thermodynamic laws → termodinamički zakoni
Thermodynamic laws are the foundation of the science of thermodynamics:
First law: The internal energy of an isolated system is constant; if energy is supplied to the system in the form of heat dq and work dw, then the change in energy dU = dq + dw.
Second law: No process is possible in which the only result is the transfer of heat from a reservoir and its complete conversion to work.
Third law: The entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero as the thermodynamic temperature approaches zero.
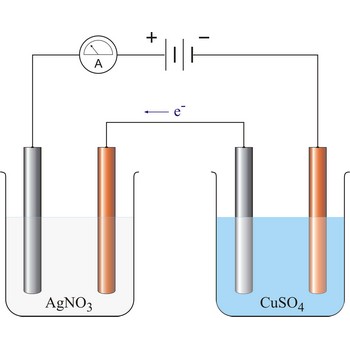
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis → Faradayevi zakoni elektrolize
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are two laws found by British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) in his experiments on electrolysis:
1. The quantity of matter extracted on the electrode is proportional to the quantity of charge (Q = I·t) which has flown in electrolysis time.
where z = number of electrons changed in reaction and F = Faraday’s constant which equals 96 487 C mol-1.
2. The masses of the elements liberated by the same quantity of electricity are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
96 487 C will discharge 1 mol Ag and 1/2 mol Cu. The relevant half reactions are:
Gibbs phase rule → Gibbsov zakon faza
Gibbs phase rule is the relationship used to determine the number of state variables, usually chosen from among temperature, pressure, and species composition in each phase, which must be specified to fix the thermodynamic state of a system in equilibrium:
where C is the number of components in a mixture, P is the number of phases, and F is the degrees of freedom, i.e., the number of intensive variables that can be changed independently without affecting the number of phases.
Avogadro’s law → Avogadrov zakon
Avogadro’s law: Equal volumes of all gases contain equal numbers of molecules at the same pressure and temperature. The law, often called Avogadro’s hypothesis, is true only for ideal gases. It was proposed in 1811 by Italian chemist Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856).
Beer’s law → Beerov zakon
Beer’s law (or Beer-Lambert law) is the functional relationship between the quantity measured in an absorption method (A) and the quantity sought, the analyte concentration (c). As a consequence of interactions between the photons and absorbing particles, the power of the beam is attenuated from Po to P. Beer’s law can be written
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
Biot-Savart law → Biot-Savartov zakon
The magnetic field B due to a current-carrying conductor can be determined by Biot-Savart law. The contribution to magnetic field set up at distance r by the current element IdL is given by expression:
where μ0 is permeability constant. It plays a role in magnetic problems equivalent to the role of permittivity constant μ0 in electrostatics problems. In order to obtain B, contributions of all current elements have to be integrated. In case of a long straight conductor, carrying current I, Biot-Savart law gives:
SI unit for magnetic field B is tesla (T).
Permaeability constant μ0 has value 4π×10-7 T m A-1.
Fick’s law → Fickov zakon
Fick’s law is the statement that the flux J of a diffusing substance is proportional to the concentration gradient, i.e.,
where D is called the diffusion coefficient.
first law of thermo-dynamics → prvi zakon termodinamike
First law of thermo-dynamics is: Energy can be neither created nor destroyed, but can cross from one shape to another.
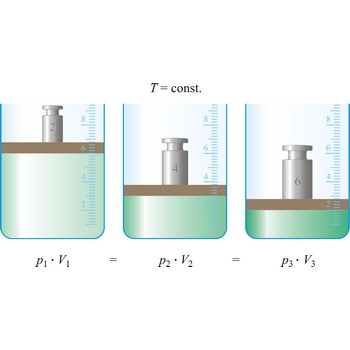
Boyle’s law → Boyleov zakon
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle-Mariott’s law) is the empirical law, exact only for an ideal gas, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Termodinamički zakoni." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table