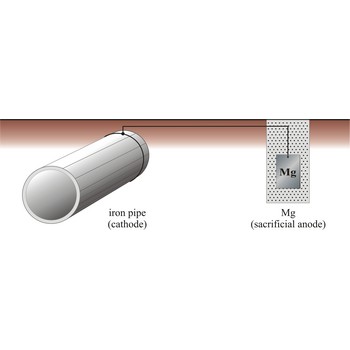
sacrificial protection → zaštita žrtvovanom elektrodom
Sacrificial protection is the protection of iron or steel against corrosion by using a more reactive metal. Pieces of zinc or magnesium alloy are attached to pump bodies and pipes. The protected metal becomes the cathode and does not corrode. The anode corrodes, thereby providing the desired sacrificial protection. These items are known as sacrificial anodes and "attract" the corrosion to them rather than the iron/steel. The sacrificial anodes must be replaced periodically as they corrode.
The iron pipe will be connected to a more reactive metal such as magnesium through cooper wires, the magnesium will donate its electrons to the iron preventing it from rusting. Iron which is oxidises will immediately be reduced back to iron.
scandium → skandij
Scandium was discovered by Lars Fredrik Nilson (Sweden) in 1879. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word Scandia meaning Scandinavia. It is fairly soft, silvery-white metal. Burns easily. Tarnishes readily in air. Reaction with water releases hydrogen. Reacts with air and halogens. Scandium occurs mainly in the minerals thortveitile (~34 % scandium) and wiikite. Also in some tin and tungsten ores. Pure scandium is obtained as a by-product of uranium refining. Scandium metal is used in some aerospace applications. Scandium oxide (Sc2O2) is used in the manufacture of high-intensity electric lamps. Scandium iodide (ScI3) is used in lamps that produce light having a colour closely matching natural sunlight.
seawater → more
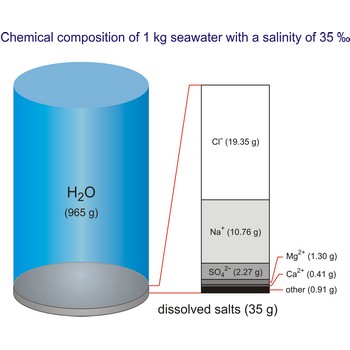
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
temporary hardness → prolazna tvrdoća
Temporary Hardness is due to the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-, being present in the water. It can be removed by water reboiling, whereby white solid emerges calcium carbonate that is limescale.
water hardness → tvrdoća vode
Hardness is defined as the concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions expressed in terms of calcium carbonate. These minerals in water can cause some everyday problems. They react with soap and produce a deposit called soap curd that remains on the skin and clothes and, because it is insoluble and sticky, cannot be removed by rinsing.
Hard water may also shorten the life of plumbing and water heaters. When water containing calcium carbonate is heated, a hard scale is formed that can plug pipes and coat heating elements. Scale is also a poor heat conductor. With increased deposits on the unit, heat is not transmitted to the water fast enough and overheating of the metal causes failure. Build-up of deposits will also reduce the efficiency of the heating unit, increasing the cost of fuel.
There are two types of water hardness, temporary and permanent.
Temporary Hardness is due to the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-, being present in the water. This type of hardness can be removed by boiling the water to expel the CO2, as indicated by the following equation:
Permanent hardness is due to calcium and magnesium nitrates, sulphates, and chlorides etc. This type of hardness cannot be eliminated by boiling.
| Water supply classification | |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Concentration of Calcium carbonate (mg/L) |
| Soft Water | 0 to 75 |
| Medium Hard Water | 75 to 150 |
| Hard Water | 150 to 300 |
| Very Hard Water | over 300 |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Magnezij." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table