alkynes → alkini
Alkynes (acetylenes) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having one or more triple carbon-carbon bond. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkyne names end in the suffix -yne. The general formula is CnH(2n+2)-4x were x is the number of triple bonds. Alkynes that have only one triple bond form a homologous series: ethyne (acetylene), CH≡CH, propyne, CH3CH≡CH, etc. Like alkenes, alkynes undergo addition reaction.
benzene → benzen
Benzene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon, C6H6, b.p. 80 °C. It is now made from petroleum by catalytic reforming (formerly obtained from coal tar). Benzene is the archetypal aromatic compound. It has an unsaturated molecule, yet will not readily undergo addition reactions. On the other hand, it does undergo substitution reactions in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by other atoms or groups.
In 1865, Friedrich August Kekulé purposed the benzene molecule structure as a hexagonal ring which consists of six carbon atoms with alternate carbon-carbon single and carbon-carbon double bond. But such a structure should be highly reactive, and so didn't account for the unreactive nature of benzene. We now know that the best representation for the structure of benzene is indeed, hexagonal, with each C-C bond distance being identical and intermediate between those for a single and double bond. The π-orbitals from each neighbouring carbon atom overlap to form a delocalised molecular orbital which extends around the ring, giving added stability and with it, decreased reactivity. That is the reason the structural formula of benzene represents as a hexagon with a circle in the center which represents the delocalized electrons.
cysteine → cistein
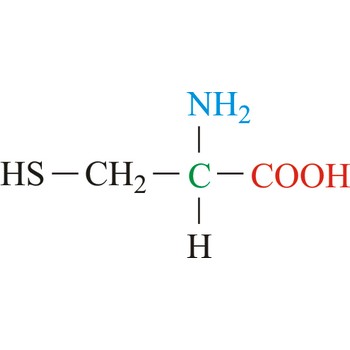
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
halogens → halogeni elementi
Halogens are the elements fluorine (F) chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). They are non-metals, and make up part of the 17 group in the periodic table. Compounds of these elements are called halogenides or halides.
The halogens all have a strong unpleasant odour and will burn flesh. They do not dissolve well in water. The five elements are strongly electronegative. They are oxidising agents, with fluorine being the strongest and astatine being the weakest. They react with most metals and many non-metals.
Halogens form molecules which consist of atoms covalently bonded. With increasing atomic weight there is a gradation in physical properties. For example: Fluorine is a pale green gas of low density. Chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas 1.892 times as dense as fluorine. Bromine is a deep reddish-brown liquid which is three times as dense as water. Iodine is a grayish-black crystalline solid with a metallic appearance. And astatine is a solid with properties which indicate that it is somewhat metallic in character.
lysine → lizin
Lysine is an electrically charged amino acids with basic side chains. Lysine is a base, as are arginine and histidine. The amino group is highly reactive and often participates in reactions at the active centers of enzymes. Lysine plays an important role in coordinating negatively charged ligands. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Lys, K
- IUPAC name: 2,6-diaminohexanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H14N2O2
- Molecular weight: 146.19 g/mol
plasma → plazma
Plasma is a highly ionised gas in which the charge of the electrons is balanced by the charge of the positive ions, so that the system as a whole is electrically neutral. Plasmas are created by exposing gases at low pressure to an electric or electromagnetic field. In semiconductor processing, plasmas are used for etching and thin film deposition (the excited state of the gas makes it very reactive). In everyday life plasmas are used to give light in fluorescent light bulbs, neon lamps, and blue insect traps.
sacrificial protection → zaštita žrtvovanom elektrodom
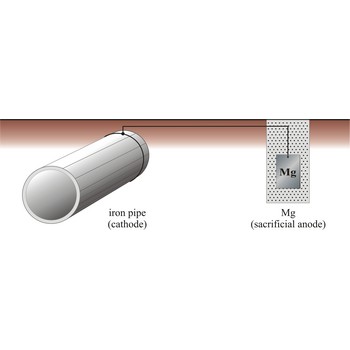
Sacrificial protection is the protection of iron or steel against corrosion by using a more reactive metal. Pieces of zinc or magnesium alloy are attached to pump bodies and pipes. The protected metal becomes the cathode and does not corrode. The anode corrodes, thereby providing the desired sacrificial protection. These items are known as sacrificial anodes and "attract" the corrosion to them rather than the iron/steel. The sacrificial anodes must be replaced periodically as they corrode.
The iron pipe will be connected to a more reactive metal such as magnesium through cooper wires, the magnesium will donate its electrons to the iron preventing it from rusting. Iron which is oxidises will immediately be reduced back to iron.
teflon → teflon
Teflon is a DuPont Company trademark for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It was discovered in 1938 by R. J. Plunkett. Teflon has the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material known to man. It is also used as a non-stick coating for pans and other cookware. Teflon is very unreactive, and so is often used in containers and pipework for reactive chemicals. Its melting point is 327 °C.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Reaktivni niz." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table