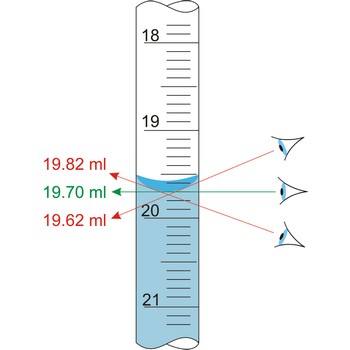
surface tension → površinska napetost
Surface tension (σ) is a property of liquids arising from unbalanced molecular cohesive forces at or near the surface, as a result of which the surface tends to contract and has properties resembling those of a stretched elastic membrane. As a result of which the surface tends to contract and has properties resembling those of a stretched elastic membrane.
surfactant → površinski aktivna tvar
Surfactants are substances which diminish the surface tension of liquids.
blanching → blanširanje
1. Blanching is a heat treatment of foodstuffs to partially or completely inactivate the naturally occurring enzymes prior to freezing.
2. Blanching is a washing process for coins cleaning. The black surface layer of cupric oxide is removing by dipping the coins in hot dilute sulphuric acid (w(H2SO4) = 10 %).
detergent → deterdžent
Detergent is a substance added to water to improve its cleaning properties. Although water is a powerful solvent for many compounds, it will not dissolve grease and natural oils. Detergents are compounds that cause such nonpolar substances to go into solution in water. Soap is the original example, owing its action to the presence of ions formed from long-chain fatty acids ion (e.g. stearat ion, CH3(CH2)16COO-).
Earth’s crust → Zemljina kora
Crust is outer layer of the solid earth, above the Mohorovicic discontinuity. Its thickness averages about 35 km on the continents and about 7 km below the ocean floor, and has the approximate chemical composition:
| Element | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| oxygen | 47 |
| silicon | 28 |
| aluminium | 8 |
| iron | 4.5 |
| calcium | 3.5 |
| sodium | 2.5 |
| potassium | 2.5 |
| magnesium | 2.2 |
fogged metal → zamagljeni metal
Fogged metal is a metal whose lustre has been reduced because of a surface film, usually a corrosion product layer.
hydrosphere → hidrosfera
Hydrosphere (from the Greek for water sphere) is a discontinuous layer of water on, under, and over the Earth's surface. It includes all liquid and frozen surface waters, groundwater held in soil and rock, and atmospheric water vapour. Water continuously circulates between these reservoirs in what is called the hydrologic cycle, which is driven by energy from the Sun.
| Reservoir | V / 106 km3 | w / % |
|---|---|---|
| oceans | 1 370.0 | 97.25 |
| ice caps and glaciers | 29.0 | 2.05 |
| groundwater | 9.5 | 0.68 |
| lakes, rivers | 0.127 | 0.01 |
| soil moisture | 0.065 | 0.005 |
| atmosphere (as liquid equivalent of water vapour) | 0.013 | 0.001 |
| biosphere | 0.0006 | 0.00004 |
| TOTAL | 1 408.7 | 100 |
micelle → micele
Micelle is an electrically charged colloidal particle, usually organic in nature, composed of aggregates of large molecules, e.g., in soaps and surfactants. For aqueous solutions, the hydrophilic end of the molecule is on the surface of the micelle, while the hydrophobic end (often a hydrocarbon chain) points toward the centre.
salinisation → salinizacija
Salinisation is the increase in salinity of fresh surface and ground water supplies.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Površinska napetost." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table