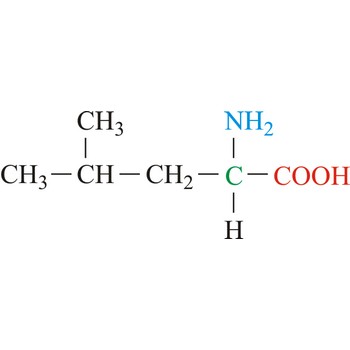
leucine → leucin
Leucine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It has one additional methylene group in its side chain compared with valine. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Leucine is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Leu, L
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular weight: 131.17 g/mol
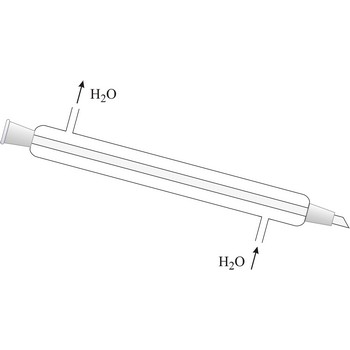
Liebig condenser → Liebigovo hladilo
Liebig condenser is used for condensing of vapours that pass trough the centre tube. It is cooled with water that passes in the outer tube (shell around the centre tube) in the opposite direction than the one of hot vapour. Though named after the German chemist Justus von Liebig (1803-1873), he cannot be given credit for having invented it because it had already been in use for some time before him.
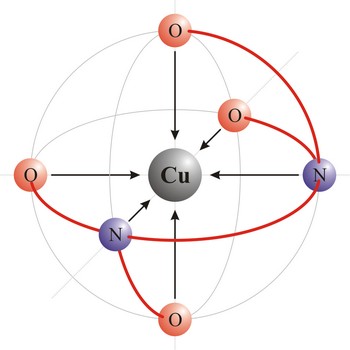
ligand → ligand
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
Zeeman, Pieter → Zeeman, Pieter
Pieter Zeeman (1865-1943) was a Dutch physicist who discovered the splitting of the spectral lines of a substance when placed in a magnetic field (known as the Zeeman effect). In 1902, Zeeman and Lorentz were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics, for their, extraordinary service they rendered by their researches into the influence of magnetism upon radiation phenomenon.
lutetium → lutecij
Lutetium was discovered by Georges Urbain (France) and independently by Carl Auer von Welsbach (Austria) in 1907. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Lutetia meaning Paris. It is silvery-white and relatively stable in air, rare earth metal. Lutetium is found with ytterbium in gadolinite and xenotime. Stable lutetium nuclides can be used as catalysts in cracking, alkylation, hydrogenation, and polymerization.
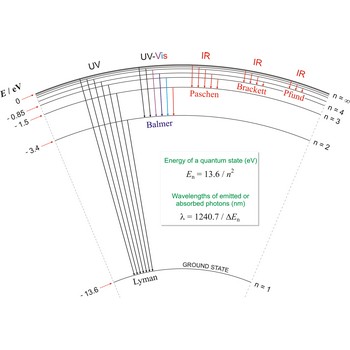
Lyman series → Lymanova serija
Lyman series is the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the ground state (principal quantum number n = 1) and successive excited states.
lysine → lizin
Lysine is an electrically charged amino acids with basic side chains. Lysine is a base, as are arginine and histidine. The amino group is highly reactive and often participates in reactions at the active centers of enzymes. Lysine plays an important role in coordinating negatively charged ligands. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Lys, K
- IUPAC name: 2,6-diaminohexanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H14N2O2
- Molecular weight: 146.19 g/mol
macromolecule → makromolekule
Macromolecule is a molecule of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetitions of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass. The types of macromolecules are natural and synthetic polymers, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins etc. Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is made up of hundreds, even thousands of glucose molecules strung together.
manganese → mangan
Manganese was discovered by Johann Gahn (Sweden) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word magnes meaning magnet, or magnesia nigri meaning black magnesia (MnO2). It is hard, brittle, grey-white metal with a pinkish tinge. Impure forms are reactive. Rusts like iron in moist air. Manganese is most abundant ores are pyrolusite (MnO2), psilomelane [(Ba,H2O)2Mn5O10] and rhodochrosite (MnCO3). Pure metal produced by mixing MnO2 with powered Al and ignited in a furnace. Used in steel, batteries and ceramics. The steel in railroad tracks can contain as much as 1.2 % manganese. It is crucial to the effectiveness of vitamin B1.
mass concentration → masena koncentracija
Mass concentration (γ) is equal to mass (mA) of soluted substance and volume (V) of the solution proportion. SI unit for mass concentration is kg m-3, but in laboratory practice g dm-3, which has the same number value, is often used.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "PloÅ¡no centrirana kubiÄna reÅ¡etka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table