in organic compounds is a system of two double bonds on the same atom of carbon (C=C=C)
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Valence bond theory." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table