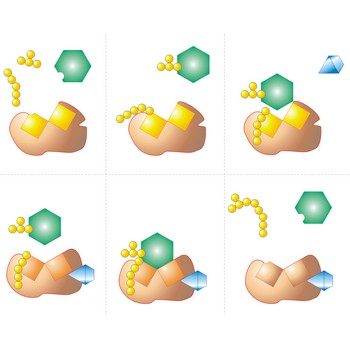
active site → aktivno mjesto
Active site is a pocket or crevice on an enzyme molecule that fits reactant molecules like a hand in a glove. The active site lowers the activation energy for reaction
asparagine → asparagin
Asparagine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. The polar amino acids are an important class of amino acids since they provide many of the functional groups found in proteins. Asparagine is a common site for attachment of carbohydrates in glycoproteins. In general this is not very reactive residues. Asparagine is amide derivative of aspartic acid. Asparagine is not essential for humans, which means that it can be synthesized from central metabolic pathway intermediates and is not required in the diet.
- Abbreviations: Asn, N
- IUPAC name: 2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H8N2O3
- Molecular weight: 132.12 g/mol
chelate → kelat
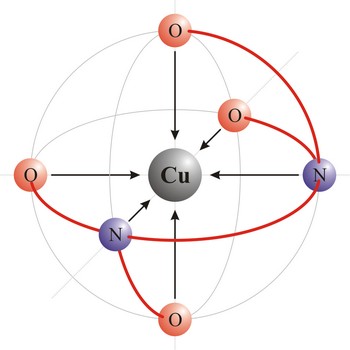
Chelate is a compound characterized by the presence of bonds from two or more bonding sites within the same ligand to a central metal atom. For example, copper complexes with EDTA to form a chelate. Chelate complexes are more stable than complexes with the corresponding monodentate ligands.
polyvalent molecule → polivalentna molekula
Polyvalent molecule is a molecule which having multiple binding sites. The antibodies of our immune system are one example.
close-packed structure → gusta slagalina
Close packing is the packing of spheres so as to occupy the minimum amount of space. The name close packed refers to the packing efficiency of 74.05 %. There are two types of close packing: hexagonal and cubic. One layer, with atoms centered on sites labeled a. Two layers, with the atoms of the second layer centered on sites labeled b. The third layer can be placed on the sites labeled c (giving cubic close-packing) or over those marked a (giving hexagonal close-packing).
enzyme → enzim
Enzyme is a protein that acts as a catalyst in biochemical reactions. Each enzyme is specific to a particular reaction or a group of similar reactions. Many require the association of certain nonprotein cofactors in order to function. The molecule undergoing a reaction (the substrate) binds to a specific active site on the enzyme molecule to form a short-lived intermediate: this greatly increases (by a factor of up to 1020) the rate at which the reaction proceeds to form the product.
poison → otrov
Poisons are substance, which upon contact or being introduced into an organism, impair or prevent normal metabolic processes from taking place, thus altering the normal functioning of organs or tissues.
Poisons are molecules or material that tends to collect on a catalyst surface, blocking access to active sites or destroying their activities.
Poisons are substance that can reduce a nuclear reaction by absorbing neutrons, thereby preventing more fission. If enough poisons are present in a reactor core, the chain reaction will die out.
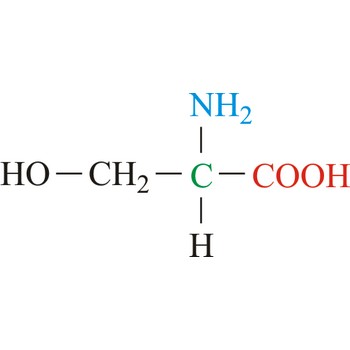
serine → serin
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sitel foundever." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table