sulfur → sumpor
Sulfur has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Sanskrit word sulvere meaning sulphur; also from the Latin word sulphurium meaning sulphur. It is pale yellow, odourless, brittle solid, which is insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulfide. Sulfur is found in pure form and in ores like cinnabar, galena, sphalerite and stibnite. Pure form is obtained from underground deposits by the Frasch process. Used in matches, gunpowder, medicines, rubber and pesticides, dyes and insecticides. Also for making sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
supercritical carbon dioxide → superkritični ugljikov dioksid
Supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is a powerful, cheap, non-toxic and environmental friendly solvent. When used at a supercritical state (over 74 bar and 31 °C), it achieves similar solvating power as its organic competitors, such as hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents. Supercritical carbon dioxide is one of few solvents that can be unrestrictedly used for food processing.
supercritical fluid extraction → superkritična fluidna ekstrakcija
Supercritical fluid extractions (SFE) have solvating powers similar to liquid organic solvents, but with higher diffusivities, lower viscosity, and lower surface tension. The main advantages of using supercritical fluids for extractions is that they are inexpensive, contaminant free, and less costly to dispose safely than organic solvents. For non-destructive isolation choose SFE, which is simply the best technology for sensitive raw materials. For these reasons supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) is the reagent used to extract caffeine from coffee and tea. Its gaslike behavior allows it to penetrate deep into the green coffee beans, and it dissolves from 97 % to 99 % of the caffeine present.
thallium → talij
Thallium was discovered by Sir William Crookes (England) in 1861. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word thallos meaning green twig or green shoot. It is soft grey metal that looks like lead. Tarnishes in moist air. Reacts in heated moist air and in acids. Compounds highly toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Cumulative effects. Thallium is found in iron pyrites. Also in crookesite, hutchinsonite and lorandite. Most is recovered from the by-products of lead and zinc refining. Its compounds are used in rat and ant poisons. Also for detecting infrared radiation.
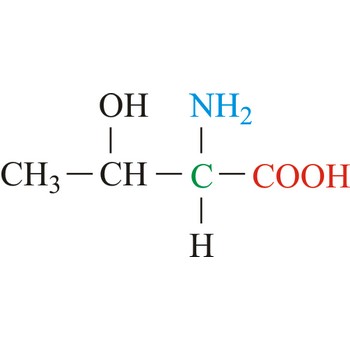
threonine → treonin
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
titanium → titanij
Titanium was discovered by William Gregor (England) in 1791. Named after the Titans, the sons of the Earth goddess in Greek mythology. It is shiny, dark-grey metal. Powdered form burns in air. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. It can be highly polished and is relatively immune to tarnishing. Unreactive with alkali and most acids. Titanium usually occurs in the minerals ilmenite (FeTiO3), rutile (TiO2) and iron ores. Pure metal produced by heating TiO2 with C and Cl2 to produce TiCl4 then heated with Mg gas in Ar atmosphere. Since it is strong and resists acids it is used in many alloys. Titanium dioxide (TiO2), a white pigment that covers surfaces very well, is used in paint, rubber, paper and many others.
triols → trioli
Trihydric alcohols (i.e. Triols) are organic compounds containing three hydroxyl groups. The simplest trihydric alcohol is 1,2,3-propane-triol, CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH2(OH), which is also known as glycerol (from the Greek glykys meaning sweet) or glycerin. Glycerol is commercially produced by the hydrolysis of fats.
Glycerol is a by-product in the soap industry and is recovered by suitable means.
tryglyceride → triglicerid
Triglyceride is an ester of glycerol and three fatty acids. It is the main constituent of vegetable oil and animal fats. The fatty acids attached to the glycerol can be the same or different. Natural fatty acids found in plants and animals are typically composed only of even numbers of carbon atoms (usually from 16 to 20) due to the way they are bio-synthesized from acetyl CoA.
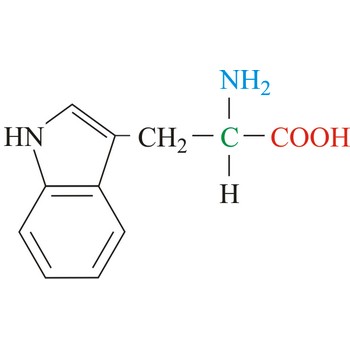
tryptophan → triptofan
Tryptophan is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tryptophan is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tryptophan has the largest side chain and is the least common amino acid in proteins. It has spectral properties that make it the best inherent probe for following protein folding and conformational changes associated with biochemical processes. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Trp, W
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C11H12N2O2
- Molecular weight: 204.23 g/mol
tungsten → volfram
Tungsten was discovered by Fausto and Juan Jose de Elhuyar (Spain) in 1783. Named after the tungsten mineral wolframite. It is hard, steel-grey to white metal. Highest melting point of all metals. Resists oxygen, acids and alkalis. Tungsten occurs in the minerals scheelite (CaWO4) and wolframite [(Fe,Mn)WO4]. Made into filaments for vacuum tubes and electric lights. Also as contact points in cars. Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and is used for making cutting tools and abrasives.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Organic acid." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table