Results 1–7 of 7 for peroksid
cetane number → cetanski broj
Cetane number is a measure of the ignition quality of diesel fuel. It denotes the volume fraction of cetane (C16H34) in a combustible mixture (containing cetane and 1-methylnapthalene) whose ignition characteristics match those of the diesel fuel being tested. Cetane is a collection of un-branched open chain alkane molecule that ignites very easily under compression, so it was assigned a cetane number of 100, while alpha-methyl naphthalene was assigned a cetane number of 0.
decomposing → raščinjavanje
Decomposing in analytical chemistry means that a certain substance is converted, by melting it with a suitable melting medium (sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, sodium peroxide, ...) in the kind of compound which will afterwards that dissolve in water, acid or base very easily.
ether → eter
Ethers are organic compounds with a formula R-O-R, where R is not equal to H. They may be derived from alcohols by elimination of water, but the major method is catalytic hydration of olefins. They are volatile highly flammable compounds; when containing peroxides they can detonate on heating. The term ether is often used synonymously with diethyl ether.
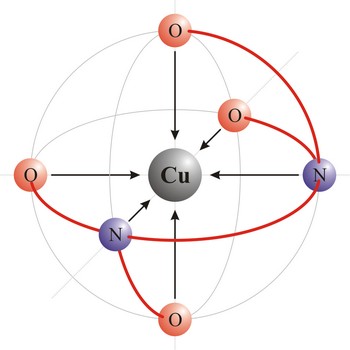
ligand → ligand
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
superoxide → superoksid
Superoxides are binary compounds containing oxygen in the -½ oxidation state. Sodium superoxide (NaO2) can be prepared with high oxygen pressures, whereas the superoxides of rubidium, potassium, and cesium can be prepared directly by combustion in air. These compounds are yellow to orange paramagnetic solids. Superoxide ion, O2-, has an unpaired electron, is not particularly stable, and spontaneously decomposes into peroxide over time.
They are strong oxidising agents that vigorously hydrolyze (react with water) to produce superoxide and oxygen gas.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Peroksid." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table