EDTA → EDTA
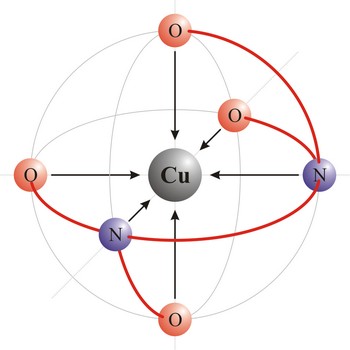
Ethyldiaminetetraacetic acid (C10H16N2O8) or shortened EDTA is a hexadentant ligand, and it forms chelates with both transition-metal ions and main-group ions. EDTA is used as a negative ion - EDTA4-. The diagram shows the structure of the ion with the important atoms picked out. The EDTA ion entirely wraps up a metal ion using all 6 of the positions. The co-ordination number is again 6 because of the 6 co-ordinate bonds being formed by the central metal ion.
EDTA is frequently used in soaps and detergents, because it forms a complexes with calcium and magnesium ions. These ions are in hard water and interfere with the cleaning action of soaps and detergents. EDTA is also used extensively as a stabilizing agent in the food industry and as an anticoagulant for stored blood in blood banks. EDTA is the most common reagent in complexometric titration.
ligand → ligand
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
non-metal → nemetal
Non-metals are defined as elements that are not metals.
Their physical properties generally include:
- They are poor conductors.
- They are brittle, not ductile in their solid state.
- They show no metallic lustre.
- They may be transparent or translucent.
- They have low density.
- They form molecules which consists of atoms covalently bonded; the noble gases are monoatomic.
Their chemical properties are generally:
- They usually have four to eight valence electrons.
- They have high electron affinities (except the noble gases)
- They are good oxidising agents (except the noble gases)
- They have hydroxides which are acidic (except the noble gases)
- They are electronegative.
addition reactions → reakcije adicije
Addition reactions are normally occur with unsaturated compounds and involve the addition of one molecule (called the reactant) across the unsaturated bond (i.e. the double bond or the triple bond) of another molecule (called the substrate) to give a single product, formed by the combination of both reacting molecules.
For example, bromine adds across the double bond of ethene in an addition reaction to form dibromoethane.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Metalna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table