polymer → polimer
Polymer is a substance composed of molecules of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass (monomers). In most cases the number of monomers is quite large and is often not precisely known. A single molecule of a polymer is called a macromolecule. Polystyrene is light solid material obtained by polymerisation of styrene (vinyl benzene).
polymorphism → polimorfija
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid substance to crystallise into more than one different crystal structure. Different polymorphs have different arrangements of atoms within the unit cell, and this can have a profound effect on the properties of the final crystallised compound. The change that takes place between crystal structures of the same chemical compound is called polymorphic transformation.
The set of unique crystal structures a given compound may form are called polymorphs. Calcium carbonate is dimorphous (two forms), crystallizing as calcite or aragonite. Titanium dioxide is trimorphous; its three forms are brookite, anatase, and rutile. The prevailing crystal structure depends on both the temperature and the external pressure.
Iron is a metal with polymorphism structure. Each structure stable in the range of temperature, for example, when iron crystallizes at 1 538 °C it is bcc (δ-iron), at 1 394 °C the structure changes to fcc (γ-iron or austenite), and at 912 °C it again becomes bcc (α-iron or ferrite).
Polymorphism of an element is called allotropy.
potassium → kalij
Potassium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word qali meaning alkali (the origin of the symbol K comes from the Latin word kalium). It is soft, waxy, silver-white metal. Fresh surface has silvery sheen. Quickly forms dull oxide coating on exposure to air. Reacts strongly with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Reacts violently with oxidants. Occurs only in compounds. Potassium is found in minerals like carnallite [(KMgCl3)·6H2O] and sylvite (KCL). Pure metal is produced by the reaction of hot potassium chloride and sodium vapours in a special retort. Used as potash in making glass and soap. Also as saltpetre, potassium nitrate (KNO3) to make explosives and to colour fireworks in mauve. Vital to function of nerve and muscle tissues.
proton → proton
Proton is a stable elementary particle of unit positive charge and spin 1/2. Protons and neutrons, which are collectively called nucleons, are the constituents of the nucleus.
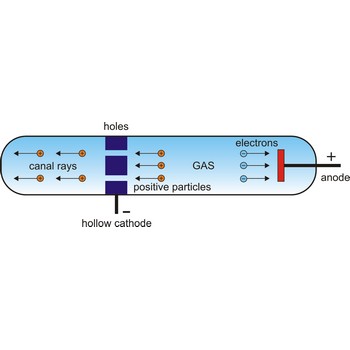
In 1886, German physicist Eugene Goldstein (1850-1930) discovered positive particles by using a modified Crookes tube with holes in the cathode in an evacuated tube. When cathode rays were given off in one direction toward the anode, other rays found their way through the holes in the cathode and sped off in the opposite direction. Since these other rays traveled in the direction opposite to the negatively charged cathode rays, it seemed that they must be composed of positively charged particles. Rutherford suggested that this fundamental positive particle be called the proton.
qualitative analysis → kvalitativna analiza
Qualitative analysis involves determining the nature of a pure unknown compound or the compounds present in a mixture. Qualitative inorganic analysis is used to separate and detect cations and anions in a sample substance. According to their properties, cations are usually classified into six groups. Each group has a common reagent which can be used to separate them from the solution.
radioactive indicator → radioaktivni indikator
By use of suitable radioactive isotopes biochemical processes can be observed in plants, animals and humans, by measuring radioactive radiation of radioactive indicator. Artificial radioactive isotopes have the same chemical properties as natural ones, which enable us to mark those natural isotopes with addition of artificial ones and in this way follow the path of those elements during a chemical reaction. One of the most important radioactive indicators is the radioactive carbon 14C.
refractometer → refraktometar
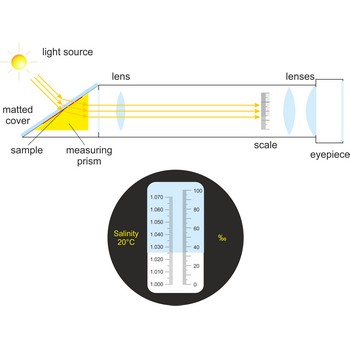
Refractometer is an optical device used from measurement of refractive index. A refractometer takes advantage of the fact that light bends as it passes through different materials. It can be used to measure the salinity of water or the amount of sugar in fresh grapes. Refractometers are available with or without automatic temperature compensation (ATC).
When using a conventional saltwater refractometer, a sample is placed on an optical prism in the sample window. As light shines through the sample, it is bent according to the salinity of the water, and casts a shadow on the scale that is visible through the eyepiece. Salinity is read directly through the eyepiece.
relative density → relativna gustoća
Relative density (d) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of some reference substance. For liquids or solids it is the ratio of the density (usually at 20 °C) to the density of water at 4 °C. Since one must specify the temperature of both the sample and the water to have a precisely defined quantity, the use of this term is now discouraged. This quantity was formerly called specific gravity.
relative molecular mass → relativna molekularna masa
Relative molecular mass (Mr) is the ratio of the average mass per molecule or specified entity of a substance to 1/12 of the mass of nuclide 12C. Also called molecular weight. It is equal to the sum of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms that comprise a molecule. For example
Mr(H2SO4) = 2·Ar(H) + Ar(S) + 4·Ar(O)
= 2·1.0079 + 32.066 + 4·15.999
= 2.0158 + 32.066 + 63.996
= 98.078
sacrificial protection → zaštita žrtvovanom elektrodom
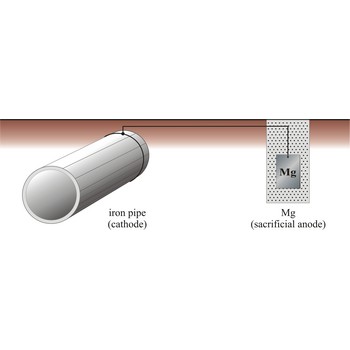
Sacrificial protection is the protection of iron or steel against corrosion by using a more reactive metal. Pieces of zinc or magnesium alloy are attached to pump bodies and pipes. The protected metal becomes the cathode and does not corrode. The anode corrodes, thereby providing the desired sacrificial protection. These items are known as sacrificial anodes and "attract" the corrosion to them rather than the iron/steel. The sacrificial anodes must be replaced periodically as they corrode.
The iron pipe will be connected to a more reactive metal such as magnesium through cooper wires, the magnesium will donate its electrons to the iron preventing it from rusting. Iron which is oxidises will immediately be reduced back to iron.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sửa báo cáo khoản vay nước ngoài." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table