Results 1–9 of 9 for pigment
pigment → pigment
Pigments are the substances that give paint colour. Pigments are derived from natural or synthetic materials that have been ground into fine powders. A pigment is different from a dye in that a pigment is insoluble in the media in which it is used.
Pigment is an organic substance found in plant and animal cells that creates colouring.
cadmium → kadmij
Cadmium was discovered by Friedrich Strohmeyer (Germany) in 1817. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word cadmia meaning calamine (zinc carbonate, ZnCO3), or from the Greek word kadmeia with the same meaning. It is soft, malleable, blue-white metal. Tarnishes in air, soluble in acids, insoluble in alkalis. Boiling cadmium gives off a weird, yellow-colored vapour that is poisonous. Cadmium can cause a variety of health problems, including kidney failure and high blood pressure. Cadmium is obtained as a by product of zinc refining. The mayor use of cadmium is in electroplating of steel to protect it from corrosion. Also used to make nickel-cadmium batteries. The ability of cadmium to adsorb neutrons has made it of great importance in the design of nuclear reactors. Its compounds are found in paint pigments and a wide variety of intense colours.
carotenoids → karotenoidi
Carotenoids are a group of natural pigments in plants responsible for yellow and orange colours, meltable in fats.
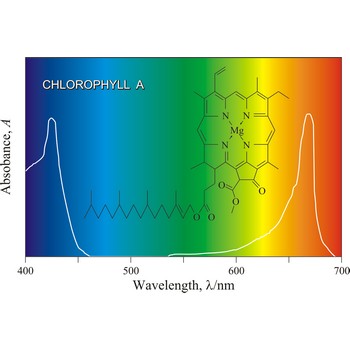
chlorophyll → klorofil
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in green plants and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyll is essential in the transformation of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light mostly in the blue and red ends of the visible spectrum, and very little in the green wavelengths. That green light is reflected, giving us the leaf colour we see.
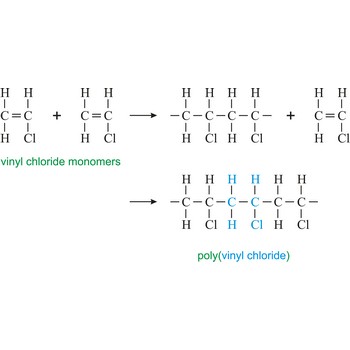
polyvinyl chloride → polivinil klorid
Poly(vinyl chloride) or the PVC is hard and resistant homopolymer produced by the polymerization of the gas vinyl chloride [CH2CHCl]. The pure polymer is hard, brittle and difficult to process, but it becomes flexible when plasticizers are added. After mixing with plasticizers, stabilizers, and pigments, the resin may be fabricated by techniques such as calendering, molding, or extrusion into flexible articles such as raincoats, shower curtains, and packaging films. The resin is not plasticized for use in making rigid products such as water pipe, plumbing fittings, and phonograph records.
glycoside → glikozid
Glycoside is one of a group of organic compounds in which a sugar group is bonded through its anomeric carbon to another group via a glycosidic bond. The sugar group is known as the glycon and the non-sugar group as the aglycon. According to the IUPAC definition, all disaccharides and polysaccharides are glycosides where the aglycone is another sugar.
In the free hemiacetal form, sugars will spontaneously equilibrate between the α and β anomers. However, once the glycosidic bond is formed, the anomeric configuration of the ring is locked as either α or β. Therefore, the alpha and beta glycosides are chemically distinct. They will have different chemical, physical, and biological properties. Many glycosides occur abundantly in plants, especially as flower and fruit pigments.
The term glycoside was later extended to cover not only compounds in which the anomeric hydroxy group is replaced by a group -OR, but also those in which the replacing group is -SR (thioglycosides), -SeR (selenoglycosides), -NR1R2 (N-glycosides), or even -CR1R2R3 (C-glycosides). Thioglycoside and selenoglycoside are legitimate generic terms; however the use of N-glycoside, although widespread in biochemical literature, is improper and not recommended here (glycosylamine is a perfectly acceptable term). C-Glycoside is even less acceptable. All other glycosides are hydrolysable; the C-C bond of C-glycosides is usually not. The use and propagation of names based on C-glycoside terminology is therefore strongly discouraged.
titanium → titanij
Titanium was discovered by William Gregor (England) in 1791. Named after the Titans, the sons of the Earth goddess in Greek mythology. It is shiny, dark-grey metal. Powdered form burns in air. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. It can be highly polished and is relatively immune to tarnishing. Unreactive with alkali and most acids. Titanium usually occurs in the minerals ilmenite (FeTiO3), rutile (TiO2) and iron ores. Pure metal produced by heating TiO2 with C and Cl2 to produce TiCl4 then heated with Mg gas in Ar atmosphere. Since it is strong and resists acids it is used in many alloys. Titanium dioxide (TiO2), a white pigment that covers surfaces very well, is used in paint, rubber, paper and many others.
uranium → uranij
Uranium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) in 1789. Named after the planet Uranus. It is silvery-white, dense, ductile, malleable, radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; tarnishes in air; attacked by steam and acids. Radiotoxic. Uranium occurs in many rocks, but in large amounts only in such minerals as pitchblende and carnotite. For many centuries it was used as a pigment for glass. Now it is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors and in bombs.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Pigment." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table