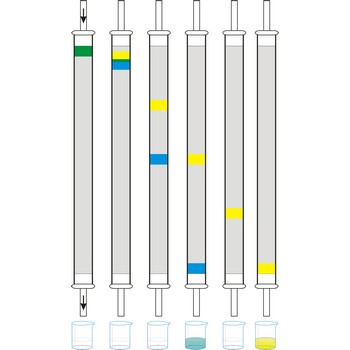
supercritical fluid chromatography → superkritična fluidna kromatografija
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is a hybrid of gas and liquid chromatography. SFC is of importance because it permits the separation and determination of a group of compounds that are not conveniently handled by either gas or liquid chromatography. These compounds are either nonvolatile or thermally labile so that gas chromatography cannot be used and they do not contain functional groups that make possible detection by liquid chromatography. SFC has been applied to a wide variety of materials including natural prodcuts, drugs, foods, pesticides and herbicides, fossil fuels, explosives and propellants.
supercritical fluid extraction → superkritična fluidna ekstrakcija
Supercritical fluid extractions (SFE) have solvating powers similar to liquid organic solvents, but with higher diffusivities, lower viscosity, and lower surface tension. The main advantages of using supercritical fluids for extractions is that they are inexpensive, contaminant free, and less costly to dispose safely than organic solvents. For non-destructive isolation choose SFE, which is simply the best technology for sensitive raw materials. For these reasons supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is the reagent used to extract caffeine from coffee and tea. Its gaslike behavior allows it to penetrate deep into the green coffee beans, and it dissolves from 97 % to 99 % of the caffeine present.
chromatography → kromatografija
Chromatography is a method of separation of the components of a sample in which the components are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary while the other moves. In gas chromatography, the gas moves over a liquid or solid stationary phase. In liquid chromatography, the liquid mixture moves through another liquid, a solid, or a gel. The mechanism of separation of components may be adsorption, differential solubility, ion-exchange, permeation, or other mechanisms.
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
paper chromatography → papirna kromatografija
Paper chromatography is one of the types of chromatography procedures which runs on a piece of specialized paper. It is a planar chromatography systems wherein a cellulose filter paper acts as a stationary phase on which separation of compounds occurs. The edge of the paper is immersed in a solvent, and the solvent moves up the paper by capillary action.
thin layer chromatography → tankoslojna kromatografija
Thin layer chromatography. (TLC) is a technique for separating components in a mixture on the basis of their differing polarities. A spot of sample is placed on a flat sheet coated with silica and then carried along by a solvent that soaks the sheet. Different components will move different distances over the surface. TLC is a useful screening technique in clinical chemistry; for example, it can be used to detect the presence of drugs in urine.
supercritical carbon dioxide → superkritični ugljikov dioksid
Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is a powerful, cheap, non-toxic and environmental friendly solvent. When used at a supercritical state (over 74 bar and 31 °C), it achieves similar solvating power as its organic competitors, such as hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents. Supercritical carbon dioxide is one of few solvents that can be unrestrictedly used for food processing.
supercritical fluid → superkritični fluid
Supercritical fluid is any substance above its critical temperature and critical pressure (see phase diagram). It shows unique properties that are different from those of either gases or liquids under standard conditions. A supercritical fluid has both the gaseous property of being able to penetrate anything, and the liquid property of being able to dissolve materials into their components. Solublity increases with increasing density (i.e. with increasing pressure). An example of this is naphthalene which is practically insoluble in low pressure carbon dioxide. At 100 bar the solubility is 10 g/L and at 200 bar it is 50 g/L. Rapid expansion of supercritical solutions leads to precipitation of a finely divided solid.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Superkritična fluidna kromatografija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table