reactivity series → reaktivni niz
Reactivity series or activity series is a series of elements (usually metals) ranked by their reactivity degree, made for comparison of reactions of elements with other substances, e.g. acids and oxygen.
Balmer series → Balmerova serija
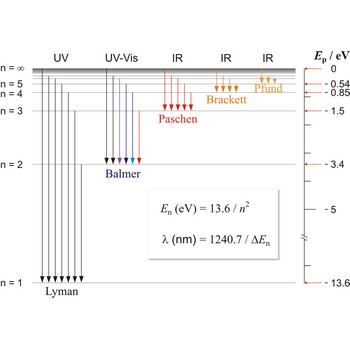
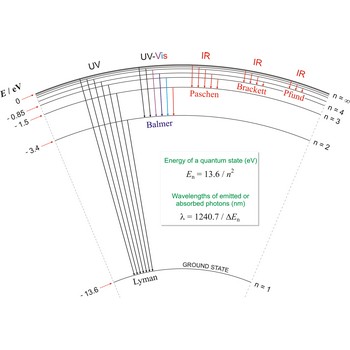
Balmer series, Balmer lines is a series of lines in the emission spectrum of hydrogen that involve transitions to the n=2 state from states with n>2.
decay series → raspadni niz
Decay series is a series of decay in which radioactive element is decomposed in different elements until it produces one stable atom.
electrochemical series → elektrokemijski niz
Electrochemical series is a series of chemical elements arranged in order of their standard electrode potentials. The hydrogen electrode
is taken as having zero electrode potential. An electrode potential is, by definition, a reduction potential.
Elements that have a greater tendency than hydrogen to lose electrons to their solution are taken as electropositive; those that gain electrons from their solution are below hydrogen in the series and are called electronegative.
The series shows the order in which metals replace one another from their salts; electropositive metals will replace hydrogen from acids.
homologous series → homologni niz
Series of compounds which have a common general formula and in which each member differs from the next member by a constant unit, which is the methylene group (-CH2-) is called the homologous series. Members of a homologous series are called homolog.
An example of the homologous series with some of their homologs are given below. Straight chain alkanes having general formula CnH2n+2
| Structure | Name |
|---|---|
| CH4 | methane |
| CH3-CH3 | ethane |
| CH3-CH2-CH3 | propane |
| CH3-CH2CH2CH3 | butane |
| CH3-(CH2)3-CH3 | pentane |
| CH3-(CH2)4-CH3 | hexane |
| CH3-(CH2)5-CH3 | heptane |
| CH3-(CH2)6-CH3 | octane |
| CH3-(CH2)7-CH3 | nonane |
| CH3-(CH2)8-CH3 | decane |
Lyman series → Lymanova serija
Lyman series is the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the ground state (principal quantum number n = 1) and successive excited states.
Paschen series → Paschenova serija
Paschen series are the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the state with principal quantum number n = 3 and successive higher states.
radioactive series → radioaktivni niz
Radioactive series is a sequence of nuclides formed by successive radioactive decays until a stable decay product, the end product, is formed. A famous example of a radioactive series is the decay of uranium, which through a series of steps decays into stable lead.
serine → serin
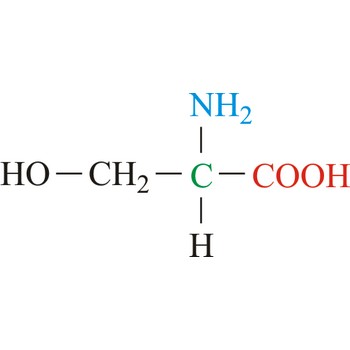
Serine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group. Serine often serves as a nucleophile in many enzyme active sites, and is best known for its role in the serine proteases. Serine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine.
- Abbreviations: Ser, S
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular weight: 105.09 g/mol
actinides → aktinoidi
Actinides (actinons or actinoids) are the fourteen elements from thorium to lawrencium inclusive, which follow actinium in the periodic table. The position of actinium is somewhat equivocal and, although not itself an actinide, it is often included with them for comparative purpose. The series includes the following elements: thorium (Th), protactinium (Pa), uranium (U), neptunium (Np), plutonium (Pu), amercium (Am), curium (Cm), berkelium (Bk), californium (Cf), einsteinium (Es), fermium (Fm), mendelevium (Md), nobelium (No) and lawrencium (Lr). Every known isotope of the actinide elements is radioactive. Traces of Pa, Np and Pu are consequently found, but only Th and U occur naturally to any useful extent.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Serin." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table